
Hitachi 6309
Encyclopedia

Hitachi, Ltd.
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate headquartered in Marunouchi 1-chome, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. The company is the parent of the Hitachi Group as part of the larger DKB Group companies...
CMOS version of the Motorola 6809
Motorola 6809
The Motorola 6809 is an 8-bit microprocessor CPU from Motorola, designed by Terry Ritter and Joel Boney and introduced 1978...
microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
. While in "Emulation Mode" it is fully compatible with the 6809. To the 6809 specifications it adds higher clock rates, enhanced features, new instructions, and additional registers
Processor register
In computer architecture, a processor register is a small amount of storage available as part of a CPU or other digital processor. Such registers are addressed by mechanisms other than main memory and can be accessed more quickly...
. Most new instructions were added to support the additional registers, as well as up to 32-bit math, hardware division, bit manipulations, and block transfers. The 6309 is generally 30% faster in native mode
Native mode
The term native mode or native code is used in computing in two related senses.*to describe something running on a computer natively or in native mode meaning that it is running without any external support as contrasted to running in emulation....
than the 6809.
Surprisingly, this information was never published by Hitachi. The April 1988 issue of Oh! FM, a Japanese magazine for Fujitsu personal computer users, contained the first description of the 6309's additional capabilities. Later, Hirotsugu Kakugawa posted details of the 6309's new features and instructions to comp.sys.m6809. This led to the development of NitrOS9 for the Tandy Color Computer 3.
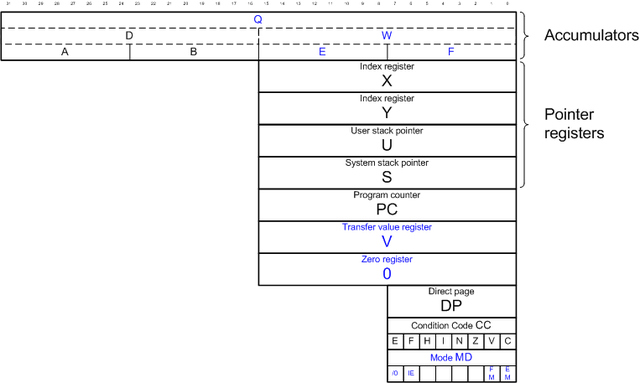
Programming Model
Process Technology
The 6309 is fabricated in CMOSCMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
technology, while the 6809 is an NMOS
NMOS logic
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors to implement logic gates and other digital circuits...
device. As a result, the 6309 requires less power to operate than the 6809. It is also a fully static device, which will not lose internal state information. This means it can be used with external DMA without needing refresh every 14 cycles as the 6809 does.
Clock Speed
The 6309 has B (2 MHz) versions as the 6809 does. However, a "C" speed rating was produced with either a 3.0 or 3.5 MHz maximum clock rate, depending on which datasheet is referenced. (Several Japanese computers had 63C09 CPUs clocked at 3.58 MHz, the NTSCNTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
colorburst
Colorburst
Colorburst is a analog video, composite video signal generated by a video-signal generator used to keep the chrominance subcarrier synchronized in a color television signal...
frequency, so the 3.5 rating seems most likely). Anecdotal and individual reports indicate that the 63C09 variant can be clocked at 5 MHz with no ill effects. Like the 6809, the Hitachi CPU comes in both internal and external clock versions (HD63B/C09 and HD63B/C09E respectively)
Computational Efficiency
When switched into 6309 Native Mode (as opposed to the default 6809-compatible mode) many key instructions will complete in fewer clock cycles. This often improves execution speeds by up to 30%.Additional Registers
- There are two additional 8-bit accumulatorsAccumulator (computing)In a computer's central processing unit , an accumulator is a register in which intermediate arithmetic and logic results are stored. Without a register like an accumulator, it would be necessary to write the result of each calculation to main memory, perhaps only to be read right back again for...
, E and F. These can be concatenated to form a 16-bit accumulator called W. The existing 6809 16-bit accumulator, D, can also be concatenated with W to form a 32-bit accumulator Q. (Presumably standing for "Quad"). - A "Transfer register", V, which is only accessible via inter-register instructions. Its value is not cleared during a hardware reset, so it can maintain a constant 'Value', hence "V".
- An 8/16-bit Zero register, called 0, is provided for speeding up operations where a zero constant is used. This register always returns a zero value, and writing to it has no effect.
- A new mode register, MD, which controls the 6309's operating mode and operates as a secondary condition code. Only 4 bits of this register are defined.
Additional Instructions
Most of the new instructions are modifications of existing instructions to handle the existence of the additional registers, such as load, store, add, and the like. Genuine 6309 additions include inter-register arithmetic, block transfers, hardware division, and bit-level manipulations.Despite the user-friendliness of the additional instructions, analysis by 6809 programming gurus indicates that many of the new instructions are actually slower than the equivalent 6809 code, especially in tight loops. Careful analysis should be done to ensure that the programmer uses the most efficient code for the particular application.
Additional Hardware Features
It is possible to change the mode of operation for the FIRQ interrupt. Instead of stacking the PC and CC registers (normal 6809 behavior) the FIRQ interrupt can be set to stack the entire register set, as the IRQ interrupt does. In addition, the 6309 has two possible trap modes, one for an illegal instruction fetch and one for division by zero. The illegal instruction fetch is not maskable, and many TRS-80 Color ComputerTRS-80 Color Computer
The Radio Shack TRS-80 Color Computer was a home computer launched in 1980. It was one of the earliest of the first generation of computers marketed for home use in English-speaking markets...
users reported that their 6309's were "buggy" when in reality it was an indicator of enhanced and unknown features.

