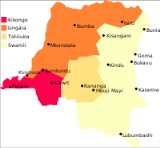
Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Encyclopedia
| Official language | French French language French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts... |
|---|---|
| National languages | Kikongo, Lingala, Swahili Swahili language Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia... and Tshiluba. |
| Other indigenous languages | More than 200 |
| Lingue france | French African French African French is the generic name of the varieties of French spoken by an estimated 115 million African people spread across 31 francophone African countries... , Kikongo, Lingala, Swahili Swahili language Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia... and Tshiluba. |
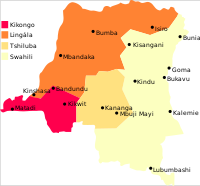
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a state located in Central Africa. It is the second largest country in Africa by area and the eleventh largest in the world...
is a multilingual country where an estimated total of 242 languages are spoken (Ethnologue.com lists 214 living languages). The official language
Official language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
, inherited from the colonial period, is French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
. Four indigenous languages have the status of national language
National language
A national language is a language which has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a people and perhaps by extension the territory they occupy. The term is used variously. A national language may for instance represent the national identity of a nation or country...
: Kikongo, Lingala, Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
and Tshiluba.
When the country was a Belgian colony, it had already instituted teaching and use of the four national languages in primary schools, making it one of the few African nations to have had literacy in local languages during the European colonial period. During the colonial period both Dutch and French were the official languages but French was by far the most important.
French
FrenchFrench language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
is the official language of the country since its colonial period under Belgian
Belgian colonial empire
The Belgian colonial empire consisted of three colonies possessed by Belgium between 1901 and 1962: Belgian Congo , Rwanda and Burundi...
rule. Therefore, the variety of French used in the DRC has many similarities with Belgian French
Belgian French
Belgian French is the variety of French spoken mainly in the French Community of Belgium, alongside related minority regional languages such as Walloon, Picard, Champenois and Gaumais. The French spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Burundi, which were formerly Belgian...
. The colonial language has been kept as the official language since the time of independence because it is widely spoken around the educated groups in the country, as it belongs to none of the indigenous ethnic groups and eases communication between them as well as with the rest of the Francophonie. According to the OIF
OIF
-Geoengineering:*Ocean Iron Fertilization, the practice of adding iron or iron compounds to the ocean to stimulate phytoplankton growth-Formats:*Object Interchange Format, a database management protocol developed by the Object Data Management Group-Foundations:...
, 6,080,000 or 10% of the population were proficient French speakers in 2005 whereas another 18,240,000 or 30,0% were partially French speaking. The Democratic Republic of the Congo is currently the most populous French-speaking country.
See also: French in Africa
African French
African French is the generic name of the varieties of French spoken by an estimated 115 million African people spread across 31 francophone African countries...
Kikongo
The constitution says Kikongo is one of the national languages, but it's a dialect continuumDialect continuum
A dialect continuum, or dialect area, was defined by Leonard Bloomfield as a range of dialects spoken across some geographical area that differ only slightly between neighboring areas, but as one travels in any direction, these differences accumulate such that speakers from opposite ends of the...
with several varieties which may not be mutually intelligible.
It is commonly accepted that the Kituba
Kituba
Kituba is a widely used lingua franca in Central Africa. It is a creole language based on Kikongo, a family of closely related Bantu languages. It is an official language in Congo-Brazzaville and Congo-Kinshasa....
variant, also called Kikongo ya Leta (Kikongo of the government, Leta <= l'État) is the language used in the administration in the provinces of Bas-Congo
Bas-Congo
Bas-Congo is one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the only province with a coastline and it borders Bandundu province to the east and Kinshasa to the northeast...
(which is inhabited by the Bakongo), Kwango
Kwango District
Kwango District is a district located in the Bandundu province, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo .It contains the Kasongo-Lunda, Kahemba, Feshi, Popokabaka and Kenge territories.The main town is Kenge...
and Kwilu
Kwilu District
Kwilu District is a district located in the Bandundu province, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo....
. Kituba has become a vernacular language in many urban centres including Kikwit
Kikwit
Kikwit is the largest city of Kwilu District, lying on the Kwilu River in the southwestern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Kikwit is also known in the region under the nickname "The Mother". The population is approximately 294,210...
, Bandundu
Bandundu
Bandundu, formerly known as Banningville or Banningstad, is a city in Bandundu Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.Bandundu is the capital of Bandundu Province. It is located on the north bank of the Kwango River, just below the juncture of the Kwango and the Kwilu, 8 km upstream from...
, Matadi
Matadi
Matadi is the chief sea port of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the capital of the Bas-Congo province. It has a population of 245,862 . Matadi is situated on the left bank of the Congo River from the mouth and below the last navigable point before rapids make the river impassable for a...
, Boma
Boma
The port town of Boma in Bas-Congo province was the capital city of the Congo Free State and Belgian Congo from 1 May 1886 to 1926, when it was moved to Léopoldville . It exports tropical timber, bananas, cacao, and palm products...
and Muanda
Muanda
Muanda or Moanda is a town lying on the Atlantic Ocean coast of the Democratic Republic of Congo at the mouth of the Congo River. It is situated in Bas-Congo Province, and has a population of 50,000...
.
Lingala
Lingala is a language which gained its modern form in the colonial period, with the push of missionaries to uniformize and teach a local vehicular language. It was originally spoken in the upper Congo river area but rapidly spread to the middle Congo area and eventually became the major Bantu language in Kinshasa for many reasons.Lingala was made the official language of the army under Mobutu
Mobutu Sese Seko
Mobutu Sese Seko Nkuku Ngbendu wa Za Banga , commonly known as Mobutu or Mobutu Sese Seko , born Joseph-Désiré Mobutu, was the President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1965 to 1997...
, but since the rebellions the army has also used Swahili in the east. With the transition period and the consolidation of different armed groups into the Congolese Army, the linguistic policy has returned to its previous form and Lingala is again the official language of the Army.
Swahili
SwahiliSwahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
is the most spoken vehicular language spoken in Eastern Equatorial Africa
Equatorial Africa
Equatorial Africa is an ambiguous term that is sometimes used to refer to tropical Africa, or the region of Sub-Saharan Africa traversed by the equator....
. Many variations of Swahili are spoken in the country but the major one is Kingwana, sometimes called Copperbelt Swahili especially in the Katanga area.
Tshiluba
The constitution does not specify which variation of Tshiluba is a national language. There are two major variations of Tshiluba: Luba-Kasai, spoken in the East Kasai Region (Luba peopleLuba people
The Luba are one of the Bantu peoples of Central Africa. They are indigenous to the Katanga, Kasai, and Maniema regions which were historic provinces of present-day Democratic Republic of the Congo...
) and Luba-Lulua, in the West Kasai Region (Bena Lulua people). Luba-Kasai seems to be the language used by the administration.
Sign languages
There are 12 deaf institutions in the country, most teach French Sign LanguageFrench Sign Language
French Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf in the nation of France. According to Ethnologue, it has 50,000 to 100,000 native signers....
or variations. American Sign Language
American Sign Language
American Sign Language, or ASL, for a time also called Ameslan, is the dominant sign language of Deaf Americans, including deaf communities in the United States, in the English-speaking parts of Canada, and in some regions of Mexico...
is also practiced in the country.
Other languages
The most noticeable other languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo are MongoMongo language
Mongo, also called Nkundo or Mongo-Nkundu, is a language spoken by several of the Mongo peoples in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Mongo speakers reside in central DRC, mostly south of the Congo River. Mongo is a tonal language....
, Lunda
Lunda language
Lunda, also known as Chilunda, is a Bantu language spoken in Zambia, Angola and, to a lesser extent, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Lunda and its dialects are spoken and understood by perhaps 2.6% of Zambians , and the language is used mainly in the northern part of that...
, Tetela
Tetela language
Tetela , also Sungu, is a Bantu language of northern Kasai-Oriental Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is a member of the Tetela family of Bantu languages and is closely related to Nkutu, Kusu, and Yela....
, Chokwe
Chokwe language
Chokwe is the Bantu language spoken by the Chokwe people of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola and Zambia. It is recognized as a national language of Angola, where about 456,000 people spoke it as of 1991. Another half a million speakers lived in the Congo in 1990, and some 44,200 in...
, Budza
Budza language
Budza or Buja is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of Congo....
, Lendu, Mangbetu
Mangbetu language
Mangbetu, or Nemangbetu, is one of the most populous of the Central Sudanic languages. It is spoken by the Mangbetu people of northeastern Congo. It, or its speakers, are also known as Amangbetu, Kingbetu, Mambetto. The most populous dialect, and the one most widely understood, is called Medje....
, Nande
Nande language
Nande, also known as Ndandi and Yira, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.The Nande of Congo and the Konjo people of Uganda are a single ethnic group, which they call Yira . They trace their origins to the Ruwenzori Mountains between the two countries. The languages...
, Ngbaka, and Eborna
Eborna language
Borna, or Eborna, is a dubious Southern Bantoid language reportedly spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It may not exist, but only be another name for Boma....
.
As of 2010 the government decided to include Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
as an optional language at schools as a reflex of the increasing influence in the continent.
Among the slangs
Slang
Slang is the use of informal words and expressions that are not considered standard in the speaker's language or dialect but are considered more acceptable when used socially. Slang is often to be found in areas of the lexicon that refer to things considered taboo...
spoken in Congo, Indubil
Indubil
Indubil is a slang spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has been noted since around sixties - musician Sam Mangwana mentions its use in lyrics before the seventies...
has been noted since around the sixties and continues to evolve nowadays.
External links
- Linguistic map of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from Muturzikin.com
- Ethnologue.com: Ethnologue report for the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- PanAfrican L10n: Democratic Republic of Congo, languages and software localization Linguistic situation in RDC New Technologies and languages of both Congos ONG Éveil du Congo, NGO working in localization and translations in Congolese national languages

