Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome
Encyclopedia
Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome is a disorder that affects development of the limbs, head, and face. The features of this syndrome are highly variable, ranging from very mild to severe. People with this condition typically have one or more extra fingers or toes (polydactyly
Polydactyly
Polydactyly or polydactylism , also known as hyperdactyly, is a congenital physical anomaly in humans, dogs, and cats having supernumerary fingers or toes....
) or an abnormally wide thumb or big toe (hallux
Hallux
In tetrapods, the hallux is the innermost toe of the foot. Despite its name it may not be the longest toe on the foot of some individuals...
).
The skin between the fingers and toes may be fused (cutaneous syndactyly). This disorder is also characterized by widely spaced eyes (ocular hypertelorism), an abnormally large head size (macrocephaly
Macrocephaly
Macrocephaly , occurs when the head is abnormally large; this includes the scalp, the cranial bone, and the contents of the cranium.-Causes:...
), and a high, prominent forehead. Rarely, affected individuals may have more serious medical problems including seizures, mental retardation, and developmental delay.
Pathophysiology

Different genetic changes involving the Gli3
Gli3
Zinc finger protein GLI3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI3 gene.This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the C2H2-type zinc finger proteins subclass of the Gli family. They are characterized as DNA-binding transcription factors and are mediators of Sonic hedgehog signaling...
gene can cause Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome. In some cases, the condition results from a chromosomal abnormality, such as a large deletion or translocation of genetic material, in the region of chromosome 7 that contains the GLI3 gene. In other cases, a mutation in the GLI3 gene itself is responsible for the disorder. Each of these genetic changes prevents one copy of the gene in each cell from producing any functional protein. It remains unclear how a reduced amount of this protein disrupts early development and causes the characteristic features of Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome.
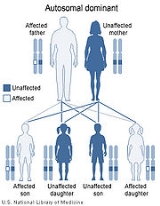
This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and only one copy of the defective GLI3 gene is sufficient to cause the disorder. In cases of dominant inheritance, an affected person inherits the genetic mutation or chromosomal abnormality from one affected parent.
Rare instances of this disorder are sporadic, and occur in people with no history of the condition in their family.

