
Dipole model of the Earth's magnetic field
Encyclopedia
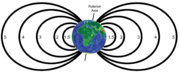
Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's inner core to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of energetic particles emanating from the Sun...
. Due to effects of the interplanetary magnetic field
Interplanetary Magnetic Field
The interplanetary magnetic field is the term for the solar magnetic field carried by the solar wind among the planets of the Solar System....
, and the solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
, the dipole model is particularly inaccurate at high L-shell
L-shell
The L-shell, L-value, or McIlwain L-parameter is a parameter describing a particular set of planetary magnetic field lines. Colloquially, L-value often describes the set of magnetic field lines which cross the Earth's magnetic equator at a number of Earth-radii equal to the L-value...
s (e.g., above L=3), but may be a good approximation for lower L-shells. For more precise work, or for any work at higher L-shells, a more accurate model that incorporates solar effects, such as the Tsyganenko magnetic field model, is recommended.
Equations
The following equations describe the dipole magnetic field.First, define
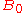 as the mean value of the magnetic field at the magnetic equator on the Earth's surface. Typically
as the mean value of the magnetic field at the magnetic equator on the Earth's surface. Typically 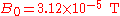 .
.Then, the radial and azimuthal fields can be described as
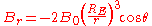
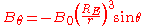
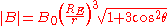
where
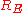 is the mean radius of the Earth
is the mean radius of the EarthEarth radius
Because the Earth is not perfectly spherical, no single value serves as its natural radius. Distances from points on the surface to the center range from 6,353 km to 6,384 km...
(approximately 6370 km),
 is the radial distance from the center of the Earth (using the same units as used for
is the radial distance from the center of the Earth (using the same units as used for 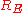 ), and
), and 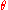 is the azimuth measured from the north magnetic pole.
is the azimuth measured from the north magnetic pole.It is sometimes more convenient to express the magnetic field in terms of magnetic latitude and distance in earth radii. The magnetic latitude
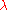 is measured northwards from the equator (analogous to geographic latitude
is measured northwards from the equator (analogous to geographic latitudeLatitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
) and is related to
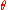 by
by 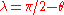 . In this case, the radial and azimuthal components of the magnetic field (the latter still in the
. In this case, the radial and azimuthal components of the magnetic field (the latter still in the 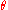 direction, measured from the axis of the north pole) are given by
direction, measured from the axis of the north pole) are given by
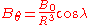
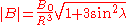
where
 in this case has units of Earth radii (
in this case has units of Earth radii (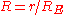 ).
).Invariant latitude
Invariant latitude is a parameter that describes where a particular magnetic field line touches the surface of the Earth. It is given by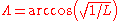
or
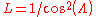
where
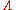 is the invariant latitude and
is the invariant latitude and 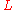 is the L-shell describing the magnetic field line in question.
is the L-shell describing the magnetic field line in question.On the surface of the earth, the invariant latitude (
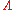 ) is equal to the magnetic latitude (
) is equal to the magnetic latitude (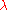 ).
).External links
- Instant run of Tsyganenko magnetic field model from NASA CCMC
- Nikolai Tsyganenko's website including Tsyganenko model source code

