
GTP-binding protein regulators
Encyclopedia
G protein
G proteins are a family of proteins involved in transmitting chemical signals outside the cell, and causing changes inside the cell. They communicate signals from many hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling factors. G protein-coupled receptors are transmembrane receptors...
s in several different ways. Small GTPase
Small GTPase
Small GTPases are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate . They are a form of G-proteins found in the cytosol which are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function...
s act as molecular switches in signaling pathways, which act to regulate functions of other proteins. They are active or 'ON' when it is bound to GTP
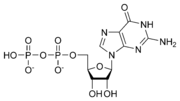
Guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
and inactive or 'OFF' when bound to GDP
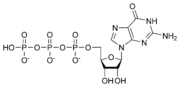
Guanosine diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine....
. Activation and deactivation of small GTPases can be regarded as occurring in a cycle, between the GTP-bound and GDP-bound form, regulated by other regulatory proteins.
Exchangers
The inactive form of GTPases (GDP-form) are activated by a class of proteins called Guanosine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). GEFs catalyse nucleotide exchange by encouraging the release of GDP from the small GTPase (by displacement of the small GTPase-associated Mg2+ ion) and GDP's replacement by GTP (which is in at least a 10-fold excess within the cell) . Inactivation of the active small GTPase is achieved through hydrolysis of the GTP by the small GTPase's intrinsic GTP hydrolytic activity.Stimulators
The rate of GTP hydrolysis for small GTPases is generally too slow to create physiologically relevant transient signals, and thus requires another class of regulatory proteins to accelerate this activity, the GTPase activating proteinGTPase activating protein
GTPase-Activating Proteins, or GAPs, or GTPase-Accelerating Proteins are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event...
s (GAPs).
Inhibitors
Another class of regulatory proteins, the Guanosine nucleotide dissociation inhibitorsGuanosine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors
The Guanosine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors , bind to the GDP-bound form of Rho and Rab small GTPases and not only prevent exchange , but also prevent the small GTPase from localizing at the membrane, which is their place of action. This inhibition can be removed by the action of a Guanine...
(GDIs), bind to the GDP-bound form of Rho and Rab small GTPases and not only prevent exchange (maintaining the small GTPase in an off-state), but also prevent the small GTPase from localizing at the membrane, which is their place of action.

