
Egli Model
Encyclopedia
The Egli Model is a terrain model for radio frequency propagation
. This model, which was first introduced by John Egli in his 1957 paper, was derived from real-world data on UHF and VHF television transmissions in several large cities. It predicts the total path loss
for a point-to-point
link. Typically used for outdoor line-of-sight
transmission, this model provides the path loss as a single quantity.
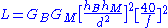
Where,
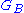 = Gain
= Gain
of the base station
antenna
. Unit: dimensionless
 = Gain of the mobile station
= Gain of the mobile station
antenna. Unit: dimensionless
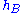 = Height of the base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of the base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
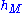 = Height of the mobile station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of the mobile station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
 = Distance from base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Distance from base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
 = Frequency
= Frequency
of transmission. Unit: megahertz
(MHz)
ITU Terrain Model
International telecommunication union
Radio propagation model
A radio propagation model, also known as the Radio Wave Propagation Model or the Radio Frequency Propagation Model, is an empirical mathematical formulation for the characterization of radio wave propagation as a function of frequency, distance and other conditions...
. This model, which was first introduced by John Egli in his 1957 paper, was derived from real-world data on UHF and VHF television transmissions in several large cities. It predicts the total path loss
Path loss
Path loss is the reduction in power density of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system....
for a point-to-point
Point-to-point
Point-to-point or point to point may refer to:Computing* Point-to-point construction, an electronics assembly technique* Point-to-point * Point-to-Point Protocol , part of the Internet protocol suite...
link. Typically used for outdoor line-of-sight
Line-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
transmission, this model provides the path loss as a single quantity.
Applicable to/under conditions
The Egli model is typically suitable for cellular communication scenarios where one antenna is fixed and another is mobile. The model is applicable to scenarios where the transmission has to go over an irregular terrain. However, the model does not take into account travel through some vegetative obstruction, such as trees or shrubbery.Coverage
Frequency: The model is typically applied to VHF and UHF spectrum transmissions.Mathematical formulation
The Egli model is formally expressed as: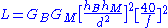
Where,
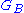 = Gain
= GainGain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
of the base station
Base station
The term base station can be used in the context of land surveying and wireless communications.- Land surveying :In the context of external land surveying, a base station is a GPS receiver at an accurately-known fixed location which is used to derive correction information for nearby portable GPS...
antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
. Unit: dimensionless
 = Gain of the mobile station
= Gain of the mobile stationMobile Station
The mobile station comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network.The mobile station refers to global system connected to the mobile network, i.e. mobile phone or mobile computer connected using a mobile broadband adapter. This is the terminology of 2G...
antenna. Unit: dimensionless
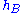 = Height of the base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of the base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)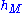 = Height of the mobile station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Height of the mobile station antenna. Unit: meter (m) = Distance from base station antenna. Unit: meter (m)
= Distance from base station antenna. Unit: meter (m) = Frequency
= FrequencyFrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of transmission. Unit: megahertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
(MHz)
Limitations
This model predicts the path loss as a whole and does not subdivide the loss into free space loss and other losses.Further reading
Introduction to RF propagation, John S. Seybold, 2005, John Willey and Sons Inc.See also
Longley-Rice ModelITU Terrain Model
ITU Terrain Model
The ITU Terrain Loss Model is a radio propagation model that provides a method to predict the median path loss for a telecommunication link. Developed on the basis of diffraction theory, this model predicts the path loss as a function of the height of path blockage and the First Fresnel zone for...
International telecommunication union
Itu
Itu is an old and historic municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2009 was 157,384 and the area is 641.68 km². The elevation is 583 m. This place name comes from the Tupi language, meaning big waterfall. Itu is linked with the highway numbered the SP-75 and are flowed...

