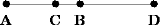
Harmonic division
Encyclopedia
In geometry
, harmonic division of a line segment
AB means identifying two point
s C and D such that AB is divided internally and externally in the same ratio
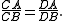
In the example shown below, the ratio is two. Specifically, the distance AC is one inch, the distance CB is half an inch, the distance AD is three inches, and the distance BD is 1.5 inches.
 Harmonic division of a line segment is reciprocal; if points C and D divide the line segment AB harmonically, the points A and B also divide the line segment CD harmonically. In that case, the ratio is given by
Harmonic division of a line segment is reciprocal; if points C and D divide the line segment AB harmonically, the points A and B also divide the line segment CD harmonically. In that case, the ratio is given by
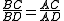
which equals one-third in the example above. (Note that the two ratios are not equal!)
Harmonic division of a line segment is a special case of Apollonius'
definition of the circle
. It is also related to the cross-ratio
.
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, harmonic division of a line segment
Line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a line that is bounded by two end points, and contains every point on the line between its end points. Examples of line segments include the sides of a triangle or square. More generally, when the end points are both vertices of a polygon, the line segment...
AB means identifying two point
Point (geometry)
In geometry, topology and related branches of mathematics a spatial point is a primitive notion upon which other concepts may be defined. In geometry, points are zero-dimensional; i.e., they do not have volume, area, length, or any other higher-dimensional analogue. In branches of mathematics...
s C and D such that AB is divided internally and externally in the same ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
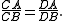
In the example shown below, the ratio is two. Specifically, the distance AC is one inch, the distance CB is half an inch, the distance AD is three inches, and the distance BD is 1.5 inches.

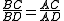
which equals one-third in the example above. (Note that the two ratios are not equal!)
Harmonic division of a line segment is a special case of Apollonius'
Apollonius of Perga
Apollonius of Perga [Pergaeus] was a Greek geometer and astronomer noted for his writings on conic sections. His innovative methodology and terminology, especially in the field of conics, influenced many later scholars including Ptolemy, Francesco Maurolico, Isaac Newton, and René Descartes...
definition of the circle
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
. It is also related to the cross-ratio
Cross-ratio
In geometry, the cross-ratio, also called double ratio and anharmonic ratio, is a special number associated with an ordered quadruple of collinear points, particularly points on a projective line...
.

