
Moffat distribution
Encyclopedia
The Moffat distribution, named after the physicist
Anthony Moffat, is a continuous probability distribution based upon the Lorentzian distribution
. Its particular importance in astrophysics
is due to its ability to accurately reconstruct point spread function
s, whose wings cannot be accurately portrayed by either a Gaussian or Lorentzian
function.
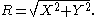
In terms of the random vector (X,Y), the distribution has the probability density function
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who studies or practices physics. Physicists study a wide range of physical phenomena in many branches of physics spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic particles of which all ordinary matter is made to the behavior of the material Universe as a whole...
Anthony Moffat, is a continuous probability distribution based upon the Lorentzian distribution
Cauchy distribution
The Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy and Hendrik Lorentz, is a continuous probability distribution. As a probability distribution, it is known as the Cauchy distribution, while among physicists, it is known as the Lorentz distribution, Lorentz function, or Breit–Wigner...
. Its particular importance in astrophysics
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physics of the universe, including the physical properties of celestial objects, as well as their interactions and behavior...
is due to its ability to accurately reconstruct point spread function
Point spread function
The point spread function describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob...
s, whose wings cannot be accurately portrayed by either a Gaussian or Lorentzian
Cauchy distribution
The Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy and Hendrik Lorentz, is a continuous probability distribution. As a probability distribution, it is known as the Cauchy distribution, while among physicists, it is known as the Lorentz distribution, Lorentz function, or Breit–Wigner...
function.
Probability density function
The Moffat distribution can be described in two ways. Firstly as the distribution of a bivariate random variable (X,Y) centred at zero, and secondly as the distribution of the corresponding radii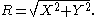
In terms of the random vector (X,Y), the distribution has the probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
-
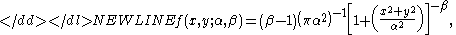
where and
and 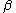 are seeingAstronomical seeingAstronomical seeing refers to the blurring and twinkling of astronomical objects such as stars caused by turbulent mixing in the Earth's atmosphere varying the optical refractive index...
are seeingAstronomical seeingAstronomical seeing refers to the blurring and twinkling of astronomical objects such as stars caused by turbulent mixing in the Earth's atmosphere varying the optical refractive index...
dependent parameters. In this form, the distribution is a reparameterisation of a bivariate Student distribution with zero correlation.
In terms of the random variable R, the distribution has density -


