
Multi-Frequency Receiver
Encyclopedia
Multi-Frequency signalling, (MF), is similar to the European version, CCITT Signaling System 5, (SS5)
. The original format was five tones used in pairs. This later evolved to six tones. Because its six tones are used only in pairs, this signaling format is sometimes referred to as "two-out-of-five code
" or "two of six."
 Multi-Frequency receivers have been present in US telephony at least since the late 1940s. In 1940s technology, receivers in 4XB and similar equipment used vacuum tube
Multi-Frequency receivers have been present in US telephony at least since the late 1940s. In 1940s technology, receivers in 4XB and similar equipment used vacuum tube
s. Later ones used RC filters and transistors. Digital filter
s became commonplace in electronic switching system
s of the 1980s. For example, in 5ESS switch
such jobs were done by DSPs in the Global Digital Services Unit (GDSU).
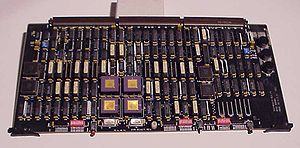
(DSP) based printed circuit card designed at Computer Consoles Inc.
(CCI) in Rochester, NY. The MFR was a service circuit module developed as part of the companies digital telephony switching system. The main function of the card was the processing of incoming digital audio to detect the presence of various voice-band tone base signaling systems present during a call connection. The CCI digital switch was deployed as part of the Digital Audio Intercept System (DAIS II), Automatic Voice Response (AVR), and Interactive Voice System (IVS) products. The initial MFR board, MFR-I, is notable for being designed in early 1983 prior to Texas Instruments
officially announcing the TMS320C10 DSP April 8, 1983.
Signaling System No. 5
CCITT5 was a multi-frequency telephone signalling system in use from the 1970s for International Direct Distance Dialing . It was sometimes nicknamed "Atlantic Code" because the first IDD connections between Europe and North America used it....
. The original format was five tones used in pairs. This later evolved to six tones. Because its six tones are used only in pairs, this signaling format is sometimes referred to as "two-out-of-five code
Two-out-of-five code
In telecommunication, a two-out-of-five code is an m of n code that provides exactly ten possible combinations, and thus is popular for representing decimal digits using five bits...
" or "two of six."

Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s. Later ones used RC filters and transistors. Digital filter
Digital filter
In electronics, computer science and mathematics, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filter, the analog filter, which is...
s became commonplace in electronic switching system
Electronic switching system
In telecommunications, an electronic switching system is:* A telephone exchange based on the principles of time-division multiplexing of digitized analog signals. An electronic switching system digitizes analog signals from subscriber loops, and interconnects them by assigning the digitized...
s of the 1980s. For example, in 5ESS switch
5ESS Switch
The 5ESS Switch is a Class 5 telephone electronic switching system sold by Alcatel-Lucent. This digital central office telephone circuit switching system is used by many telecommunications service providers.-History:...
such jobs were done by DSPs in the Global Digital Services Unit (GDSU).
Receivers
One example of an MF receiver built 35 years after the format's original US use is a Digital Signal ProcessorDigital signal processor
A digital signal processor is a specialized microprocessor with an architecture optimized for the fast operational needs of digital signal processing.-Typical characteristics:...
(DSP) based printed circuit card designed at Computer Consoles Inc.
Computer Consoles Inc.
Computer Consoles Inc. or CCI was a telephony and computer company located in Rochester, New York, USA, which did business first as a private, and then ultimately a public company from 1968 to 1990...
(CCI) in Rochester, NY. The MFR was a service circuit module developed as part of the companies digital telephony switching system. The main function of the card was the processing of incoming digital audio to detect the presence of various voice-band tone base signaling systems present during a call connection. The CCI digital switch was deployed as part of the Digital Audio Intercept System (DAIS II), Automatic Voice Response (AVR), and Interactive Voice System (IVS) products. The initial MFR board, MFR-I, is notable for being designed in early 1983 prior to Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Inc. , widely known as TI, is an American company based in Dallas, Texas, United States, which develops and commercializes semiconductor and computer technology...
officially announcing the TMS320C10 DSP April 8, 1983.

Variants
- MFR-I:
- This printed circuit card, designed by Mark A. Indovina, was introduced in 1983 and contained a single TMS320C10 16-bit fixed point DSP chip operating at 20 MHz.
- MFR-II:
- This printed circuit card, also designed by Mark A. Indovina, was introduced in late 1985 and contained two TMS320C25 16-bit fixed point DSP chips operating at 40 MHz.
- MFR-III:
- This printed circuit card contained two TMS320C30 32-bit floating point DSP chips operating at 40 MHz. Although a prototype was designed and tested, this card never went into volume production.
Features
- The MFR firmware, written entirely in TMS320 assembly language due to the poor efficiency of DSP C compilers at the time, was capable of decoding multiple channels of PCM digital audio while detecting the following signaling systems:
- MF, Multi-FrequencyMulti-frequencyIn telephony, multi-frequency signaling is an outdated, in-band signaling technique. Numbers were represented in a two-out-of-five code for transmission from a multi-frequency sender, to be received by a multi-frequency receiver in a distant telephone exchange...
Tones - DTMF, Dual-Tone Band, Multi-Frequency Tones
- Call Progress Tones
- Other system audio frequencies as needed for on-line, and off-line system testing
- MF, Multi-Frequency
- A highly optimized version of the Goertzel algorithmGoertzel algorithmThe Goertzel algorithm is a digital signal processing technique for identifying frequency components of a signal, published by Gerald Goertzel in 1958...
was used as part of the firmware's frequency detection algorithms. - Due to the tight timing involved in the designs, controlled impedance printed circuit board design techniques was introduced with the MFR-I layout in 1983.

