Half-logistic distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
and statistics
, the half-logistic distribution is a continuous probability distribution
—the distribution of the absolute value of a random variable
following the logistic distribution. That is, for

where Y is a logistic random variable, X is a half-logistic random variable.
(cdf) of the half-logistic distribution is intimately related to the cdf of the logistic distribution. Formally, if F(k) is the cdf for the logistic distribution, then G(k) = 2F(k) − 1 is the cdf of a half-logistic distribution. Specifically,

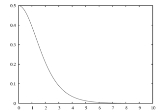
(pdf) of the half-logistic distribution is g(k) = 2f(k) if f(k) is the pdf of the logistic distribution. Explicitly,

Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the half-logistic distribution is a continuous probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
—the distribution of the absolute value of a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
following the logistic distribution. That is, for

where Y is a logistic random variable, X is a half-logistic random variable.
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution functionCumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
(cdf) of the half-logistic distribution is intimately related to the cdf of the logistic distribution. Formally, if F(k) is the cdf for the logistic distribution, then G(k) = 2F(k) − 1 is the cdf of a half-logistic distribution. Specifically,

Probability density function
Similarly, the probability density functionProbability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
(pdf) of the half-logistic distribution is g(k) = 2f(k) if f(k) is the pdf of the logistic distribution. Explicitly,


