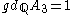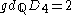Generic polynomial
Encyclopedia
In Galois theory
, a branch of modern algebra, a generic polynomial for a finite group
G and field F is a monic polynomial P with coefficients in the field
L = F(t1, ..., tn) of F with n indeterminate
s adjoined, such that the splitting field
M of P has Galois group
G over L, and such that every extension K/F with Galois group G can be obtained as the splitting field of a polynomial which is the specialization of P resulting from setting the n indeterminates to n elements of F. This is sometimes called F-generic relative to the field F, with a Q-generic polynomial, generic relative to the rational numbers, being called simply generic.
The existence, and especially the construction, of a generic polynomial for a given Galois group provides a complete solution to the inverse Galois problem
for that group. However, not all Galois groups have generic polynomials, a counterexample being the cyclic group
of order eight.
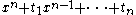
is a generic polynomial for Sn.
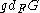 , is defined as the minimal number of parameters in a generic polynomial for G over F, or
, is defined as the minimal number of parameters in a generic polynomial for G over F, or 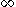 if no generic polynomial exists.
if no generic polynomial exists.
Examples:
Galois theory
In mathematics, more specifically in abstract algebra, Galois theory, named after Évariste Galois, provides a connection between field theory and group theory...
, a branch of modern algebra, a generic polynomial for a finite group
Finite group
In mathematics and abstract algebra, a finite group is a group whose underlying set G has finitely many elements. During the twentieth century, mathematicians investigated certain aspects of the theory of finite groups in great depth, especially the local theory of finite groups, and the theory of...
G and field F is a monic polynomial P with coefficients in the field
Field (mathematics)
In abstract algebra, a field is a commutative ring whose nonzero elements form a group under multiplication. As such it is an algebraic structure with notions of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, satisfying certain axioms...
L = F(t1, ..., tn) of F with n indeterminate
Indeterminate
Indeterminate has a variety of meanings in mathematics:* Indeterminate * Indeterminate system* Indeterminate equation* Statically indeterminate* Indeterminate formIt is also a term in botany and gardening:*Indeterminate growth...
s adjoined, such that the splitting field
Splitting field
In abstract algebra, a splitting field of a polynomial with coefficients in a field is a smallest field extension of that field over which the polynomial factors into linear factors.-Definition:...
M of P has Galois group
Galois group
In mathematics, more specifically in the area of modern algebra known as Galois theory, the Galois group of a certain type of field extension is a specific group associated with the field extension...
G over L, and such that every extension K/F with Galois group G can be obtained as the splitting field of a polynomial which is the specialization of P resulting from setting the n indeterminates to n elements of F. This is sometimes called F-generic relative to the field F, with a Q-generic polynomial, generic relative to the rational numbers, being called simply generic.
The existence, and especially the construction, of a generic polynomial for a given Galois group provides a complete solution to the inverse Galois problem
Inverse Galois problem
In Galois theory, the inverse Galois problem concerns whether or not every finite group appears as the Galois group of some Galois extension of the rational numbers Q. This problem, first posed in the 19th century, is unsolved....
for that group. However, not all Galois groups have generic polynomials, a counterexample being the cyclic group
Cyclic group
In group theory, a cyclic group is a group that can be generated by a single element, in the sense that the group has an element g such that, when written multiplicatively, every element of the group is a power of g .-Definition:A group G is called cyclic if there exists an element g...
of order eight.
Groups with generic polynomials
- The symmetric groupSymmetric groupIn mathematics, the symmetric group Sn on a finite set of n symbols is the group whose elements are all the permutations of the n symbols, and whose group operation is the composition of such permutations, which are treated as bijective functions from the set of symbols to itself...
Sn. This is trivial, as
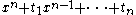
is a generic polynomial for Sn.
- Cyclic groups Cn, where n is not divisible by eight. LenstraHendrik LenstraHendrik Willem Lenstra, Jr. is a Dutch mathematician.-Biography:Lenstra received his doctorate from the University of Amsterdam in 1977 and became a professor there in 1978...
showed that a cyclic group does not have a generic polynomial if n is divisible by eight, and SmithGene Ward SmithGene Ward Smith is an American mathematician and music theorist. In mathematics he has worked in the areas of Galois theory and Moonshine theory. In music theory, he is noted for a number of innovations in the theory of musical tuning, such as the introduction of multilinear algebra and for being...
explicitly constructs such a polynomial in case n is not divisible by eight.
- The cyclic group construction leads to other classes of generic polynomials; in particular the dihedral groupDihedral groupIn mathematics, a dihedral group is the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, including both rotations and reflections. Dihedral groups are among the simplest examples of finite groups, and they play an important role in group theory, geometry, and chemistry.See also: Dihedral symmetry in three...
Dn has a generic polynomial if and only if n is not divisible by eight.
- The quaternion groupQuaternion groupIn group theory, the quaternion group is a non-abelian group of order eight, isomorphic to a certain eight-element subset of the quaternions under multiplication...
Q8.
- Heisenberg groups
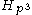 for any odd prime p.
for any odd prime p.
- The alternating group A4.
- The alternating group A5.
- Reflection groups defined over Q, including in particular groups of the root systems for E6, E7, and E8
- Any group which is a direct productDirect product of groupsIn the mathematical field of group theory, the direct product is an operation that takes two groups and and constructs a new group, usually denoted...
of two groups both of which have generic polynomials.
- Any group which is a wreath productWreath productIn mathematics, the wreath product of group theory is a specialized product of two groups, based on a semidirect product. Wreath products are an important tool in the classification of permutation groups and also provide a way of constructing interesting examples of groups.Given two groups A and H...
of two groups both of which have generic polynomials.
Examples of generic polynomials
| Group | Generic Polynomial |
|---|---|
| C2 | 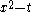 |
| C3 | 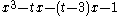 |
| C4 | 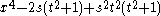 |
| D4 | 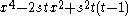 |
Generic Dimension
The generic dimension for a finite group G over a field F, denoted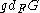 , is defined as the minimal number of parameters in a generic polynomial for G over F, or
, is defined as the minimal number of parameters in a generic polynomial for G over F, or 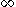 if no generic polynomial exists.
if no generic polynomial exists.Examples:
Publications
- Jensen, Christian U., Ledet, Arne, and Yui, Noriko, Generic Polynomials, Cambridge University Press, 2002