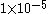Hazard analysis
Encyclopedia
A hazard analysis is used as the first step in a process used to assess risk
. The result of a hazard analysis is the identification of risks. Preliminary risk levels can be provided in the hazard analysis. The validation, more precise prediction and acceptance of risk is determined in the Risk assessment
(analysis). The main goal of both is to provide the best selection of means of controlling or eliminating the risk. The term is used in several engineering specialties, including avionics
, chemical process safety
, safety engineering
, reliability engineering
and food safety
. Alternative definitions include:
Identification, studies and monitoring of any hazard to determine its potential, origin, characteristics and behaviour.
http://www.unisdr.org/eng/library/lib-terminology-eng%20home.htm
The process of collecting and evaluating information on hazards associated with the food under consideration to decide which are significant and must be addressed in the HACCP plan.
http://demo.unl.edu/haccp/start/glossary.html
An analysis or identification of the hazards which could occur at each step in the process, and a description and implementation of the measures to be taken for their control.
http://www.specialistcheesemakers.co.uk/best_practice/Glossary_of_terms.htm
While in some cases safety risk can be eliminated, in most cases a certain degree of safety risk must be accepted. In order to quantify expected accident costs before the fact, the potential consequences of an accident, and the probability of occurrence must be considered. Assessment of risk is made by combining the severity of consequence with the likelihood of occurrence in a matrix. Risks that fall into the "unacceptable" category (e.g., high severity and high probability) must be mitigated by some means to reduce the level of safety risk.
IEEE STD-1228-1994 Software Safety Plans prescribes industry best practices for conducting software safety hazard analyses to help ensure safety requirements and attributes are defined and specified for inclusion in software that commands, controls or monitors critical functions. When software is involved in a system, the development and design assurance of that software is often governed by DO-178B
. The severity of consequence identified by the hazard analysis establishes the criticality level of the software. Software criticality levels range from A to E, corresponding to severities of Catastrophic to No Safety Effect. Higher levels of rigor are required for level A and B software and corresponding functional tasks and work products is the system safety domain are used as objective evidence of meeting safety criteria and requirements.
Recently a leading edge commercial standard was promulgated based on decades of proven system safety processes in DoD and NASA. ANSI/GEIA-STD-0010-2009 (Standard Best Practices for System Safety Program Development and Execution) is a demilitarized commercial best practice that uses proven hostistic, comprehensive and tailorable approaches for hazard prevention, elimination and control. It is centered around the hazard analysis and functional based safety process.
Risk
Risk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
. The result of a hazard analysis is the identification of risks. Preliminary risk levels can be provided in the hazard analysis. The validation, more precise prediction and acceptance of risk is determined in the Risk assessment
Risk assessment
Risk assessment is a step in a risk management procedure. Risk assessment is the determination of quantitative or qualitative value of risk related to a concrete situation and a recognized threat...
(analysis). The main goal of both is to provide the best selection of means of controlling or eliminating the risk. The term is used in several engineering specialties, including avionics
Avionics
Avionics are electronic systems used on aircraft, artificial satellites and spacecraft.Avionic systems include communications, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to meet individual roles...
, chemical process safety
Process engineering
Process engineering focuses on the design, operation, control, and optimization of chemical, physical, and biological processes through the aid of systematic computer-based methods...
, safety engineering
Safety engineering
Safety engineering is an applied science strongly related to systems engineering / industrial engineering and the subset System Safety Engineering...
, reliability engineering
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is an engineering field, that deals with the study, evaluation, and life-cycle management of reliability: the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It is often measured as a probability of...
and food safety
Food safety
Food safety is a scientific discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent foodborne illness. This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potentially severe health hazards....
. Alternative definitions include:
Identification, studies and monitoring of any hazard to determine its potential, origin, characteristics and behaviour.
http://www.unisdr.org/eng/library/lib-terminology-eng%20home.htm
The process of collecting and evaluating information on hazards associated with the food under consideration to decide which are significant and must be addressed in the HACCP plan.
http://demo.unl.edu/haccp/start/glossary.html
An analysis or identification of the hazards which could occur at each step in the process, and a description and implementation of the measures to be taken for their control.
http://www.specialistcheesemakers.co.uk/best_practice/Glossary_of_terms.htm
Hazards and risk
A hazard is defined in FAA Order 8040.4 as a "Condition, event, or circumstance that could lead to or contribute to an unplanned or undesirable event." Seldom does a single hazard cause an accident. More often, an accident occurs as the result of a sequence of causes. A hazard analysis will consider system state, for example operating environment, as well as failures or malfunctions.While in some cases safety risk can be eliminated, in most cases a certain degree of safety risk must be accepted. In order to quantify expected accident costs before the fact, the potential consequences of an accident, and the probability of occurrence must be considered. Assessment of risk is made by combining the severity of consequence with the likelihood of occurrence in a matrix. Risks that fall into the "unacceptable" category (e.g., high severity and high probability) must be mitigated by some means to reduce the level of safety risk.
IEEE STD-1228-1994 Software Safety Plans prescribes industry best practices for conducting software safety hazard analyses to help ensure safety requirements and attributes are defined and specified for inclusion in software that commands, controls or monitors critical functions. When software is involved in a system, the development and design assurance of that software is often governed by DO-178B
DO-178B
DO-178B, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is a document dealing with the safety of software used in airborne systems....
. The severity of consequence identified by the hazard analysis establishes the criticality level of the software. Software criticality levels range from A to E, corresponding to severities of Catastrophic to No Safety Effect. Higher levels of rigor are required for level A and B software and corresponding functional tasks and work products is the system safety domain are used as objective evidence of meeting safety criteria and requirements.
Recently a leading edge commercial standard was promulgated based on decades of proven system safety processes in DoD and NASA. ANSI/GEIA-STD-0010-2009 (Standard Best Practices for System Safety Program Development and Execution) is a demilitarized commercial best practice that uses proven hostistic, comprehensive and tailorable approaches for hazard prevention, elimination and control. It is centered around the hazard analysis and functional based safety process.
Severity definitions - Safety Related
| Severity | Definition |
|---|---|
| Catastrophic | Results in multiple fatalities and/or loss of the system |
| Hazardous | Reduces the capability of the system or the operator ability to cope with adverse conditions to the extent that there would be:
|
| Major | Reduces the capability of the system or the operators to cope with adverse operating conditions to the extent that there would be:
including injuries
|
| Minor | Does not significantly reduce system safety. Actions required by operators are well within their capabilities. Include:
|
| No Safety Effect | Has no effect on safety |
Likelihood of occurrence
| Likelihood | Definition |
|---|---|
| Probable |
|
| Remote |
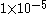 , but greater than , but greater than 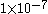 |
| Extremely Remote |
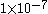 but greater than but greater than 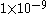 |
| Extremely Improbable |
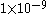 |
See also
- HAZOP
- HAZID
- Safety engineeringSafety engineeringSafety engineering is an applied science strongly related to systems engineering / industrial engineering and the subset System Safety Engineering...
- Reliability engineeringReliability engineeringReliability engineering is an engineering field, that deals with the study, evaluation, and life-cycle management of reliability: the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It is often measured as a probability of...
- Occupational safety and healthOccupational safety and healthOccupational safety and health is a cross-disciplinary area concerned with protecting the safety, health and welfare of people engaged in work or employment. The goal of all occupational safety and health programs is to foster a safe work environment...
- RTCA DO-178BDO-178BDO-178B, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is a document dealing with the safety of software used in airborne systems....
(Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification) - RTCA DO-254DO-254RTCA/DO-254, DESIGN ASSURANCE GUIDANCE FOR AIRBORNE ELECTRONIC HARDWARE is a document providing guidance for the development of airborne electronic hardware, published by RTCA, Incorporated.-Outline of contents:1...
(similar to DO-178B, but for hardware) - SAE ARP4761ARP4761ARP4761, Guidelines and Methods for Conducting the Safety Assessment Process on Civil Airborne Systems and Equipment is a standard from the Society of Automotive Engineers . In conjunction with SAE ARP4754, ARP4761 is used to demonstrate compliance with 14 CFR 25.1309 in the U.S...
(System safety assessment process) - SAE ARP4754ARP4754ARP4754 is a standard from SAE, dealing with the development processes and certification of Aircraft systems. EUROCAE jointly issues the document as ED–79...
(System development process) - MIL-STD-882 (Standard practice for system safety)
- ANSI/GEIA-STD-0010-2009 (Standard Best Practices for System Safety Program Development and Execution)
- IEEE STD 1228-1994 Software Safety Plans
- IEEE STD 1584-2002 IEEE Guide for Performing Arc Flash Hazard Calculations
External links
- CFR, Title 29-Labor, Part 1910--Occupational Safety and Health Standards, § 1910.119
U.S. OSHA regulations regarding "Process safety management of highly hazardous chemicals" (especially Appendix C). - FAA Order 8040.4 establishes FAA safety risk management policy.
- The FAA publishes a System Safety Handbook that provides a good overview of the system safety process used by the agency.
- IEEE 1584-2002 Standard which provides guidelines for doing arc flash hazard assessment.