
Minnaert function
Encyclopedia
The Minnaert
function is a photometric
function used to interpret astronomical observations and remote sensing
data for the Earth
. This function expresses the radiance factor (RADF) as a function the phase angle
( ) and the photometric latitude (
) and the photometric latitude (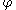 ) and the photometric longitude (
) and the photometric longitude (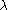 ).
).
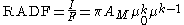
where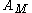 is the Minnaert albedo
is the Minnaert albedo
,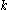 is an empirical parameter,
is an empirical parameter, 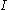 is the scattered radiance
is the scattered radiance
in the direction ,
, 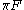 is the incident radiance, and
is the incident radiance, and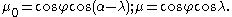
The phase angle is the angle between the light source and the observer with the object as the center.
The assumptions made are:
Minnaert's contribution is the introduction of the parameter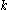 , having a value between 0 and 1 , originally for a better interpretation of observations of the Moon
, having a value between 0 and 1 , originally for a better interpretation of observations of the Moon
. In remote sensing the use of this function is referred to as Minnaert topographic correction, a necessity when interpreting images of rough terrain.
Marcel Minnaert
Marcel Gilles Jozef Minnaert was a Belgian astronomer.He obtained a PhD in biology at Ghent University in 1914....
function is a photometric
Photometry (astronomy)
Photometry is a technique of astronomy concerned with measuring the flux, or intensity of an astronomical object's electromagnetic radiation...
function used to interpret astronomical observations and remote sensing
Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon, without making physical contact with the object. In modern usage, the term generally refers to the use of aerial sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth by means of propagated signals Remote sensing...
data for the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. This function expresses the radiance factor (RADF) as a function the phase angle
Phase angle
In the context of vectors and phasors, the term phase angle refers to the angular component of the polar coordinate representation. The notation A\ang \!\ \theta, for a vector with magnitude A and phase angle θ, is called angle notation.In the context of periodic phenomena, such as a wave,...
(
 ) and the photometric latitude (
) and the photometric latitude (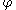 ) and the photometric longitude (
) and the photometric longitude (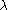 ).
).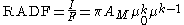
where
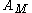 is the Minnaert albedo
is the Minnaert albedoAlbedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
,
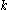 is an empirical parameter,
is an empirical parameter, 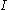 is the scattered radiance
is the scattered radianceRadiance
Radiance and spectral radiance are radiometric measures that describe the amount of radiation such as light or radiant heat that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle in a specified direction. They are used to characterize both emission from...
in the direction
 ,
, 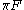 is the incident radiance, and
is the incident radiance, and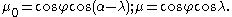
The phase angle is the angle between the light source and the observer with the object as the center.
The assumptions made are:
- the surface is illuminated by a distant point source.
- the surface is isotropic and flat.
Minnaert's contribution is the introduction of the parameter
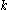 , having a value between 0 and 1 , originally for a better interpretation of observations of the Moon
, having a value between 0 and 1 , originally for a better interpretation of observations of the MoonMoon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
. In remote sensing the use of this function is referred to as Minnaert topographic correction, a necessity when interpreting images of rough terrain.

