
Geophysical Tomography Group
Encyclopedia
The Geophysical Tomography Group was part of the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris
(Jussieu Campus
). During the years 1985-2000 it made developments in the domain of nonlinear fitting of seismic waveforms. The work of the group has been described as pioneering.
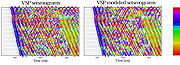 By the year 1985, the imaging methods used by the oil industry were based in signal-processing concepts, and it seemed that modern methods, based on careful waveform modeling and waveform fitting optimization were desirable. The team tried to made real-life demonstrations that the methods of inverse theory could be applied to the imaging problem typical of seismic exploration. The GtG was founded by Albert Tarantola
By the year 1985, the imaging methods used by the oil industry were based in signal-processing concepts, and it seemed that modern methods, based on careful waveform modeling and waveform fitting optimization were desirable. The team tried to made real-life demonstrations that the methods of inverse theory could be applied to the imaging problem typical of seismic exploration. The GtG was founded by Albert Tarantola
, who authored an influential paper on the inversion of seismic reflection data. The GTG published work on fully nonlinear waveform fitting is possible on seismic exploration data, using elastic modeling and gradient-based optimization techniques (adjoint methods).
The group's work in Monte Carlo method
for waveform fitting is being integrated in present-day developments.
Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris
The Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris is a French governmental, non-profit research and higher education establishment located in Paris, dedicated to the study of earth and planetary sciences by combining observations, laboratory analysis and construction of conceptual analogical and...
(Jussieu Campus
Jussieu Campus
The Jussieu Campus is a higher education campus located in the 5th arrondissement of Paris, France, which is the main campus of the Pierre and Marie Curie University ....
). During the years 1985-2000 it made developments in the domain of nonlinear fitting of seismic waveforms. The work of the group has been described as pioneering.
History

Albert Tarantola
Albert Tarantola was a Spanish-born physicist , of the University of Paris , and author of the book probabilistic formulation of inverse problems...
, who authored an influential paper on the inversion of seismic reflection data. The GTG published work on fully nonlinear waveform fitting is possible on seismic exploration data, using elastic modeling and gradient-based optimization techniques (adjoint methods).
The group's work in Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo methods are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to compute their results. Monte Carlo methods are often used in computer simulations of physical and mathematical systems...
for waveform fitting is being integrated in present-day developments.

