
Jackson Structured Programming
Encyclopedia
Structured programming
Structured programming is a programming paradigm aimed on improving the clarity, quality, and development time of a computer program by making extensive use of subroutines, block structures and for and while loops - in contrast to using simple tests and jumps such as the goto statement which could...
based on correspondences between data stream structure and program structure. JSP structures programs and data in terms of sequences, iterations and selections, and as a consequence it is applied when designing a program's detailed control structure, below the level where object-oriented methods
Object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming is a programming paradigm using "objects" – data structures consisting of data fields and methods together with their interactions – to design applications and computer programs. Programming techniques may include features such as data abstraction,...
become important.
Introduction
Michael A. JacksonMichael A. Jackson
Michael Anthony Jackson is a British computer scientist, and independent computing consultant in London, England. He is also part-time researcher at AT&T Research, Florham Park, NJ, U.S., and visiting research professor at the Open University in the UK.- Biography :Jackson was educated at Harrow...
originally developed JSP in the 1970s. He documented the system in his 1975 book Principles of Program Design. Jackson's aim was to make COBOL
COBOL
COBOL is one of the oldest programming languages. Its name is an acronym for COmmon Business-Oriented Language, defining its primary domain in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments....
batch file processing programs easier to modify and maintain, but the method can be used to design programs for any programming language
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
that has structured control constructs, languages such as C
C (programming language)
C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
, Java
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
and Perl
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Perl was originally developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions and become widely popular...
. Despite its age, JSP is still in use and is supported by diagramming tools such as Microsoft's Visio and CASE tools such as Jackson Workbench
Jackson Structured Programming was seen by many as related to Warnier Structured Programming
Warnier/Orr Diagrams
A Warnier/Orr diagram is a kind of hierarchical flowchart that allow the description of the organization of data and procedures. They were initially developed in France by Jean-Dominique Warnier and in the US by Kenneth Orr...
, but the latter method focused almost exclusively on the structure of the output stream. JSP and Warnier's method both structure programs and data using only sequences, iterations and selections, so they essentially create programs that are parsers for regular expression
Regular expression
In computing, a regular expression provides a concise and flexible means for "matching" strings of text, such as particular characters, words, or patterns of characters. Abbreviations for "regular expression" include "regex" and "regexp"...
s which simultaneously match the program's input and output data streams.
Because JSP focusses on the existing input and output data streams, designing a program using JSP is claimed to be more straightforward than with other structured programming methods, avoiding the leaps of intuition needed to successfully program using methods such as top-down decomposition.
Another consequence of JSP's focus on data streams is that it creates program designs with a very different structure to the kind created by the stepwise refinement methods of Wirth
Niklaus Wirth
Niklaus Emil Wirth is a Swiss computer scientist, best known for designing several programming languages, including Pascal, and for pioneering several classic topics in software engineering. In 1984 he won the Turing Award for developing a sequence of innovative computer languages.-Biography:Wirth...
and Dijkstra
Edsger Dijkstra
Edsger Wybe Dijkstra ; ) was a Dutch computer scientist. He received the 1972 Turing Award for fundamental contributions to developing programming languages, and was the Schlumberger Centennial Chair of Computer Sciences at The University of Texas at Austin from 1984 until 2000.Shortly before his...
. One typical feature of the structure of JSP programs is that they have several input operations distributed throughout the code in contrast to programs designed using stepwise refinement, which tend to have only one input operation. Jackson illustrates this difference in Chapter 3 of Principles of Program Design. He presents two versions of a program, one designed using JSP, the other using "traditional" methods.
Structural equivalent
The JSP version of the program is structurally equivalent to
String line;
line = in.readLine;
while (line != null) {
int count = 0;
String firstLineOfGroup = line;
while (line != null && line.equals(firstLineOfGroup)) {
count++;
line = in.readLine;
}
System.out.println(firstLineOfGroup + " " + count);
}
and the traditional version of the program is equivalent to
String line;
int count = 0;
String firstLineOfGroup = null;
while ((line = in.readLine) != null) {
if (firstLineOfGroup null
|| !line.equals(firstLineOfGroup)) {
if (firstLineOfGroup != null) {
System.out.println(firstLineOfGroup + " " + count);
}
count = 0;
firstLineOfGroup = line;
}
count++;
}
if (firstLineOfGroup != null) {
System.out.println(firstLineOfGroup + " " + count);
}
Jackson criticises the traditional version, claiming that it hides the relationships which exist between the input lines, compromising the program's understandability and maintainability by, for example, forcing the use of a special case for the first line and forcing another special case for a final output operation.
The method
JSP uses semi-formal steps to capture the existing structure of a program's inputs and outputs in the structure of the program itself.
The intent is to create programs which are easy to modify over their lifetime. Jackson's major insight was that requirement changes are usually minor tweaks to the existing structures. For a program constructed using JSP, the inputs, the outputs, and the internal structures of the program all match, so small changes to the inputs and outputs should translate into small changes to the program.
JSP structures programs in terms of four component types:
- fundamental operations
- sequences
- iterations
- selections
The method begins by describing a program's inputs in terms of the four fundamental component types. It then goes on to describe the program's outputs in the same way. Each input and output is modelled as a separate Data Structure Diagram
Data structure diagram
A Data Structure Diagram is a data model used to describe conceptual data models by providing graphical notations which document entities and their relationships, and the constraints that binds them....
(DSD). To make JSP work for compute-intensive applications, such as digital signal processing (DSP) it is also necessary to draw algorithm structure diagrams, which focus on internal data structures rather than input and output ones.
The input and output structures are then unified or merged into a final program structure, known as a Program Structure Diagram (PSD). This step may involve the addition of a small amount of high level control structure to marry up the inputs and outputs. Some programs process all the input before doing any output, whilst others read in one record, write one record and iterate. Such approaches have to be captured in the PSD.
The PSD, which is language neutral, is then implemented in a programming language. JSP is geared towards programming at the level of control structures, so the implemented designs use just primitive operations, sequences, iterations and selections. JSP is not used to structure programs at the level of classes and objects, although it can helpfully structure control flow within a class's methods.
JSP uses a diagramming notation to describe the structure of inputs, outputs and programs, with diagram elements for each of the fundamental component types.
A simple operation is drawn as a box.

An operation
A sequence of operations is represented by boxes connected with lines. In the example below, operation A consists of the sequence of operations B, C and D.
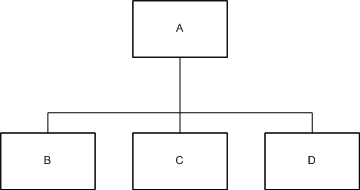
A sequence
An iteration is again represented with joined boxes. In addition the iterated operation has a star in the top right corner of its box. In the example below, operation A consists of an iteration of zero or more invocations of operation B.
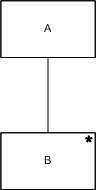
An iteration
Selection is similar to a sequence, but with a circle drawn in the top right hand corner of each optional operation. In the example, operation A consists of one and only one of operations B, C or D.
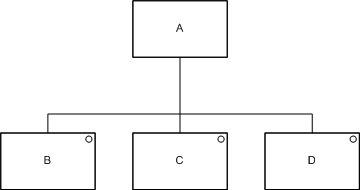
A selection
A worked example
As an example, here is how a programmer would design and code a run length encoder
Run-length encoding
Run-length encoding is a very simple form of data compression in which runs of data are stored as a single data value and count, rather than as the original run...
using JSP.
A run length encoder is a program which takes as its input a stream of bytes. It outputs a stream of pairs consisting of a byte along with a count of the byte's consecutive occurrences. Run length encoders are often used for crudely compressing bitmaps.
With JSP, the first step is to describe the structure of a program's inputs. A run length encoder has only one input, a stream of bytes which can be viewed as zero or more runs. Each run consists of one or more bytes of the same value. This is represented by the following JSP diagram.
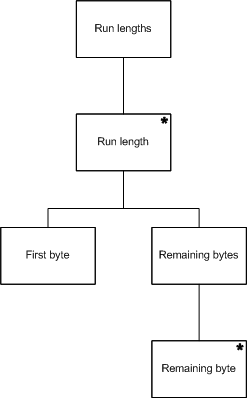
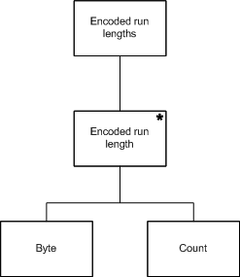
The run length encoder input
The second step is to describe the structure of the output. The run length encoder output can be described as zero or more pairs, each pair consisting of a byte and its count. In this example, the count will also be a byte.

The run length encoder output
The next step is to describe the correspondences between the operations in the input and output structures.
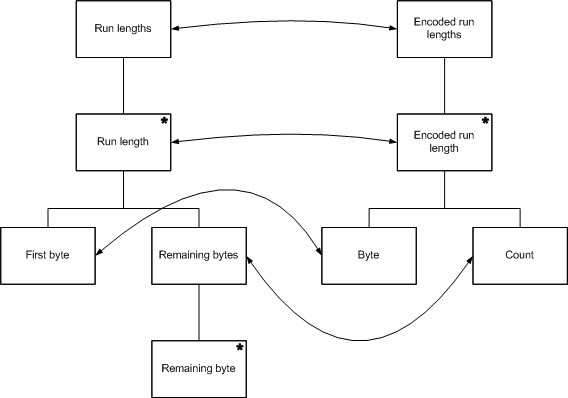
The correspondences between the run length encoders inputs and its outputs
It is at this stage that the astute programmer may encounter a structure clash, in which there is no obvious correspondence between the input and output structures. If a structure clash is found, it is usually resolved by splitting the program into two parts, using an intermediate data structure to provide a common structural framework with which the two program parts can communicate. The two programs parts are often implemented as processes
Process (computing)
In computing, a process is an instance of a computer program that is being executed. It contains the program code and its current activity. Depending on the operating system , a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently.A computer program is a...
or coroutine
Coroutine
Coroutines are computer program components that generalize subroutines to allow multiple entry points for suspending and resuming execution at certain locations...
s.
In this example, there is no structure clash, so the two structures can be merged to give the final program structure.
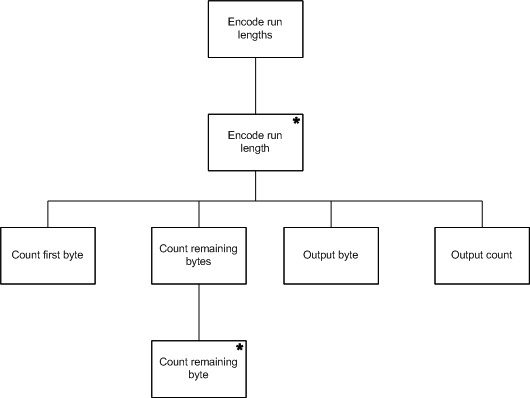
The run length encoder program structure
At this stage the program can be fleshed out by hanging various primitive operations off the elements of the structure. Primitives which suggest themselves are
- read a byte
- remember byte
- set counter to zero
- increment counter
- output remembered byte
- output counter
The iterations also have to be fleshed out. They need conditions added. Suitable conditions would be
- while there are more bytes
- while there are more bytes and this byte is the same as the run's first byte and the count will still fit in a byte
If we put all this together, we can convert the diagram and the primitive operations into C, maintaining a one-to-one correspondence between the code and the operations and structure of the program design diagram.
- include
- include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char c;
c = getchar;
while (c != EOF) {
char count = 1;
char first_byte = c;
c = getchar;
while (c != EOF && c first_byte && count < 255) {
count++;
c = getchar;
}
putchar(first_byte);
putchar(count);
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Criticism
This method will work only when translation from input to output is equivalent to a context-free grammarContext-free grammar
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar is a formal grammar in which every production rule is of the formwhere V is a single nonterminal symbol, and w is a string of terminals and/or nonterminals ....
.
See also
- Jackson System DevelopmentJackson System DevelopmentJackson System Development is a linear software development methodology developed by Michael A. Jackson and John Cameron in the 1980s.- History :...
- Warnier Structured Programming

