
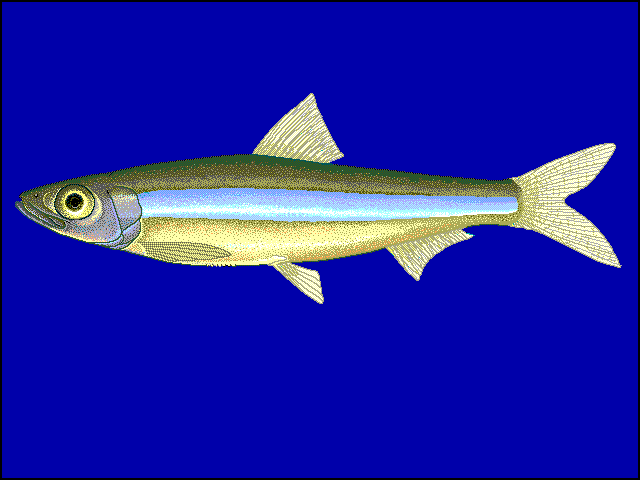
Kapenta
Encyclopedia
Zambia
Zambia , officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west....
and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
or Dagaa or Ndgaa elsewhere, is really two species (Lake Tanganyika sardine
Lake Tanganyika sardine
The Lake Tanganyika sardine is a species of fish in the Clupeidae family. It is monotypic within the genus Limnothrissa. It is found in Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, Rwanda, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Its natural habitat is freshwater lakes...
Limnothrissa miodon and Lake Tanganyika sprat
Lake Tanganyika sprat
The Lake Tanganyika sprat is a species of fish in the Clupeidae family. It is monotypic within the genus Stolothrissa. It is found in Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, and Zambia. Its natural habitat is freshwater lakes. It and the Lake Tanganyika sardine are known...
Stolothrissa tanganicae) both of which are small, planktivorous, pelagic
Pelagic fish
Pelagic fish live near the surface or in the water column of coastal, ocean and lake waters, but not on the bottom of the sea or the lake. They can be contrasted with demersal fish, which do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish which are associated with coral reefs.The marine pelagic...
, freshwater
Freshwater
Fresh water is naturally occurring water on the Earth's surface in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, bogs, ponds, lakes, rivers and streams, and underground as groundwater in aquifers and underground streams. Fresh water is generally characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and...
clupeid originating from Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika is an African Great Lake. It is estimated to be the second largest freshwater lake in the world by volume, and the second deepest, after Lake Baikal in Siberia; it is also the world's longest freshwater lake...
in East Africa
East Africa
East Africa or Eastern Africa is the easterly region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics. In the UN scheme of geographic regions, 19 territories constitute Eastern Africa:...
. They form the major biomass of pelagic fish in Lake Tanganyika, swimming in large schools in the open lake, feeding on copepods and potentially jellyfish. Their major predators are four species of Lates
Lates
Lates is a genus of freshwater and marine fish in the family Latidae of the order Perciformes. The type species is Lates niloticus, the Nile perch. The Lates species are native to the Indian and western Pacific Oceans and to rivers and lakes in Africa; several species are endemic to the Rift...
which are also endemic to Lake Tanganyika, and are related to (but not the same as) the Nile Perch
Nile perch
The Nile perch is a species of freshwaterfish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is widespread throughout muchof the Afrotropic ecozone, being native to the Congo, Nile, Senegal, Niger, and Lake Chad, Volta, Lake Turkana and other river basins. It also occurs in the brackish waters of...
in Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. The lake was named for Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom, by John Hanning Speke, the first European to discover this lake....
. All of these pelagic fish have suffered from overfishing
Overfishing
Overfishing occurs when fishing activities reduce fish stocks below an acceptable level. This can occur in any body of water from a pond to the oceans....
in the last two decades.
Limnothrissa miodon has been successfully introduced in both natural and artificial African lakes. Large kapenta fisheries now take place in the Lake Kariba
Lake Kariba
Lake Kariba is the world's largest artificial lake and reservoir. It lies 1300 kilometers upstream from the Indian Ocean, along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe...
(Zambia
Zambia
Zambia , officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west....
/Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
) and Cahora Bassa
Cahora Bassa
The Cahora Bassa lake is Africa's fourth-largest artificial lake, situated in the Tete Province in Mozambique. The name Cabora Bassa is an earlier misspelling of the name...
(Mozambique
Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique , is a country in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west and Swaziland and South Africa to the southwest...
).
This fish is caught at night using lights to attract it. A dip net
Hand net
A hand net, also called a scoop net, is a net or mesh basket held open by a hoop. It may or may not be on the end of a handle. Hand nets have been used since antiquity and can be used for scooping fish near the surface of the water, such as muskellunge or northern pike.A hand net with a long handle...
generally about six metres in diameter is used to bring the fish up from anything from 40 metres (130 ft). It is then salted at a ratio normally of 2.5 kg per 30 kg (1 lb per 12 lb) of fish, and dried in the hot Zambezi Valley sun. It is hugely important staple, providing refrigeration-free protein to people of Africa. A cup of dried kapenta will feed a family.
It is an important bait fish
Bait fish
Bait fish are small fish caught for use as bait to attract large predatory fish, particularly game fish. Species used are typically those that are common and breed rapidly, making them easy to catch and in regular supply. Examples of marine bait fish are anchovies, halfbeaks such as ballyhoo, and...
for the Tigerfish
Tigerfish
Tigerfish is the common name for a variety of species from several different families of fish, usually on account of their colouration or otherwise fearsome appearance and teeth.- Alestiidae :...
(Alestidae family) and although introduced in Kariba and Cahora Bassa, does not seem to have harmed the environment.
It is an important contributor to the economies of the areas it is caught in.
In Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
dried kapenta fish are shallow fried with onions and tomatoes. They are eaten with traditional staple meal called Isitshwala/sadza
Sadza
Sadza in Shona, Isitshwala in isiNdebele, pap in South Africa or nsima in the Chichewa language of Malawi, is a cooked corn meal that is the staple food in Zimbabwe and other parts of southern and eastern Africa. This food is cooked widely in other countries of the region.Sadza in appearance is a...
.

