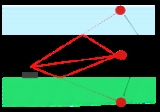
Multipath
Encyclopedia
In wireless
telecommunication
s, multipath is the propagation
phenomenon that results in radio
signals
reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection
and refraction
, and reflection
from water bodies and terrestrial objects such as mountains and buildings.
The effects of multipath include constructive and destructive interference, and phase shifting
of the signal. This causes Rayleigh fading
. The standard statistical model of this gives a distribution known as the Rayleigh distribution.
Rayleigh fading
with a strong line of sight content is said to have a Rician distribution
, or to be Rician fading
.
In facsimile
and television
transmission
, multipath causes jitter
and ghosting
, seen as a faded duplicate image to the right of the main image. Ghosts occur when transmissions bounce off a mountain or other large object, while also arriving at the antenna by a shorter, direct route, with the receiver picking up two signals separated by a delay.
In radar
processing, multipath causes ghost targets to appear, deceiving the radar receiver
. These ghosts are particularly bothersome since they move and behave like the normal targets (which they echo), and so the receiver has difficulty in isolating the correct target echo. These problems can be overcome by incorporating a ground map of the radar's surroundings and eliminating all echoes which appear to originate below ground or above a certain height.
In digital radio communications (such as GSM) multipath can cause errors and affect the quality of communications. The errors are due to intersymbol interference
(ISI). Equalisers are often used to correct the ISI. Alternatively, techniques such as orthogonal frequency division modulation and rake receiver
s may be used.
In a Global Positioning System receiver, Multipath Effect can cause a stationary receiver's output to indicate as if it were randomly jumping about or creeping. When the unit is moving the jumping or creeping is hidden, but it still degrades the displayed accuracy.
.
High-speed power line communication systems usually employ multi-carrier modulations (such as OFDM or Wavelet
OFDM) to avoid the intersymbol interference that multipath propagation would cause.
The ITU-T
G.hn
standard provides a way to create a high-speed (up to 1 Gigabit/s) local area network
using existing home wiring (power lines
, phone lines and coaxial cables
). G.hn uses OFDM with a cyclic prefix
to avoid ISI. Because multipath propagation behaves differently in each kind of wire, G.hn uses different OFDM parameters (OFDM symbol duration, Guard Interval duration) for each media.
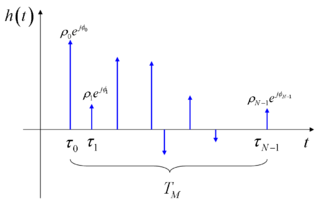 The mathematical model of the multipath can be presented using the method of the impulse response
The mathematical model of the multipath can be presented using the method of the impulse response
used for studying linear system
s.
Suppose to transmit a single, ideal Dirac pulse
of electromagnetic
power at time 0, i.e.
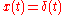
At the receiver, due to the presence of the multiple electromagnetic paths, more than one pulse will be received (we suppose here that the channel
has infinite bandwidth, thus the pulse shape is not modified at all), and each one of them will arrive at different times. In fact, since the electromagnetic signals travel at the speed of light
, and since every path has a geometrical length possibly different from that of the other ones, there are different air travelling times (consider that, in free space, the light takes 3 μs to cross a 1 km span). Thus, the received signal will be expressed by
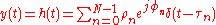
where is the number of received impulses (equivalent to the number of electromagnetic paths, and possibly very large),
is the number of received impulses (equivalent to the number of electromagnetic paths, and possibly very large), 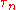 is the time delay of the generic
is the time delay of the generic 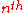 impulse, and
impulse, and 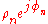 represent the complex amplitude (i.e., magnitude and phase) of the generic received pulse. As a consequence,
represent the complex amplitude (i.e., magnitude and phase) of the generic received pulse. As a consequence, 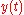 also represents the impulse response function
also represents the impulse response function 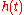 of the equivalent multipath model.
of the equivalent multipath model.
More in general, in presence of time variation of the geometrical reflection conditions, this impulse response is time varying, and as such we have
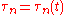
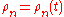
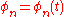
Very often, just one parameter is used to denote the severity of multipath conditions: it is called the multipath time,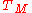 , and it is defined as the time delay existing between the first and the last received impulses
, and it is defined as the time delay existing between the first and the last received impulses
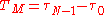
 In practical conditions and measurement, the multipath time is computed by considering as last impulse the first one which allows to receive a determined amount of the total transmitted power (scaled by the atmospheric and propagation losses), e.g. 99%.
In practical conditions and measurement, the multipath time is computed by considering as last impulse the first one which allows to receive a determined amount of the total transmitted power (scaled by the atmospheric and propagation losses), e.g. 99%.
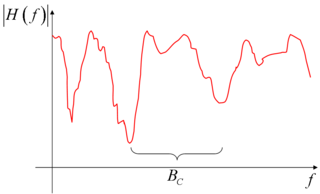
Keeping our aim at linear, time invariant systems, we can also characterize the multipath phenomenon by the channel transfer function , which is defined as the continuous time Fourier transform
, which is defined as the continuous time Fourier transform
of the impulse response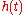
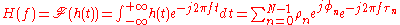
where the last right-hand term of the previous equation is easily obtained by remembering that the Fourier transform of a Dirac pulse is a complex exponential function, an eigenfunction
of every linear system.
The obtained channel transfer characteristic has a typical appearance of a sequence of peaks and valleys (also called notches); it can be shown that, on average, the distance (in Hz) between two consecutive valleys (or two consecutive peaks), is roughly inversely proportional to the multipath time. The so-called coherence bandwidth is thus defined as
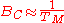
For example, with a multipath time of 3 μs (corresponding to a 1 km of added on-air travel for the last received impulse), there is a coherence bandwidth of about 330 kHz.
Wireless
Wireless telecommunications is the transfer of information between two or more points that are not physically connected. Distances can be short, such as a few meters for television remote control, or as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications...
telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s, multipath is the propagation
Radio propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves when they are transmitted, or propagated from one point on the Earth to another, or into various parts of the atmosphere...
phenomenon that results in radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
signals
Signalling (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, signaling has the following meanings:*the use of signals for controlling communications...
reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection
Ionospheric reflection
Ionospheric reflection is a bending, through a complex process involving reflection and refraction, of electromagnetic waves propagating in the ionosphere back toward the Earth....
and refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
, and reflection
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
from water bodies and terrestrial objects such as mountains and buildings.
The effects of multipath include constructive and destructive interference, and phase shifting
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of the signal. This causes Rayleigh fading
Rayleigh fading
Rayleigh fading is a statistical model for the effect of a propagation environment on a radio signal, such as that used by wireless devices.Rayleigh fading models assume that the magnitude of a signal that has passed through such a transmission medium will vary randomly, or fade, according to a...
. The standard statistical model of this gives a distribution known as the Rayleigh distribution.
Rayleigh fading
Fading
In wireless communications, fading is deviation of the attenuation that a carrier-modulated telecommunication signal experiences over certain propagation media. The fading may vary with time, geographical position and/or radio frequency, and is often modelled as a random process. A fading channel...
with a strong line of sight content is said to have a Rician distribution
Rice distribution
In probability theory, the Rice distribution or Rician distribution is the probability distribution of the absolute value of a circular bivariate normal random variable with potentially non-zero mean. It was named after Stephen O...
, or to be Rician fading
Rician fading
Ricean fading is a stochastic model for radio propagation anomaly caused by partial cancellation of a radio signal by itself — the signal arrives at the receiver by several different paths , and at least one of the paths is changing...
.
In facsimile
Fax
Fax , sometimes called telecopying, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material , normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device...
and television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
transmission
Transmission (telecommunications)
Transmission, in telecommunications, is the process of sending, propagating and receiving an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless...
, multipath causes jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
and ghosting
Ghosting (television)
In television, a ghost is a replica of the transmitted image, offset in position, that is super-imposed on top of the main image on an analogue broadcast.-Common causes:Common causes of ghosts are:...
, seen as a faded duplicate image to the right of the main image. Ghosts occur when transmissions bounce off a mountain or other large object, while also arriving at the antenna by a shorter, direct route, with the receiver picking up two signals separated by a delay.
In radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
processing, multipath causes ghost targets to appear, deceiving the radar receiver
Receiver (radio)
A radio receiver converts signals from a radio antenna to a usable form. It uses electronic filters to separate a wanted radio frequency signal from all other signals, the electronic amplifier increases the level suitable for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through...
. These ghosts are particularly bothersome since they move and behave like the normal targets (which they echo), and so the receiver has difficulty in isolating the correct target echo. These problems can be overcome by incorporating a ground map of the radar's surroundings and eliminating all echoes which appear to originate below ground or above a certain height.
In digital radio communications (such as GSM) multipath can cause errors and affect the quality of communications. The errors are due to intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
(ISI). Equalisers are often used to correct the ISI. Alternatively, techniques such as orthogonal frequency division modulation and rake receiver
Rake receiver
A rake receiver is a radio receiver designed to counter the effects of multipath fading. It does this by using several "sub-receivers" called fingers, that is, several correlators each assigned to a different multipath component...
s may be used.
In a Global Positioning System receiver, Multipath Effect can cause a stationary receiver's output to indicate as if it were randomly jumping about or creeping. When the unit is moving the jumping or creeping is hidden, but it still degrades the displayed accuracy.
Multipath propagation in wired media
Multipath propagation may also happen in wired media, especially in cases in which impedance mismatches cause signal reflections. A well-known example is power line communicationPower line communication
Power line communication or power line carrier , also known as power line digital subscriber line , mains communication, power line telecom , power line networking , or broadband over power lines are systems for carrying data on a conductor also used for electric power transmission.A wide range...
.
High-speed power line communication systems usually employ multi-carrier modulations (such as OFDM or Wavelet
Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that starts out at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one might see recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are purposefully crafted to have...
OFDM) to avoid the intersymbol interference that multipath propagation would cause.
The ITU-T
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
G.hn
G.hn
G.hn is the common name for a home network technology family of standards developed under the International Telecommunication Union's Standardization arm and promoted by the HomeGrid Forum...
standard provides a way to create a high-speed (up to 1 Gigabit/s) local area network
Local area network
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building...
using existing home wiring (power lines
Power line communication
Power line communication or power line carrier , also known as power line digital subscriber line , mains communication, power line telecom , power line networking , or broadband over power lines are systems for carrying data on a conductor also used for electric power transmission.A wide range...
, phone lines and coaxial cables
Ethernet over coax
Ethernet over Coax is a family of technologies that supports the transmission of Ethernet frames over coaxial cable.- History :The first Ethernet standard, known as 10BASE5 in the family of IEEE 802.3, specified baseband operation over coaxial cable...
). G.hn uses OFDM with a cyclic prefix
Cyclic prefix
In telecommunications, the term cyclic prefix refers to the prefixing of a symbol with a repetition of the end. Although the receiver is typically configured to discard the cyclic prefix samples, the cyclic prefix serves two purposes....
to avoid ISI. Because multipath propagation behaves differently in each kind of wire, G.hn uses different OFDM parameters (OFDM symbol duration, Guard Interval duration) for each media.
Mathematical modeling

Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
used for studying linear system
Linear system
A linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator.Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the general, nonlinear case....
s.
Suppose to transmit a single, ideal Dirac pulse
Dirac delta function
The Dirac delta function, or δ function, is a generalized function depending on a real parameter such that it is zero for all values of the parameter except when the parameter is zero, and its integral over the parameter from −∞ to ∞ is equal to one. It was introduced by theoretical...
of electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
power at time 0, i.e.
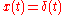
At the receiver, due to the presence of the multiple electromagnetic paths, more than one pulse will be received (we suppose here that the channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
has infinite bandwidth, thus the pulse shape is not modified at all), and each one of them will arrive at different times. In fact, since the electromagnetic signals travel at the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, and since every path has a geometrical length possibly different from that of the other ones, there are different air travelling times (consider that, in free space, the light takes 3 μs to cross a 1 km span). Thus, the received signal will be expressed by
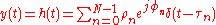
where
 is the number of received impulses (equivalent to the number of electromagnetic paths, and possibly very large),
is the number of received impulses (equivalent to the number of electromagnetic paths, and possibly very large), 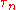 is the time delay of the generic
is the time delay of the generic 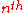 impulse, and
impulse, and 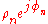 represent the complex amplitude (i.e., magnitude and phase) of the generic received pulse. As a consequence,
represent the complex amplitude (i.e., magnitude and phase) of the generic received pulse. As a consequence, 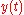 also represents the impulse response function
also represents the impulse response function 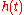 of the equivalent multipath model.
of the equivalent multipath model.More in general, in presence of time variation of the geometrical reflection conditions, this impulse response is time varying, and as such we have

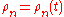

Very often, just one parameter is used to denote the severity of multipath conditions: it is called the multipath time,
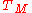 , and it is defined as the time delay existing between the first and the last received impulses
, and it is defined as the time delay existing between the first and the last received impulses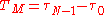

Keeping our aim at linear, time invariant systems, we can also characterize the multipath phenomenon by the channel transfer function
 , which is defined as the continuous time Fourier transform
, which is defined as the continuous time Fourier transformFourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
of the impulse response
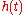
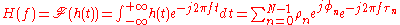
where the last right-hand term of the previous equation is easily obtained by remembering that the Fourier transform of a Dirac pulse is a complex exponential function, an eigenfunction
Eigenfunction
In mathematics, an eigenfunction of a linear operator, A, defined on some function space is any non-zero function f in that space that returns from the operator exactly as is, except for a multiplicative scaling factor. More precisely, one has...
of every linear system.
The obtained channel transfer characteristic has a typical appearance of a sequence of peaks and valleys (also called notches); it can be shown that, on average, the distance (in Hz) between two consecutive valleys (or two consecutive peaks), is roughly inversely proportional to the multipath time. The so-called coherence bandwidth is thus defined as
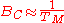
For example, with a multipath time of 3 μs (corresponding to a 1 km of added on-air travel for the last received impulse), there is a coherence bandwidth of about 330 kHz.
See also
- Choke ring antennaChoke ring antennaright|thumb|Patent Diagram of a Choke Ring AntennaA choke ring antenna is a particular form of omnidirectional antenna for use at high frequencies. It consists of a number of conductive concentric cylinders around a central antenna...
, a design that can reject extraneous multipath signals - Diversity schemeDiversity schemeIn telecommunications, a diversity scheme refers to a method for improving the reliability of a message signal by using two or more communication channels with different characteristics. Diversity plays an important role in combatting fading and co-channel interference and avoiding error bursts...
s - FadingFadingIn wireless communications, fading is deviation of the attenuation that a carrier-modulated telecommunication signal experiences over certain propagation media. The fading may vary with time, geographical position and/or radio frequency, and is often modelled as a random process. A fading channel...
- Olivia MFSKOlivia MFSKOlivia MFSK is an amateur radioteletype protocol designed to work in difficult conditions on shortwave bands. The signal can still be properly copied when it is buried 10 dB below the noise floor...
- Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexingOrthogonal frequency-division multiplexingOrthogonal frequency-division multiplexing is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, whether wireless or over copper wires, used in applications such as digital television and audio...
- Signal flowSignal flowAudio signal flow is the path an audio signal takes from source to output, including all the processing involved in generating audible sound from electronic impulses or recorded media.- Analog recording :...
- Ultra wide-band
- Doppler spread

