
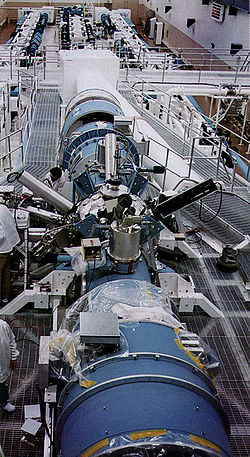
Novette laser
Encyclopedia
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite...
glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
(phosphate glass
Phosphate glass
Phosphate glass is a class of optical glasses composed of metaphosphates of various metals. Instead of SiO2 in silicate glasses, the glass forming substrate is P2O5....
) testbed laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
built at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory , just outside Livermore, California, is a Federally Funded Research and Development Center founded by the University of California in 1952...
in about 15 months throughout 1981 and 1982 and was completed in January 1983. Novette was made using recycled parts from the dismantled Shiva
Shiva laser
The Shiva laser was a powerful 20-beam infrared neodymium glass laser built at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in 1977 for the study of inertial confinement fusion and long-scale-length laser-plasma interactions. The device was named after the multi-armed form of the Hindu god Shiva, due...
and Argus
Argus laser
Argus was a two-beam high power infrared neodymium doped silica glass laser with a output aperture built at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in 1976 for the study of inertial confinement fusion...
lasers and borrowed parts from the future Nova laser
Nova laser
Nova was a high-power laser built at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in 1984 which conducted advanced inertial confinement fusion experiments until its dismantling in 1999. Nova was the first ICF experiment built with the intention of reaching "ignition", a chain reaction of nuclear...
. Its main intended purpose was to validate the proposed design and expected performance of the then planned Nova laser. In addition to being used for the further study of enhanced laser to target plasma energy coupling utilizing frequency tripled light and examining its benefits with respect to inertial confinement fusion
Inertial confinement fusion
Inertial confinement fusion is a process where nuclear fusion reactions are initiated by heating and compressing a fuel target, typically in the form of a pellet that most often contains a mixture of deuterium and tritium....
, Novette was also used in the world's first laboratory demonstration of an x-ray laser
X-ray laser
An X-ray laser is a device that uses stimulated emission to generate or amplify electromagnetic radiation in the near X-ray or extreme ultraviolet region of the spectrum, that is, usually on the order of several of tens of nanometers wavelength.Because of high gain in the lasing medium, short...
in 1984.
External links
- http://www.llnl.gov/50science/lasers.html
- http://www.osti.gov/bridge/servlets/purl/16710-UOC0xx/native/16710.pdf
- http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1985EnTR........15.

