Glutaric acidemia type 2
Encyclopedia
Glutaric acidemia type 2 is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that is characterised by defects in the ability of the body to use protein
s and fat
s for energy. Incompletely processed proteins and fats can build up, leading to a dangerous chemical imbalance called acidosis
.
) cause weakness, behavior changes, and vomiting. There may also be enlargement of the liver
, heart failure, and a characteristic odor resembling that of sweaty feet. Some infants with glutaric acidemia type 2 have birth defects, including multiple fluid-filled growths in the kidneys (polycystic kidneys). Glutaric acidemia type 2 is a very rare disorder. Its precise incidence is unknown. It has been reported in several different ethnic groups.
 Mutations in the ETFA
Mutations in the ETFA
, ETFB
, and ETFDH
gene
s cause glutaric acidemia type II. Glutaric acidemia type 2 is caused by a deficiency in either of two enzymes, called electron transfer flavoprotein and electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase. These enzymes are normally active in the mitochondria, which are the energy-producing centers of cells. When one of these enzymes is defective or missing, partially broken-down nutrients accumulate in the cells and damage them, causing the signs and symptoms of glutaric acidemia type II.
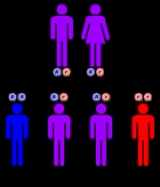
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - are needed to inherit the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers
of one copy of the defective gene, but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder themselves.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s and fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
s for energy. Incompletely processed proteins and fats can build up, leading to a dangerous chemical imbalance called acidosis
Acidosis
Acidosis is an increased acidity in the blood and other body tissue . If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma....
.
Diagnosis
Glutaric acidemia type 2 often appears in infancy as a sudden metabolic crisis, in which acidosis and low blood sugar (hypoglycemiaHypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
) cause weakness, behavior changes, and vomiting. There may also be enlargement of the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, heart failure, and a characteristic odor resembling that of sweaty feet. Some infants with glutaric acidemia type 2 have birth defects, including multiple fluid-filled growths in the kidneys (polycystic kidneys). Glutaric acidemia type 2 is a very rare disorder. Its precise incidence is unknown. It has been reported in several different ethnic groups.
Genetics

ETFA
Electron-transfer-flavoprotein, alpha polypeptide , also known as ETFA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ETFA gene.ETFA participates in catalyzing the initial step of the mitochondrial fatty acid beta oxidation...
, ETFB
ETFB
Electron transfer flavoprotein subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ETFB gene.-Further reading:...
, and ETFDH
ETFDH
Electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ETFDH gene.-Further reading:...
gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s cause glutaric acidemia type II. Glutaric acidemia type 2 is caused by a deficiency in either of two enzymes, called electron transfer flavoprotein and electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase. These enzymes are normally active in the mitochondria, which are the energy-producing centers of cells. When one of these enzymes is defective or missing, partially broken-down nutrients accumulate in the cells and damage them, causing the signs and symptoms of glutaric acidemia type II.
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - are needed to inherit the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
of one copy of the defective gene, but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder themselves.

