
Lysophosphatidic acid
Encyclopedia
Lysophosphatidic acid is a phospholipid
derivative that can act as a signaling
molecule.
due to its activation of three high-affinity G-protein-coupled receptors called LPA1
, LPA2
, and LPA3
(also known as EDG2, EDG4, and EDG7). Additional, newly identified LPA receptors include LPA4 (p2y9/GPR23), LPA5 (GPR92) and LPA6 (GPR87).
or the LPA receptors can lead to hyperproliferation, which may contribute to oncogenesis and metastasis
.
LPA may be the cause of pruritus (itching) in individuals with cholestatic (impaired bile flow) diseases.
can be activated, subsequently activating Rho kinase. This can lead to the formation of stress fibers and cell migration through the inhibition of myosin light-chain phosphatase.
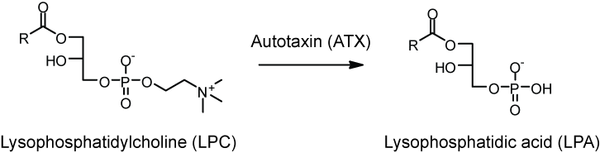
called autotaxin
, which removes the choline
group from lysophosphatidylcholine
.
Lysophosphatidic acid is also an intermediate in the synthesis of phosphatidic acid.
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of all cell membranes as they can form lipid bilayers. Most phospholipids contain a diglyceride, a phosphate group, and a simple organic molecule such as choline; one exception to this rule is sphingomyelin, which is derived from...
derivative that can act as a signaling
Lipid signaling
Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses...
molecule.
Function
LPA acts as a potent mitogenMitogen
A mitogen is a chemical substance that encourages a cell to commence cell division, triggering mitosis. A mitogen is usually some form of a protein.Mitogenesis is the induction of mitosis, typically via a mitogen....
due to its activation of three high-affinity G-protein-coupled receptors called LPA1
Lysophospholipid receptor
The lysophospholipid receptor group are members of the G protein-coupled receptor family of integral membrane proteins that are important for lipid signaling. In humans, there are eight LPL receptors, each encoded by a separate gene...
, LPA2
Lysophospholipid receptor
The lysophospholipid receptor group are members of the G protein-coupled receptor family of integral membrane proteins that are important for lipid signaling. In humans, there are eight LPL receptors, each encoded by a separate gene...
, and LPA3
Lysophospholipid receptor
The lysophospholipid receptor group are members of the G protein-coupled receptor family of integral membrane proteins that are important for lipid signaling. In humans, there are eight LPL receptors, each encoded by a separate gene...
(also known as EDG2, EDG4, and EDG7). Additional, newly identified LPA receptors include LPA4 (p2y9/GPR23), LPA5 (GPR92) and LPA6 (GPR87).
Clinical significance
Because of its ability to stimulate cell proliferation, aberrant LPA-signaling has been linked to cancer in numerous ways. Dysregulation of autotaxinAutotaxin
Autotaxin also known as ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENPP2 gene.- Function :...
or the LPA receptors can lead to hyperproliferation, which may contribute to oncogenesis and metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
.
LPA may be the cause of pruritus (itching) in individuals with cholestatic (impaired bile flow) diseases.
GTPase activation
Downstream of LPA receptor activation, the small GTPase RhoRho
Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"...
can be activated, subsequently activating Rho kinase. This can lead to the formation of stress fibers and cell migration through the inhibition of myosin light-chain phosphatase.
Metabolism
There are a number of potential routes to its biosynthesis, but the most well-characterized is by the action of a lysophospholipase DPhospholipase D
Phospholipase D is an enzyme which is located in the plasma membrane and catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine to form phosphatidic acid , releasing the soluble choline headgroup into the cytosol...
called autotaxin
Autotaxin
Autotaxin also known as ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENPP2 gene.- Function :...
, which removes the choline
Choline
Choline is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
group from lysophosphatidylcholine
Lysophosphatidylcholine
Lysophosphatidylcholines , also called lysolecithins, are a class of chemical compounds which are derived from phosphatidylcholines. They result from partial hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholines, which removes one of the fatty acid groups. The hydrolysis is generally the result of the enzymatic...
.
Lysophosphatidic acid is also an intermediate in the synthesis of phosphatidic acid.


