
Incremental capital-output ratio
Encyclopedia
The Incremental Capital-Output Ratio (ICOR), is the ratio of investment
to growth which is equal to 1 divided by the marginal product of capital
. The higher the ICOR, the lower the productivity
of capital
. The ICOR can be thought of as a measure of the inefficiency
with which capital is used. In most countries the ICOR is in the neighborhood of 3. It is a topic discussed in Economic growth
.
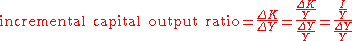
K: capital stock
Y: output
(GDP
)
I: net investment
According to this formula the incremental capital output ration can be computed by dividing the investment share in GDP by the rate of growth of GDP.
: Fundamental Determinants of the Asian Crisis: The Role of Financial Fragility and
External Imbalances, in Takatoshi Ito and Anne Krueger, eds. Regional and Global Capital Flows: Macroeconomic Causes and Consequences, (Chicago: University of Chicago Press for the NBER, 2001), 42-45
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
to growth which is equal to 1 divided by the marginal product of capital
Marginal product of capital
Marginal product of capital is the additional output resulting from the use of an additional unit of capital . It equals 1 divided by the Incremental capital-output ratio...
. The higher the ICOR, the lower the productivity
Productivity
Productivity is a measure of the efficiency of production. Productivity is a ratio of what is produced to what is required to produce it. Usually this ratio is in the form of an average, expressing the total output divided by the total input...
of capital
Capital (economics)
In economics, capital, capital goods, or real capital refers to already-produced durable goods used in production of goods or services. The capital goods are not significantly consumed, though they may depreciate in the production process...
. The ICOR can be thought of as a measure of the inefficiency
Inefficiency
The term inefficiency has several meanings depending on the context in which its used:*Algorithmic inefficiency - refers to less than optimum computer programs that might exhibit one of more of the symptoms of:** slow execution...
with which capital is used. In most countries the ICOR is in the neighborhood of 3. It is a topic discussed in Economic growth
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
.

K: capital stock
Y: output
Output (economics)
Output in economics is the "quantity of goods or services produced in a given time period, by a firm, industry, or country," whether consumed or used for further production.The concept of national output is absolutely essential in the field of macroeconomics...
(GDP
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
)
I: net investment
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
According to this formula the incremental capital output ration can be computed by dividing the investment share in GDP by the rate of growth of GDP.
Literature
Giancarlo Corsetti, Paolo Pesenti, and Nouriel RoubiniNouriel Roubini
Nouriel Roubini is an American economist. He claims to have predicted both the collapse of the United States housing market and the worldwide recession which started in 2008. He teaches at New York University's Stern School of Business and is the chairman of Roubini Global Economics, an economic...
: Fundamental Determinants of the Asian Crisis: The Role of Financial Fragility and
External Imbalances, in Takatoshi Ito and Anne Krueger, eds. Regional and Global Capital Flows: Macroeconomic Causes and Consequences, (Chicago: University of Chicago Press for the NBER, 2001), 42-45

