
Equivalent latitude
Encyclopedia
Equivalent latitude is a Lagrangian coordinate
used in atmospheric science,
particularly in the study of stratospheric
dynamics.
Each isoline in a map of equivalent latitude follows that of an atmospheric
tracer
and encloses the same area as the latitude line
of equivalent value, hence "equivalent latitude."
Equivalent latitude is calculated from potential vorticity
,
from passive tracer simulations
and from actual measurements of atmospheric tracer
s such as ozone
.
monotonic mapping
between the values of equivalent latitude and
the tracer it is based upon: higher values of the tracer map to higher
values of equivalent latitude.
A precise method is to assign a
representative area to each of the tracer measurements, filling the entire globe.
Thus, for a tracer field regularly gridded in longitude and latitude,
grid points closer to the pole will take up a smaller area,
in proportion to the cosine of the latitude.
Now, rank
all the tracer values then form the cumulative sum.
The equivalent latitude from the area is given as:
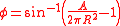
where A is the area enclosed to the South (A = 0 corresponds to the equivalent South Pole) and R is the radius of the Earth.
This method generates a mapping that is as continuous as the data allows
as opposed to binning which produces a coarse-grained mapping.
used in atmospheric science,
particularly in the study of stratospheric
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second major layer of Earth's atmosphere, just above the troposphere, and below the mesosphere. It is stratified in temperature, with warmer layers higher up and cooler layers farther down. This is in contrast to the troposphere near the Earth's surface, which is cooler...
dynamics.
Each isoline in a map of equivalent latitude follows that of an atmospheric
tracer
Flow tracer
thumb|right|300px|On May 2, [[2001]], the Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer obtained this spectacular image of the [[Atlantic Ocean]]'s [[Gulf Stream]]. The [[false color]]s in the image represent "[[brightness temperature]]" observed at the top of the [[atmosphere]]...
and encloses the same area as the latitude line
of equivalent value, hence "equivalent latitude."
Equivalent latitude is calculated from potential vorticity
Potential vorticity
Potential vorticity is a quantity which is proportional to the dot product of vorticity and stratification that, following a parcel of air or water, can only be changed by diabatic or frictional processes...
,
from passive tracer simulations
and from actual measurements of atmospheric tracer
Tracer
Tracer may refer to:* Histochemical tracer, a substance used for tracing purposes in histochemistry, the study of the composition of cells and tissues...
s such as ozone
Ozone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
.
Calculation of equivalent latitude
The calculation of equivalent latitude involves creating amonotonic mapping
Monotonic function
In mathematics, a monotonic function is a function that preserves the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory....
between the values of equivalent latitude and
the tracer it is based upon: higher values of the tracer map to higher
values of equivalent latitude.
A precise method is to assign a
representative area to each of the tracer measurements, filling the entire globe.
Thus, for a tracer field regularly gridded in longitude and latitude,
grid points closer to the pole will take up a smaller area,
in proportion to the cosine of the latitude.
Now, rank
Sorting
Sorting is any process of arranging items in some sequence and/or in different sets, and accordingly, it has two common, yet distinct meanings:# ordering: arranging items of the same kind, class, nature, etc...
all the tracer values then form the cumulative sum.
The equivalent latitude from the area is given as:
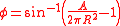
where A is the area enclosed to the South (A = 0 corresponds to the equivalent South Pole) and R is the radius of the Earth.
This method generates a mapping that is as continuous as the data allows
as opposed to binning which produces a coarse-grained mapping.

