
Dyall Hamiltonian
Encyclopedia
In quantum chemistry
, the Dyall Hamiltonian is a modified Hamiltonian
with two-electron nature. It can be written as follows:
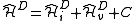
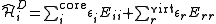
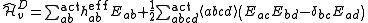
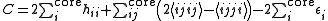
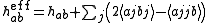
where labels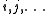 ,
, 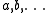 ,
, 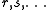 denote core, active and virtual orbitals (see Complete active space
denote core, active and virtual orbitals (see Complete active space
) respectively,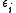 and
and 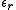 are the orbital energies of the involved orbitals, and
are the orbital energies of the involved orbitals, and 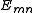 operators are the spin-traced operators
operators are the spin-traced operators 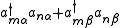 . These operators commute with
. These operators commute with 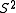 and
and 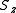 , therefore the application of these operators on a spin-pure function produces again a spin-pure function.
, therefore the application of these operators on a spin-pure function produces again a spin-pure function.
The Dyall Hamiltonian behaves like the true Hamiltonian inside the CAS space, having the same eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the true Hamiltonian projected onto the CAS space.
Quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry is a branch of chemistry whose primary focus is the application of quantum mechanics in physical models and experiments of chemical systems...
, the Dyall Hamiltonian is a modified Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian H, also Ȟ or Ĥ, is the operator corresponding to the total energy of the system. Its spectrum is the set of possible outcomes when one measures the total energy of a system...
with two-electron nature. It can be written as follows:
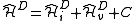
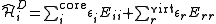
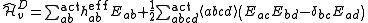
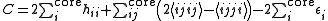
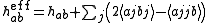
where labels
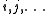 ,
, 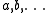 ,
, 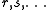 denote core, active and virtual orbitals (see Complete active space
denote core, active and virtual orbitals (see Complete active spaceComplete active space
In quantum chemistry, a complete active space is a type of classification of molecular orbitals. Spatial orbitals are classified as belonging to three classes:* core, always hold two electrons* active, partially occupied orbitals...
) respectively,
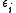 and
and 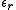 are the orbital energies of the involved orbitals, and
are the orbital energies of the involved orbitals, and 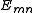 operators are the spin-traced operators
operators are the spin-traced operators 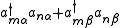 . These operators commute with
. These operators commute with 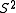 and
and 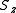 , therefore the application of these operators on a spin-pure function produces again a spin-pure function.
, therefore the application of these operators on a spin-pure function produces again a spin-pure function.The Dyall Hamiltonian behaves like the true Hamiltonian inside the CAS space, having the same eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the true Hamiltonian projected onto the CAS space.

