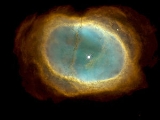
NGC 3132
Encyclopedia
NGC 3132 is a bright and extensively studied planetary nebula
in the constellation
Vela
. Its distance from Earth
is estimated at about 550 kpc. or 2,000 light-year
s.
, the other 16th. The central planetary nebula nucleus (PNN) or white dwarf
central star is the fainter of these two stars. This hot central star of about 100,000 K
has now blown off its layers and is making the nebula fluoresce brightly from the emission of its intense ultraviolet
radiation
.
Planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Vela
Vela (constellation)
Vela is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship Argo Navis, which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis.-Stars:...
. Its distance from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
is estimated at about 550 kpc. or 2,000 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s.
Planetary nebula nucleus (PNN)
Images of NGC 3132 reveal two stars close together within the nebulosity, one of 10th magnitudeApparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
, the other 16th. The central planetary nebula nucleus (PNN) or white dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
central star is the fainter of these two stars. This hot central star of about 100,000 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
has now blown off its layers and is making the nebula fluoresce brightly from the emission of its intense ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
.
External links
- Hubble Heritage release – A Glowing Pool of Light
- Hubble Heritage Project – Image of NGC 3132

