
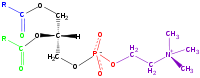
Phospholipid
Encyclopedia
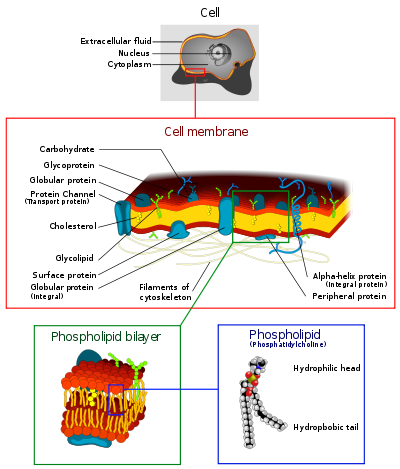
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
s as they can form lipid bilayer
Lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer is a thin membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around cells. The cell membrane of almost all living organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the membranes surrounding the cell nucleus...
s. Most phospholipids contain a diglyceride
Diglyceride
A diglyceride, or a diacylglycerol , is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages....
, a phosphate group, and a simple organic molecule such as choline
Choline
Choline is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
; one exception to this rule is sphingomyelin
Sphingomyelin
Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide...
, which is derived from sphingosine
Sphingosine
Sphingosine is an 18-carbon amino alcohol with an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain, which forms a primary part of sphingolipids, a class of cell membrane lipids that include sphingomyelin, an important phospholipid.-Functions:...
instead of glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
. The first phospholipid identified as such in biological tissues was lecithin
Lecithin
Lecithin is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues, and in egg yolk, composed of phosphoric acid, choline, fatty acids, glycerol, glycolipids, triglycerides, and phospholipids .The word lecithin was originally coined in 1847 by...
, or phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically...
, in the egg yolk, by Theodore Nicolas Gobley, a French chemist and pharmacist, in 1847. The structure of the phospholipid molecule generally consists of hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. It is usually found with cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
molecules which are found in-between the spaces of the phospholipid.
Amphipathic character
The 'head' is hydrophilic (attracted to waterWater
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
), while the hydrophobic 'tails' are repelled by water and are forced to aggregate. The hydrophillic head contains the negatively charged phosphate group, and may contain other polar groups. The hydrophobic tail usually consists of long fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
hydrocarbon chains. When placed in water, phospholipids form a variety of structures depending on the specific properties of the phospholipid. These specific properties allow phospholipids to play an important role in the phospholipid bilayer. In biological systems, the phospholipids often occur with other molecules (e.g., proteins, glycolipids, cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
) in a bilayer
Bilayer
A bilayer is a double layer of closely packed atoms or molecules. The properties of bilayers are studied in condensed matter physics, often in the context of semiconductor devices, where two distinct materials are united to form junctions ....
such as a cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
. Lipid bilayers occur when hydrophobic tails line up against one another, forming a membrane hydrophilic heads on both sides facing the water.
Such movement can be described by the Fluid Mosaic Model, that describes the membrane as a mosaic of lipid molecules that act as a solvent for all the substances and proteins within it, so proteins and lipid molecules are then free to diffuse laterally through the lipid matrix and migrate over the membrane. Cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
contributes to membrane fluidity by hindering the packing together of phospholipids. However, this model has now been superseded, as through the study of lipid polymorphism
Lipid polymorphism
Polymorphism in biophysics is the aspect of the behaviour of lipids that influences their long-range order, i.e. how they aggregate. This can be in the form of spheres of lipid molecules , pairs of layers that face one another , a tubular arrangement , or various cubic phases Polymorphism in...
it is now known that the behaviour of lipids under physiological (and other) conditions is not simple.
Diacylglyceride structures
- See: GlycerophospholipidGlycerophospholipidGlycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes.-Structures:...
- Phosphatidic acid (phosphatidate) (PA)
- PhosphatidylethanolaminePhosphatidylethanolaminePhosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,...
(cephalin) (PE) - PhosphatidylcholinePhosphatidylcholinePhosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically...
(lecithin) (PC) - PhosphatidylserinePhosphatidylserinePhosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase...
(PS) - Phosphoinositides:
- PhosphatidylinositolPhosphatidylinositolPhosphatidylinositol is a negatively charged phospholipid and a minor component in the cytosolic side of eukaryotic cell membranes....
(PI) - Phosphatidylinositol phosphatePhosphatidylinositol phosphatePhosphatidylinositol phosphate may refer to:* Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, also known as PIP* Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, also known as PIP* Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, also known as PIP...
(PIP) - Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphatePhosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphatePhosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdInsP2, also known simply as PIP2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes...
(PIP2) and - Phosphatidylinositol triphosphatePhosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphatePhosphatidylinositol -triphosphate , abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases phosphorylation on phosphatidylinositol -bisphosphate .-Discovery:...
(PIP3).
- Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphosphingolipids
- Ceramide phosphorylcholine (SphingomyelinSphingomyelinSphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide...
) (SPH) - Ceramide phosphorylethanolamine (Sphingomyelin) (Cer-PE)
- Ceramide phosphorylglycerol
Simulations
Computational simulations of phospholipids are often performed using molecular dynamicsMolecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
with force fields
Force field (chemistry)
In the context of molecular modeling, a force field refers to the form and parameters of mathematical functions used to describe the potential energy of a system of particles . Force field functions and parameter sets are derived from both experimental work and high-level quantum mechanical...
such as GROMOS
GROMOS
GROMOS is a force field for molecular dynamics simulation developed at the University of Groningen and at at the at the ETH Zurich.The united atom force field was optimized with respect to the condensed phase properties of alkanes....
, CHARMM
CHARMM
CHARMM is the name of a widely used set of force fields for molecular dynamics as well as the name for the molecular dynamics simulation and analysis package associated with them...
, or AMBER
AMBER
AMBER is a family of force fields for molecular dynamics of biomolecules originally developed by the late Peter Kollman's group at the University of California, San Francisco. AMBER is also the name for the molecular dynamics software package that simulates these force fields...
.
Characterization
Phospholipids are optically highly birefringent, i.e. their refractive index is different along their axis as opposed to perpendicular to it. Measurement of birefringenceBirefringence
Birefringence, or double refraction, is the decomposition of a ray of light into two rays when it passes through certain anisotropic materials, such as crystals of calcite or boron nitride. The effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who saw it in calcite...
can be achieved using cross polarisers in a microscope to obtain an image of e.g. vesicle
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
walls or using techniques such as dual polarisation interferometry
Dual Polarisation Interferometry
Dual polarization interferometry is an analytical technique that can probe molecular scale layers adsorbed to the surface of a waveguide by using the evanescent wave of a laser beam confined to the waveguide...
to quantify lipid order or disruption in supported bilayers.
Phospholipid synthesis
Phospholipid synthesis occurs in the cytosol adjacent to EREndoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
membrane that is studded with proteins that act in synthesis (GPAT and LPAAT acyl transferases, phosphatase and choline phosphotransferase) and allocation (flippase
Flippase
Flippases are a family of transmembrane lipid transporter enzymes located in the membrane responsible for aiding the movement of phospholipid molecules between the two leaflets that compose a cell's membrane...
and floppase). Eventually a vesicle will bud off from the ER containing phospholipids destined for the cytoplasmic cellular membrane on its exterior leaflet and phospholipids destined for the exoplasmic cellular membrane on its inner leaflet.
In signal transduction
Some types of phospholipid can be split to produce products that function as second messengers in signal transductionSignal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
. Examples include phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdInsP2, also known simply as PIP2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes...
(PIP2), that can be split by the enzyme Phospholipase C
Phospholipase C
Phosphoinositide phospholipase C is a family of eukaryotic intracellular enzymes that play an important role in signal transduction processes. In general, this enzyme is denoted as Phospholipase C, although three other families of phospholipase C enzymes have been identified in bacteria and in...
into inositol triphosphate
Inositol triphosphate
Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate , together with diacylglycerol , is a secondary messenger molecule used in signal transduction and lipid signaling in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell...
(IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), which both carry out the functions of the Gq type of G protein in response to various stimuli and intervene in various processes from long term depression in neurons to leukocyte signal pathways started by chemokine
Chemokine
Chemokines are a family of small cytokines, or proteins secreted by cells. Their name is derived from their ability to induce directed chemotaxis in nearby responsive cells; they are chemotactic cytokines...
receptors.
Phospholipids also intervene in prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
signal pathways as the raw material used by lipase
Lipase
A lipase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation or cleavage of fats . Lipases are a subclass of the esterases.Lipases perform essential roles in the digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, living organisms...
enzymes to produce the prostaglandin precursors. In plants they serve as the raw material to produce Jasmonic acid
Jasmonic acid
Jasmonic acid is derived from the fatty acid linolenic acid. It is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway....
, a plant hormone
Plant hormone
Plant hormones are chemicals that regulate plant growth, which, in the UK, are termed 'plant growth substances'. Plant hormones are signal molecules produced within the plant, and occur in extremely low concentrations. Hormones regulate cellular processes in targeted cells locally and, when moved...
similar in structure to prostaglandins that mediates defensive responses against pathogens.
Food technology
Phospholipids can act as an emulsifier, enabling oils to form a colloidColloid
A colloid is a substance microscopically dispersed evenly throughout another substance.A colloidal system consists of two separate phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase . A colloidal system may be solid, liquid, or gaseous.Many familiar substances are colloids, as shown in the chart below...
with water. Phospholipids are one of the components of lecithin
Lecithin
Lecithin is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues, and in egg yolk, composed of phosphoric acid, choline, fatty acids, glycerol, glycolipids, triglycerides, and phospholipids .The word lecithin was originally coined in 1847 by...
which is found in egg-yolks, as well as being extracted from soy beans, and is used as a food additive
Food additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance its taste and appearance.Some additives have been used for centuries; for example, preserving food by pickling , salting, as with bacon, preserving sweets or using sulfur dioxide as in some wines...
in many products, and can be purchased as a dietary supplement
Dietary supplement
A dietary supplement, also known as food supplement or nutritional supplement, is a preparation intended to supplement the diet and provide nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, or amino acids, that may be missing or may not be consumed in sufficient quantities in a person's diet...
.
Phospholipid derivatives
- See table below for an extensive list.
- Natural phospholipid derivates:
- egg PC, egg PG, soy PC, hydrogenated soy PC, sphingomyelinSphingomyelinSphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide...
as natural phospholipids.
- egg PC, egg PG, soy PC, hydrogenated soy PC, sphingomyelin
- Synthetic phospholipid derivates:
- Phosphatidic acid (DMPA, DPPA, DSPA)
- PhosphatidylcholinePhosphatidylcholinePhosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically...
(DDPC, DLPC, DMPC, DPPCDipalmitoylphosphatidylcholineDipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid consisting of two palmitic acids and is the major constituent of pulmonary surfactant. It is also the only surface active component of lung surfactant capable of lowering surface tension to near zero levels. DpPC is synthesized mainly through...
, DSPC, DOPC, POPC, DEPC) - PhosphatidylglycerolPhosphatidylglycerolPhosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded...
(DMPG, DPPG, DSPG, POPG) - PhosphatidylethanolaminePhosphatidylethanolaminePhosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,...
(DMPE, DPPE, DSPE DOPE) - PhosphatidylserinePhosphatidylserinePhosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase...
(DOPS) - PEG phospholipid (mPEG-phospholipid, polyglycerin-phospholipid, funcitionalized-phospholipid, terminal activated-phospholipid)
- Natural phospholipid derivates:
Abbreviations used and chemical information of glycerophospholipids
| Abbreviation | CAS | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDPC Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid consisting of two palmitic acids and is the major constituent of pulmonary surfactant. It is also the only surface active component of lung surfactant capable of lowering surface tension to near zero levels. DpPC is synthesized mainly through... |
3436-44-0 | 1,2-Didecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DEPA-NA | 80724-31-8 | 1,2-Dierucoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidic acid |
| DEPC | 56649-39-9 | 1,2-Dierucoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DEPE | 988-07-2 | 1,2-Dierucoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
| DEPG-NA | 1,2-Dierucoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
|
| DLOPC | 998-06-1 | 1,2-Dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DLPA-NA | 1,2-Dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidic acid | |
| DLPC | 18194-25-7 | 1,2-Dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DLPE | 1,2-Dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
|
| DLPG-NA | 1,2-Dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
|
| DLPG-NH4 | 1,2-Dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Ammonium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
|
| DLPS-NA | 1,2-Dilauroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase... |
|
| DMPA-NA | 80724-3 | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidic acid |
| DMPC | 18194-24-6 | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DMPE | 988-07-2 | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
| DMPG-NA | 67232-80-8 | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| DMPG-NH4 | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Ammonium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
|
| DMPG-NH4/NA | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium/Ammonium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
|
| DMPS-NA | 1,2-Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase... |
|
| DOPA-NA | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidic acid | |
| DOPC | 4235-95-4 | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DOPE | 4004-5-1- | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
| DOPG-NA | 62700-69-0 | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| DOPS-NA | 70614-14-1 | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase... |
| DPPA-NA | 71065-87-7 | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidic acid |
| DPPC DPPC DPPC can stand for:* Disabled Persons Protection Commission at the Commonwealth of Massachusetts* Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid* Disaster Prevention and Preparedness Commission of Ethiopia... |
63-89-8 | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DPPE | 923-61-5 | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
| DPPG-NA | 67232-81-9 | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| DPPG-NH4 | 73548-70-6 | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Ammonium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| DPPS-NA | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase... |
|
| DSPA-NA | 108321-18-2 | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidic acid |
| DSPC | 816-94-4 | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| DSPE | 1069-79-0 | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
| DSPG-NA | 67232-82-0 | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| DSPG-NH4 | 108347-80-4 | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol...) (Ammonium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| DSPS-NA | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid component, usually kept on the inner-leaflet of cell membranes by an enzyme called flippase... |
|
| Egg Egg (biology) An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo first begins to develop. In most birds, reptiles, insects, molluscs, fish, and monotremes, an egg is the zygote, resulting from fertilization of the ovum, which is expelled from the body and permitted to develop outside the body until the developing... Sphingomyelin Sphingomyelin Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide... empty Liposome Liposome Liposomes are artificially prepared vesicles made of lipid bilayer. Liposomes can be filled with drugs, and used to deliver drugs for cancer and other diseases. Liposomes are composite structures made of phospholipids and may contain small amounts of other molecules... |
|||
| EPC Phosphocholine Phosphocholine is an intermediate in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine in tissues. Phosphocholine is made in a reaction, catalyzed by choline kinase, that converts ATP + Choline into Phosphocholine and ADP... |
Egg-PC | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| HEPC | Hydrogenated Egg PC | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| HSPC | High purity Hydrogenated Soy PC | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| HSPC | Hydrogenated Soy PC | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| LYSOPC MYRISTIC | 18194-24-6 | 1-Myristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylcholines , also called lysolecithins, are a class of chemical compounds which are derived from phosphatidylcholines. They result from partial hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholines, which removes one of the fatty acid groups. The hydrolysis is generally the result of the enzymatic... |
| LYSOPC PALMITIC | 17364-16-8 | 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylcholines , also called lysolecithins, are a class of chemical compounds which are derived from phosphatidylcholines. They result from partial hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholines, which removes one of the fatty acid groups. The hydrolysis is generally the result of the enzymatic... |
| LYSOPC STEARIC | 19420-57-6 | 1-Stearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylcholines , also called lysolecithins, are a class of chemical compounds which are derived from phosphatidylcholines. They result from partial hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholines, which removes one of the fatty acid groups. The hydrolysis is generally the result of the enzymatic... |
| Milk Milk Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many... Sphingomyelin Sphingomyelin Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide... MPPC Sphingomyelin Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide... |
1-Myristoyl-2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero 3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| MSPC | 1-Myristoyl-2-stearoyl-sn-glycero-3–phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| PMPC | 1-Palmitoyl-2-myristoyl-sn-glycero-3–phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| POPC POPC POPC is a chemical compound. It is a diacylglycerol and phospholipid. The full name is 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. It is an important lipid for biophysical experiment and has been used to study various subjects such as lipid rafts. It is available commercially synthetically... |
26853-31-6 | 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
| POPE | 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine is a lipid found in biological membranes. It is synthesized by the addition of CDP-ethanolamine to diglyceride, releasing CMP. S-adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidyl ethanolamine to yield phosphatidyl choline.Cephalin is a phospholipid,... |
|
| POPG-NA | 81490-05-3 | 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol)...] (Sodium Salt) | Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded... |
| PSPC | 1-Palmitoyl-2-stearoyl-sn-glycero-3–phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| SMPC | 1-Stearoyl-2-myristoyl-sn-glycero-3–phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| SOPC | 1-Stearoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |
|
| SPPC | 1-Stearoyl-2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup.They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy beans from which they are mechanically extracted or chemically... |

