
N-carbamoylsarcosine amidase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a N-carbamoylsarcosine amidase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are N-carbamoylsarcosine and H2O
, whereas its 3 products
are sarcosine
, CO2
, and NH3
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
s, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is N-carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase. This enzyme is also called carbamoylsarcosine amidase. This enzyme participates in arginine and proline metabolism.
has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB
accession code .
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- N-carbamoylsarcosine + H2O
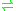 sarcosine + CO2 + NH3
sarcosine + CO2 + NH3
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are N-carbamoylsarcosine and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its 3 products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are sarcosine
Sarcosine
Sarcosine, also known as N-methylglycine, is an intermediate and byproduct in glycine synthesis and degradation. Sarcosine is metabolized to glycine by the enzyme sarcosine dehydrogenase, while glycine-N-methyl transferase generates sarcosine from glycine. Sarcosine is a natural amino acid found in...
, CO2
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, and NH3
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
s, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is N-carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase. This enzyme is also called carbamoylsarcosine amidase. This enzyme participates in arginine and proline metabolism.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, only one structureTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession code .

