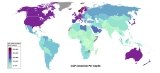
Gross domestic product
Overview
Per capita
Per capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person...
is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living
Standard of living
Standard of living is generally measured by standards such as real income per person and poverty rate. Other measures such as access and quality of health care, income growth inequality and educational standards are also used. Examples are access to certain goods , or measures of health such as...
.
Gross domestic product is related to national accounts
National accounts
National accounts or national account systems are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting...
, a subject in macroeconomics
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of the whole economy. This includes a national, regional, or global economy...
.
GDP was first developed by Simon Kuznets
Simon Kuznets
Simon Smith Kuznets was a Russian American economist at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania who won the 1971 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and...
for a US Congress report in 1934, who immediately said not to use it as a measure for welfare (see below under limitations).
GDP can be determined in three ways, all of which should, in principle, give the same result.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

