
Grand potential
Encyclopedia
The grand potential is a quantity used in statistical mechanics
, especially for irreversible
processes in open system
s.
Grand potential is defined by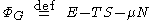
Where E is the energy
, T is the temperature
of the system, S is the entropy
, μ is the chemical potential
, and N is the number of particles in the system.
The change in the grand potential is given by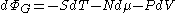
Where P is pressure
and V is volume
.
When the system is in thermodynamic equilibrium
, ΦG is a minimum. This can be seen by considering that dΦG is zero if the volume is fixed and the temperature and chemical potential have stopped evolving.
For an ideal gas,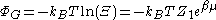
where Ξ is the grand partition function, kB is Boltzmann constant, Z1 is the partition function
for 1 particle and β is equal to 1 / kBT.
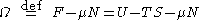
named after Russian physicist Lev Landau
, which may be a synonym for the grand potential, depending on system stipulations.
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
, especially for irreversible
Irreversible
Irreversible may refer to:*Irreversible process, in thermodynamics, a process that is not reversible*Irréversible, a 2002 film*Irréversible , soundtrack to the film Irréversible...
processes in open system
Open system
Open system may refer to:*Open system , one of a class of computers and associated software that provides some combination of interoperability, portability and open software standards, particularly Unix and Unix-like systems...
s.
Grand potential is defined by
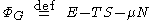
Where E is the energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
, T is the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of the system, S is the entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
, μ is the chemical potential
Chemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
, and N is the number of particles in the system.
The change in the grand potential is given by
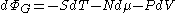
Where P is pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
and V is volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
.
When the system is in thermodynamic equilibrium
Thermodynamic equilibrium
In thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium when it is in thermal equilibrium, mechanical equilibrium, radiative equilibrium, and chemical equilibrium. The word equilibrium means a state of balance...
, ΦG is a minimum. This can be seen by considering that dΦG is zero if the volume is fixed and the temperature and chemical potential have stopped evolving.
For an ideal gas,
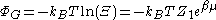
where Ξ is the grand partition function, kB is Boltzmann constant, Z1 is the partition function
Partition function (statistical mechanics)
Partition functions describe the statistical properties of a system in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is a function of temperature and other parameters, such as the volume enclosing a gas...
for 1 particle and β is equal to 1 / kBT.
Landau free energy
Some authors refer to the Landau free energy or Landau potential as: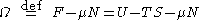
named after Russian physicist Lev Landau
Lev Landau
Lev Davidovich Landau was a prominent Soviet physicist who made fundamental contributions to many areas of theoretical physics...
, which may be a synonym for the grand potential, depending on system stipulations.

