
McCumber cube
Encyclopedia
Information Assurance
Information assurance is the practice of managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes...
) programs, now known as The McCumber Cube.
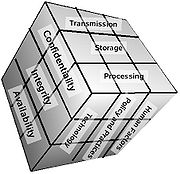
This security model is depicted as a three dimensional
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
Rubik's Cube
Rubik's Cube
Rubik's Cube is a 3-D mechanical puzzle invented in 1974 by Hungarian sculptor and professor of architecture Ernő Rubik.Originally called the "Magic Cube", the puzzle was licensed by Rubik to be sold by Ideal Toy Corp. in 1980 and won the German Game of the Year special award for Best Puzzle that...
-like grid.
The concept of this model is that, in developing information assurance
Information Assurance
Information assurance is the practice of managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes...
systems, organizations must consider the interconnectedness of all the different factors that impact them. To devise a robust information assurance
Information Assurance
Information assurance is the practice of managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes...
program, one must consider not only the security goals of the program (see below), but also how these goals relate specifically to the various states in which information can reside in a system and the full range of available security safeguards that must be considered in the design. The McCumber model helps one to remember to consider all important design aspects without becoming too focused on any one in particular (i.e., relying exclusively on technical controls at the expense of requisite policies and end-user training).
Desired goals
- ConfidentialityConfidentialityConfidentiality is an ethical principle associated with several professions . In ethics, and in law and alternative forms of legal resolution such as mediation, some types of communication between a person and one of these professionals are "privileged" and may not be discussed or divulged to...
: assurance that sensitive information is not intentionally or accidentally disclosed to unauthorized individuals. - IntegrityIntegrityIntegrity is a concept of consistency of actions, values, methods, measures, principles, expectations, and outcomes. In ethics, integrity is regarded as the honesty and truthfulness or accuracy of one's actions...
: assurance that information is not intentionally or accidentally modified in such a way as to call into question its reliability. - AvailabilityAvailabilityIn telecommunications and reliability theory, the term availability has the following meanings:* The degree to which a system, subsystem, or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, i.e., a random, time...
: ensuring that authorized individuals have both timely and reliable access to data and other resources when needed.
Information states
- Storage: Data at rest (DAR) in an information system, such as that stored in memory or on a magnetic tape or disk.
- Transmission: transferring data between information systems - also known as data in transit (DIT).
- Processing: performing operations on data in order to achieve a desired objective.
Safeguards
- Policy and practices: administrative controls, such as management directives, that provide a foundation for how information assuranceInformation AssuranceInformation assurance is the practice of managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes...
is to be implemented within an organization. (examples: acceptable use policies or incident response procedures) - also referred to as operations. - Human factors: ensuring that the users of information systems are aware of their roles and responsibilities regarding the protection of information systems and are capable of following standards. (example: end-user training on avoiding computer virus infections or recognizing social engineering tactics) - also referred to as personnel
- Technology: software and hardware-based solutions designed to protect information systems (examples: anti-virus, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, etc.)

