
Holevo's theorem
Encyclopedia
In physics
, in the area of quantum information theory, Holevo's theorem (sometimes called Holevo's bound, since it establishes an upper bound
) is an important limitative theorem in quantum computing which was published by Alexander Holevo in 1973.
According to the theorem, the amount of information accessible given a quantum state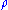 is limited by its Holevo information
is limited by its Holevo information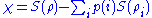 ,
,
where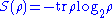 is the von Neumann entropy
is the von Neumann entropy
and the quantum state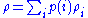 is defined in terms of the encoded state
is defined in terms of the encoded state 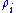 with a prior distribution
with a prior distribution 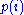 . When the state
. When the state 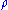 is interrogated using measurements described by a set of POVM
is interrogated using measurements described by a set of POVM
elements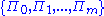 , then the mutual information
, then the mutual information
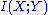 between the encoded states (indexed by
between the encoded states (indexed by 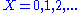 ) and the measurement outcomes (index by
) and the measurement outcomes (index by 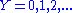 ) is bounded from above by the Holevo quantity
) is bounded from above by the Holevo quantity  as:
as:
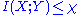
In essence, the Holevo bound proves that n qubit
s can represent only up to n classical (non-quantum encoded) bit
s. This is surprising, for two reasons: quantum computing is so often more powerful than classical computing, that results which show it to be only as good or inferior to conventional techniques are unusual, and because it takes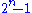 complex number
complex number
s to encode the qubits which represent a mere n bits.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, in the area of quantum information theory, Holevo's theorem (sometimes called Holevo's bound, since it establishes an upper bound
Upper bound
In mathematics, especially in order theory, an upper bound of a subset S of some partially ordered set is an element of P which is greater than or equal to every element of S. The term lower bound is defined dually as an element of P which is lesser than or equal to every element of S...
) is an important limitative theorem in quantum computing which was published by Alexander Holevo in 1973.
According to the theorem, the amount of information accessible given a quantum state
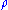 is limited by its Holevo information
is limited by its Holevo information ,
,where
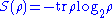 is the von Neumann entropy
is the von Neumann entropyVon Neumann entropy
In quantum statistical mechanics, von Neumann entropy, named after John von Neumann, is the extension of classical entropy concepts to the field of quantum mechanics....
and the quantum state
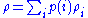 is defined in terms of the encoded state
is defined in terms of the encoded state 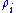 with a prior distribution
with a prior distribution 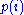 . When the state
. When the state 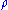 is interrogated using measurements described by a set of POVM
is interrogated using measurements described by a set of POVMPOVM
In functional analysis and quantum measurement theory, a POVM is a measure whose values are non-negative self-adjoint operators on a Hilbert space. It is the most general formulation of a measurement in the theory of quantum physics...
elements
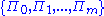 , then the mutual information
, then the mutual informationMutual information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information of two random variables is a quantity that measures the mutual dependence of the two random variables...
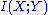 between the encoded states (indexed by
between the encoded states (indexed by 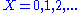 ) and the measurement outcomes (index by
) and the measurement outcomes (index by 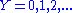 ) is bounded from above by the Holevo quantity
) is bounded from above by the Holevo quantity  as:
as: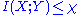
In essence, the Holevo bound proves that n qubit
Qubit
In quantum computing, a qubit or quantum bit is a unit of quantum information—the quantum analogue of the classical bit—with additional dimensions associated to the quantum properties of a physical atom....
s can represent only up to n classical (non-quantum encoded) bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s. This is surprising, for two reasons: quantum computing is so often more powerful than classical computing, that results which show it to be only as good or inferior to conventional techniques are unusual, and because it takes
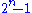 complex number
complex numberComplex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
s to encode the qubits which represent a mere n bits.

