Extragalactic background light
Encyclopedia
The Extragalactic Background Light (EBL) or simply the "extragalactic background" (EGB)
is the faint diffuse light of the night sky, consisting of the combined flux of all extragalactic sources. Its main significance for astronomers is that it contains information regarding the history and formation of other galaxies, and also the large-scale structure of the universe.
not follow strictly the usual domains of the electromagnetic spectrum
:
is the faint diffuse light of the night sky, consisting of the combined flux of all extragalactic sources. Its main significance for astronomers is that it contains information regarding the history and formation of other galaxies, and also the large-scale structure of the universe.
Phenomenological description
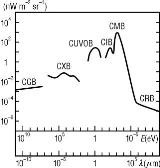
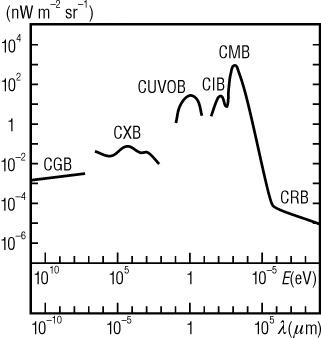
The extragalactic background is usually divided into six wavelength ranges, which donot follow strictly the usual domains of the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
:
- CGB: Cosmic gamma-ray background
- CXB: Cosmic X-ray background
- CUVOB: Cosmic ultra-violet and optical background
- CIB: Cosmic infrared backgroundCosmic infrared backgroundCosmic infrared background is a mysterious infrared light coming from outer space. It is slowly being resolved into specific sources by infrared telescopes...
- CMB: Cosmic microwave background
- CRB: Cosmic radio background

See also
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiationCosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....

