Derating
Encyclopedia
Derating is the operation of a machine at less than its rated maximum power in order to prolong its life. The term is commonly applied to electrical and electronic devices and to internal combustion engine
s.
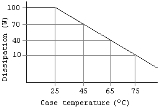
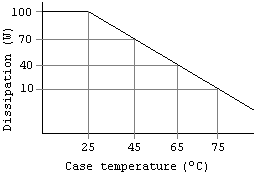 Power electronic devices have a maximum power dissipation rating usually quoted at a case temperature of 25 °C (77 °F). The datasheet for the device also includes a derating curve which indicates how much a device will dissipate without getting damaged at any given case temperature and this must be taken into account while designing a system.
Power electronic devices have a maximum power dissipation rating usually quoted at a case temperature of 25 °C (77 °F). The datasheet for the device also includes a derating curve which indicates how much a device will dissipate without getting damaged at any given case temperature and this must be taken into account while designing a system.
As can be seen from the derating curve image for a hypothetical BJT
, the device (rated for 100 W at 25 °C (77 °F)) cannot be expected to dissipate anything more than about 40 W if the ambient temperature is such that the temperature at which the device's case will stabilise (after heat-sinking
) is 65 °C (149 °F). This final case temperature is a function of the thermal resistance
between the device's case and the heat-sink; and the heat-sink and the ambient (this includes the heat-sink's temp/watt rating - with lower values implying better cooling characteristics).
s rely on heat conduction and convection to keep the electronic components cool. Similarly, power wiring (e.g., house wiring) not surrounded by an air space (e.g., inside a conduit) needs to have its current-limiting device (e.g. circuit breaker or fuse) adjusted so as not to carry as much current through that circuit. Derating is the reduction of the maximum capacity (load) a unit can reliably handle when fin
s/side sections are removed.
rated at 1,000 horsepower for locomotive
use may be de-rated by 10% to 900 horsepower for marine or stationary use.
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
s.
In electronics

As can be seen from the derating curve image for a hypothetical BJT
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
, the device (rated for 100 W at 25 °C (77 °F)) cannot be expected to dissipate anything more than about 40 W if the ambient temperature is such that the temperature at which the device's case will stabilise (after heat-sinking
Heat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
) is 65 °C (149 °F). This final case temperature is a function of the thermal resistance
Thermal resistance in electronics
Thermal resistance is a heat property - and a measure of a temperature difference, by which an object - or material resist a heat flow...
between the device's case and the heat-sink; and the heat-sink and the ambient (this includes the heat-sink's temp/watt rating - with lower values implying better cooling characteristics).
In electrical installations
All dimmerDimmer
Dimmers are devices used to vary the brightness of a light. By decreasing or increasing the RMS voltage and, hence, the mean power to the lamp, it is possible to vary the intensity of the light output...
s rely on heat conduction and convection to keep the electronic components cool. Similarly, power wiring (e.g., house wiring) not surrounded by an air space (e.g., inside a conduit) needs to have its current-limiting device (e.g. circuit breaker or fuse) adjusted so as not to carry as much current through that circuit. Derating is the reduction of the maximum capacity (load) a unit can reliably handle when fin
Fin
A fin is a surface used for stability and/or to produce lift and thrust or to steer while traveling in water, air, or other fluid media, . The first use of the word was for the limbs of fish, but has been extended to include other animal limbs and man-made devices...
s/side sections are removed.
Internal combustion engines
Internal combustion engines are normally given different ratings for different applications. For example, a diesel engineDiesel engine
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber...
rated at 1,000 horsepower for locomotive
Diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railroad locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine, a reciprocating engine operating on the Diesel cycle as invented by Dr. Rudolf Diesel...
use may be de-rated by 10% to 900 horsepower for marine or stationary use.

