
Jamin interferometer
Encyclopedia
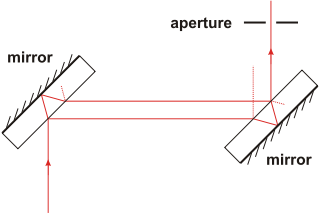
Mach-Zehnder interferometer
The Mach–Zehnder interferometer is a device used to determine the relative phase shift between two collimated beams from a coherent light source. The interferometer has been used, amongst other things, to measure small phase shifts in one of the two beams caused by a small sample or the change in...
. It was developed in 1856 by the French physicist Jules Jamin
Jules Jamin
Jules Célestin Jamin was a French physicist. He was professor of physics at École Polytechnique from 1852 to 1881 and received the Rumford Medal in 1858 for his work on light...
.
The interferometer is made up of two mirror
Mirror
A mirror is an object that reflects light or sound in a way that preserves much of its original quality prior to its contact with the mirror. Some mirrors also filter out some wavelengths, while preserving other wavelengths in the reflection...
s, made of the thickest glass possible. The Fresnel reflection
Fresnel equations
The Fresnel equations , deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel , describe the behaviour of light when moving between media of differing refractive indices...
from the first surface of the mirror acts as a beam splitter
Beam splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that splits a beam of light in two. It is the crucial part of most interferometers.In its most common form, a rectangle, it is made from two triangular glass prisms which are glued together at their base using Canada balsam...
. The incident light is split into two rays, parallel to each other and displaced by an amount depending on the thickness of the mirror. The rays are recombined at the second mirror, and ultimately imaged onto a screen.
If a phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
-shifting element is added to one arm of the interferometer, then the displacement it causes can be determined by simply counting the interference fringes (e.g., the minima).
The Jamin interferometer allows very exact measurements of the refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
and dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
of gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es; a transparent pressure chamber can be positioned in the instrument. The phase shift due to changes in pressure is quite easy to measure.

