
Military Soyuz
Encyclopedia
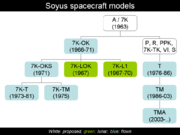
Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz , Union) is a series of spacecraft initially designed for the Soviet space programme by the Korolyov Design Bureau in the 1960s, and still in service today...
models were planned, but none actually flew in space. These versions were named Soyuz 7K-P, Soyuz 7K-PPK, Soyuz R, Soyuz 7K-VI, and Soyuz OIS (Orbital Research Station).
Soyuz 7K-P
The Soyuz 7K-P (Perekhvatchik, Interceptor) space interceptor and Soyuz R (Razvedki, intelligence) command-reconnaissance spacecraft was proposed in December 1962 by Sergei Korolev.In the initial draft project, the Soyuz 7K-P would use the Soyuz 9K rocket stage and Soyuz 11K tanker spacecraft to conduct a series of dockings and re-fueling operations. The complete complex would then could conduct intercepts of enemy satellites in orbits up to 6,000 km in altitude.
Soyuz R
The Soyuz-R system consisted of two separately launched spacecraft, including the small orbital station 11F71 with photo-reconnaissance and electronic intelligence equipment and a Soyuz 7K-TK for crew transport.Soyuz 7K-PPK
Initially the Soyuz 7K-P was designed for piloted inspection and destruction of enemy satellites. It was intended that the Soyuz would rendezvous with the target satellite. To minimize risk to the crew, a new version, Soyuz 7K-PPK (pilotiruemovo korablya-perekhvatchika, manned interceptor spacecraft) was later proposed.Soyuz 7K-VI Zvezda
The Zvezda (star) station was based on a radically modified Soyuz. Objectives were manned earth observation, orbital inspection and destruction of enemy satellites. Zvezda would be powered by two plutonium radioisotope generators and had a recoilless gun for defense. It was designed for shooting in a vacuum and defending the military research spacecraft from enemy satellite inspector and interceptor satellites. The gun was aimed by maneuvering the entire spacecraft. A special gunsight was installed in the descent module for aiming the gun. A forward docking apparatus to allow docking with AlmazAlmaz
The Almaz program was a series of military space stations launched by the Soviet Union under cover of the civilian Salyut DOS-17K program after 1971....
was also included. Work on Zvezda was canceled in 1967 with a single prototype in advanced stages of construction.
Cosmonaut training for the VI began in September 1966. The cosmonaut group selected included commander Pavel Popovich
Pavel Popovich
- Biography :He was born in Uzyn, Kiev Oblast of Soviet Union . to Roman Porfirievich Popovich and Theodosia Kasyanovna Semyonov. He had two sisters and two brothers ....
, pilot Alexei Gubarev, flight-engineers Yuri Artyukhin
Yuri Artyukhin
Yury Petrovich Artyukhin was a Soviet Russian cosmonaut and engineer who made a single flight into space.Artyukhin graduated from the Soviet Air Force Institute with a doctorate in engineering, specialising in military communication systems. He was selected for the space programme in 1963 and...
, Vladimir Gulyaev, Boris Belousov, and Gennadiy Kolesnikov. Popovich-Kolesnikov and Gubarev-Belousov were the prime crews, with the other engineers acting as reserves and then assigned to later crews.
Soyuz OIS (Orbital Research Station)
The Soyuz OIS (Orbital Research Station) would consist of a separately-launched orbital block 11F731 OB-VI and a transport Soyuz 7K-S.Soyuz OB-VI
The Soyuz OB-VI would be launched for 30 day missions in a 51.6 degree orbit at 250 x 270 km. Power was provided by solar panels, and the payload included 700 to 1,000 kg of instrumentation. The total mass would be around 6,500 kg (14,300 lb).Soyuz 7K-S
The initial Soyuz 7K-S program was to consist of four unmanned, followed by two manned test flights, then two operational launches. Cosmonauts were assigned to the project in 1973.In 1975 the project was canceled.
At that time the launch escape system for 7K-S was ready and was used for Apollo-Soyuz Test Project flights. Three complete vehicles were launched as unmanned test missions:
- Cosmos 670Cosmos 670-Mission parameters:*Spacecraft: 7K-S*Mass: 6700 kg*Crew: None*Launched: August 6, 1974*Landed: August 8, 1974 23:59 GMT.*Perigee: 221 km*Apogee: 294 km*Inclination: 50.6 deg*Duration: 2.99 days...
- Cosmos 772Cosmos 772-Mission parameters:*Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S*Mass: 6750 kg*Crew: None*Launched: September 29, 1975*Landed: October 3, 1975 4:10 GMT*Perigee: 154 km*Apogee: 245 km*Inclination: 51.8 deg*Duration: 3.99 days-Maneuver Summary:...
- Cosmos 869Cosmos 869-Mission parameters:*Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S.*Mass: 6800 kg.*Crew: None.*Launched: November 29, 1976.*Landed: December 17, 1976 10:31 GMT.*Perigee: 209 km.*Apogee: 289 km.*Inclination: 51.7 deg.*Duration: 17.99 days.-Maneuver Summary:...
Soyuz 7K-ST
The Soyuz 7K-ST transport project was develop in parallel to the military 7K-S and was redesigned for a crew of three, eventually becoming the Soyuz-TSoyuz-T
The Soyuz-T spacecraft was the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. The T stood for transport...
used with the Salyut
Salyut
The Salyut program was the first space station program undertaken by the Soviet Union, which consisted of a series of nine space stations launched over a period of eleven years from 1971 to 1982...
space stations.
Specifications
- Crew Size: 2
- Total Length: 7.5 m
- Maximum Diameter: 2.7 m
- Total Habitable Volume: 9.00 m3
- Total Mass: 6,800 kg
- Primary Engine Thrust: 400 kgf
- Main Engine Propellants: N2O4/UDMH
- Main Engine Isp: 305 sec
- Electrical System: Solar panels
External links
- Russia New Russian spaceship will be able to fly to Moon - space corp
- RSC Energia: Concept Of Russian Manned Space Navigation Development
- Mir Hardware Heritage
- David S.F. Portree, Mir Hardware Heritage, NASA RP-1357, 1995
- Mir Hardware Heritage (wikisource)
- Information on Soyuz spacecraft
- OMWorld's ASTP Docking Trainer Page
- NASA - Russian Soyuz TMA Spacecraft Details
- Space Adventures circum-lunar mission - details

