
Gyrokinetic ElectroMagnetic
Encyclopedia
GEM is short for Gyrokinetic ElectroMagnetic. GEM is a gyrokinetic plasma
turbulence simulation that uses the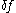 particle-in-cell
particle-in-cell
method. It is used to study waves, instabilities and nonlinear behavior of tokamak fusion plasmas. Information about GEM can be found at the GEM web page.
There are two versions of GEM, one is a flux-tube version and the other one is a global general geometry
version. Both versions of GEM use a field-aligned coordinate system. Ions are treated kinetically, but averaged over their gyro-obits and electrons are treated as drift-kinetic.
depends on the three-dimensional position, the energy and magnetic moment. The time evolution of the distribution function is described by gyrokinetic theory
which simply averages the Vlasov-Maxwell system of equations over the fast gyromotion associated with particles exhibiting cyclotron motion about the magnetic field lines. This eliminates fast time scales associated with the gyromotion and reduces the dimensionality of the problem from six down to five.
(PIC) plasma
simulation method. An expansion about an adiabatic response is made for electrons to overcome the limit of small time step, which is caused by the fast motion of electrons. GEM uses a novel electromagnetic algorithm allowing direct numerical simulation of the electromagnetic problem at high plasma pressures. GEM uses a two-dimensional domain decomposition (see domain decomposition method
) of the grid and particles to obtain good performance on massively parallel computers. A Monte Carlo method
is used to model small angle Coulomb collision
s.
plasma turbulence and transport. Tokamak turbulence driven by ion-temperature-gradient modes, electron-temperature gradient modes, trapped electron modes and micro-tearing modes has been investigated using GEM. It is also being used to look at energetic particle driven magnetohydrodynamic (see magnetohydrodynamics
) eigenmodes.
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
turbulence simulation that uses the
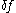 particle-in-cell
particle-in-cellParticle-in-cell
The Particle-in-Cell method refers to a technique used to solve a certain class of partial differential equations. In this method, individual particles in a Lagrangian frame are tracked in continuous phase space, whereas moments of the distribution such as densities and currents are computed...
method. It is used to study waves, instabilities and nonlinear behavior of tokamak fusion plasmas. Information about GEM can be found at the GEM web page.
There are two versions of GEM, one is a flux-tube version and the other one is a global general geometry
version. Both versions of GEM use a field-aligned coordinate system. Ions are treated kinetically, but averaged over their gyro-obits and electrons are treated as drift-kinetic.
The modeling of the tokamak plasmas
GEM solves the electromagnetic gyrokinetic equations which are the appropriate equations for well magnetized plasmas. The plasma is treated statistically as a kinetic distribution function. The distribution functionDistribution function
In molecular kinetic theory in physics, a particle's distribution function is a function of seven variables, f, which gives the number of particles per unit volume in phase space. It is the number of particles per unit volume having approximately the velocity near the place and time...
depends on the three-dimensional position, the energy and magnetic moment. The time evolution of the distribution function is described by gyrokinetic theory
Gyrokinetics
Gyrokinetics is a branch of plasma physics derived from kinetics and electromagnetism used to describe the low-frequency phenomena in a plasma. The trajectory of charged particles in a magnetic field is a helix that winds around the field line...
which simply averages the Vlasov-Maxwell system of equations over the fast gyromotion associated with particles exhibiting cyclotron motion about the magnetic field lines. This eliminates fast time scales associated with the gyromotion and reduces the dimensionality of the problem from six down to five.
Algorithm to solve the equations
GEM uses the delta-f particle-in-cellParticle-in-cell
The Particle-in-Cell method refers to a technique used to solve a certain class of partial differential equations. In this method, individual particles in a Lagrangian frame are tracked in continuous phase space, whereas moments of the distribution such as densities and currents are computed...
(PIC) plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
simulation method. An expansion about an adiabatic response is made for electrons to overcome the limit of small time step, which is caused by the fast motion of electrons. GEM uses a novel electromagnetic algorithm allowing direct numerical simulation of the electromagnetic problem at high plasma pressures. GEM uses a two-dimensional domain decomposition (see domain decomposition method
Domain decomposition method
In mathematics, the additive Schwarz method, named after Hermann Schwarz, solves a boundary value problem for a partial differential equation approximately by splitting it into boundary value problems on smaller domains and adding the results.- Overview :...
) of the grid and particles to obtain good performance on massively parallel computers. A Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo methods are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to compute their results. Monte Carlo methods are often used in computer simulations of physical and mathematical systems...
is used to model small angle Coulomb collision
Coulomb collision
A Coulomb collision is a binary elastic collision between two charged particles interacting through their own Electric Field. As with any inverse-square law, the resulting trajectories of the colliding particles is a hyperbolic Keplerian orbit...
s.
Applications
GEM is used to study nonlinear physics associated with tokamakTokamak
A tokamak is a device using a magnetic field to confine a plasma in the shape of a torus . Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that move around the torus in a helical shape...
plasma turbulence and transport. Tokamak turbulence driven by ion-temperature-gradient modes, electron-temperature gradient modes, trapped electron modes and micro-tearing modes has been investigated using GEM. It is also being used to look at energetic particle driven magnetohydrodynamic (see magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics is an academic discipline which studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes...
) eigenmodes.

