Interactomics
Encyclopedia
Interactomics is a discipline at the intersection of bioinformatics
and biology
that deals with studying both the interactions and the consequences of those interactions between and among protein
s, and other molecules within a cell
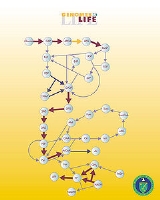
. The network of all such interactions is called the Interactome
. Interactomics thus aims to compare such networks of interactions (i.e., interactomes) between and within species in order to find how the traits of such networks are either preserved or varied. From a mathematical, or mathematical biology
viewpoint an interactome network is a graph
or a category
representing the most important interactions pertinent to the normal physiological functions of a cell or organism.
Interactomics is an example of "top-down" systems biology, which takes an overhead, as well as overall, view of a biosystem or organism. Large sets of genome-wide and proteomic data are collected, and correlations between different molecules are inferred. From the data new hypotheses are formulated about feedbacks between these molecules. These hypotheses can then be tested by new experiments.
Through the study of the interaction of all of the molecules in a cell the field looks to gain a deeper understanding of genome function and evolution than just examining an individual genome in isolation.
Interactomics goes beyond cellular proteomics
in that it not only attempts to characterize the interaction between proteins, but between all molecules in the cell.
have been screened and their interactions characterized, making it the first interactome to be nearly fully specified.
Also there have been recent systematic attempts to explore the human interactome and.
 Other species whose interactomes have been studied in some detail include Caenorhabditis elegans
Other species whose interactomes have been studied in some detail include Caenorhabditis elegans
and Drosophila melanogaster
.
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
and biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
that deals with studying both the interactions and the consequences of those interactions between and among protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s, and other molecules within a cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
. The network of all such interactions is called the Interactome
Interactome
Interactome is defined as the whole set of molecular interactions in cells. It is usually displayed as a directed graph. Molecular interactions can occur between molecules belonging to different biochemical families and also within a given family...
. Interactomics thus aims to compare such networks of interactions (i.e., interactomes) between and within species in order to find how the traits of such networks are either preserved or varied. From a mathematical, or mathematical biology
Mathematical biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology is an interdisciplinary scientific research field with a range of applications in biology, medicine and biotechnology...
viewpoint an interactome network is a graph
Graph (mathematics)
In mathematics, a graph is an abstract representation of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by mathematical abstractions called vertices, and the links that connect some pairs of vertices are called edges...
or a category
Category (mathematics)
In mathematics, a category is an algebraic structure that comprises "objects" that are linked by "arrows". A category has two basic properties: the ability to compose the arrows associatively and the existence of an identity arrow for each object. A simple example is the category of sets, whose...
representing the most important interactions pertinent to the normal physiological functions of a cell or organism.
Interactomics is an example of "top-down" systems biology, which takes an overhead, as well as overall, view of a biosystem or organism. Large sets of genome-wide and proteomic data are collected, and correlations between different molecules are inferred. From the data new hypotheses are formulated about feedbacks between these molecules. These hypotheses can then be tested by new experiments.
Through the study of the interaction of all of the molecules in a cell the field looks to gain a deeper understanding of genome function and evolution than just examining an individual genome in isolation.
Interactomics goes beyond cellular proteomics
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
in that it not only attempts to characterize the interaction between proteins, but between all molecules in the cell.
Methods of interactomics
The study of the interactome requires the collection of large amounts of data by way of high throughput experiments. Through these experiments a large number of data points are collected from a single organism under a small number of perturbations These experiments include:- Two-hybrid screeningTwo-hybrid screeningTwo-hybrid screening is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of...
- Tandem Affinity PurificationTandem Affinity PurificationTandem affinity purification is a technique for studying protein-protein interactions. It involves creating a fusion protein with a designed piece, the TAP tag, on the end...
- X-ray tomography
- Optical fluorescence microscopy
Recent developments
The field of interactomics is currently rapidly expanding and developing. While no biological interactomes have been fully characterized. Over 90% of proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiaeSaccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
have been screened and their interactions characterized, making it the first interactome to be nearly fully specified.
Also there have been recent systematic attempts to explore the human interactome and.

Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living, transparent nematode , about 1 mm in length, which lives in temperate soil environments. Research into the molecular and developmental biology of C. elegans was begun in 1974 by Sydney Brenner and it has since been used extensively as a model...
and Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of Diptera, or the order of flies, in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly or vinegar fly. Starting from Charles W...
.
Criticisms and concerns
Kiemer and Cesareni raise the following concerns with the current state of the field:- The experimental procedures associated with the field are error prone leading to "noisy results". This leads to 30% of all reported interactions being artifacts. In fact, two groups using the same techniques on the same organism found less than 30% interactions in common.
- Techniques may be biased, i.e. the technique determines which interactions are found.
- Ineractomes are not nearly complete with perhaps the exception of S. cerivisiae.
- While genomes are stable, interactomes may vary between tissues and developmental stages.
- Genomics compares amino acids, and nucleotides which are in a sense unchangeable, but interactomics compares proteins and other molecules which are subject to mutation and evolution.
- It is difficult to match evolutionarily related proteins in distantly related species.
See also
- Interaction networkInteraction networkInteraction network is a network of nodes that are connected by features. If the feature is a physical and molecular, the interaction network is molecular interactions usually found in cells...
- ProteomicsProteomicsProteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
- Metabolic networkMetabolic networkA metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell...
- Metabolic network modellingMetabolic network modellingMetabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in depth insight into comprehending the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism, especially correlating the genome with molecular physiology...
- Metabolic pathwayMetabolic pathwayIn biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
- GenomicsGenomicsGenomics is a discipline in genetics concerning the study of the genomes of organisms. The field includes intensive efforts to determine the entire DNA sequence of organisms and fine-scale genetic mapping efforts. The field also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena such as heterosis,...
- Mathematical biologyMathematical biologyMathematical and theoretical biology is an interdisciplinary scientific research field with a range of applications in biology, medicine and biotechnology...
- Systems biologySystems biologySystems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
External links
- Interactomics.org. A dedicated interactomics web site operated under BioLicense.
- Interactome.org. An interactome wiki site.
- PSIbase Structural Interactome Map of all Proteins.
- Omics.org. An omics portal site that is openfree (under BioLicense)
- Genomics.org. A Genomics wiki site.
- Comparative Interactomics analysis of protein family interaction networks using PSIMAP (protein structural interactome map)
- Interaction interfaces in proteins via the Voronoi diagram of atoms
- Using convex hulls to extract interaction interfaces from known structures. Panos Dafas, Dan Bolser, Jacek Gomoluch, Jong Park, and Michael Schroeder. Bioinformatics 2004 20: 1486-1490.
- PSIbase: a database of Protein Structural Interactome map (PSIMAP). Sungsam Gong, Giseok Yoon, Insoo Jang Bioinformatics 2005.
- Mapping Protein Family Interactions : Intramolecular and Intermolecular Protein Family Interaction Repertoires in the PDB and Yeast, Jong Park, Michael Lappe & Sarah A. Teichmann,J.M.B (2001).
- Semantic Systems Biology

