
Day count convention
Encyclopedia
In finance, a day count convention determines how interest
accrues over time for a variety of investment
s, including bonds
, notes, loan
s, mortgages
, medium-term notes, swaps, and forward rate agreements (FRAs)
. This determines the amount transferred on interest payment dates, and also the calculation of accrued interest
for dates between payments. The day count is also used to quantify periods of time when discounting a cash-flow to its present value
. When a security such as a bond is sold between interest payment dates, the seller is eligible to some fraction of the coupon amount.
The day count convention is used in many other formulae in financial mathematics as well.
There is no central authority defining day count conventions, so there is no standard terminology. Certain terms, such as "30/360", "Actual/Actual", and "money market basis" must be understood in the context of the particular market.
The conventions have evolved, and this is particularly true since the mid-1990s. Part of it has simply been providing for additional cases or clarification.
There has also been a move towards convergence in the marketplace, which has resulted in the number of conventions in use being reduced. Much of this has been driven by the introduction of the euro.
CouponFactor: The Factor to be used when determining the amount of interest paid by the issuer on coupon payment dates. The periods may be regular or irregular.
CouponRate: The interest rate on the security or loan-type agreement, e.g., 5.25%. In the formulas this would be expressed as 0.0525.
Date1 (Y1.M1.D1): Starting date for the accrual. It is usually the coupon payment date preceding Date2.
Date2 (Y2.M2.D2): Date through which interest is being accrued. You could word this as the "to" date, with Date1 as the "from" date. For a bond trade, it is the settlement date of the trade.
Date3 (Y3.M3.D3): The coupon payment date following Date2.
Days(StartDate, EndDate): Function returning the number of days between StartDate and EndDate on a Julian basis (i.e., all days are counted). For instance, Days(15 October 2007, 15 November 2007) returns 31.
EOM: Indicates that the investment always pays interest on the last day of the month. If the investment is not EOM, it will always pay on the same day of the month (e.g., the 10th).
Factor: Figure representing the amount of the CouponRate to apply in calculating Interest. It is often expressed as "days in the accrual period / days in the year". If Date2 is a coupon payment date, Factor is zero.
Freq: The coupon payment frequency. 1 = annual, 2 = semi-annual, 4 = quarterly, 12 = monthly, etc.
Principal: Par value of the investment.
For all conventions, the Interest is calculated as:

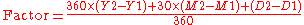
They calculate the CouponFactor as: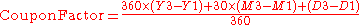
This is the same as the Factor calculation, with Date2 replaced by Date3. In the case that it is a regular coupon period, this is equivalent to: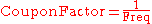
The conventions are distinguished by the manner in which they adjust Date1 and/or Date2 for the end of the month. Each convention has a set of rules directing the adjustments.
Treating a month as 30 days and a year as 360 days was devised for its ease of calculation by hand compared with manually calculating the actual days between two dates. Also, because 360 is highly factorable, payment frequencies of semi-annual and quarterly and monthly will be 180, 90, and 30 days of a 360 day year, meaning the payment amount will not change between payment periods.
This convention is used for US corporate bonds and many US agency issues. It is most commonly referred to as "30/360", but the term "30/360" may also refer to any of the other conventions of this class, depending on the context.
Other names:
Sources:
Other names:
Sources:
Other names:
Sources:
Sources:
The conventions are distinguished primarily by the amount of the CouponRate they assign to each day of the accrual period.
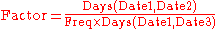
For regular coupon periods: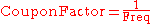
For irregular coupon periods, the period has to be divided into one or more quasi-coupon periods (also called notional periods) that match the normal frequency of payment dates. The interest in each such period (or partial period) is then computed, and then the amounts are summed over the number of quasi-coupon periods. For details, see or the SWX references (Accrued Interest Calculator and Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars).
This method ensures that all coupon payments are always for the same amount.
It also ensures that all days in a coupon period are valued equally. However, the coupon periods themselves may be of different lengths; in the case of semi-annual payment on a 365 day year, one period can be 182 days and the other 183 days. In that case, all the days in one period will be valued 1/182nd of the payment amount and all the days in the other period will be valued 1/183rd of the payment amount.
This is the convention used for US Treasury bonds and notes, among other securities.
Other names:
Sources:
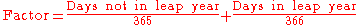
This convention accounts for days in the period based on the portion in a leap year and the portion in a non-leap year.
The days in the numerators are calculated on a Julian
day difference basis. In this convention the first day of the period is included and the last day is excluded.
The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names are:
Sources:

Each month is treated normally and the year is assumed to be 365 days. For example, in a period from February 1, 2005 to April 1, 2005, the Factor is considered to be 59 days divided by 365.
The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names:
Sources:

This convention is used in money market
s for short-term lending of currencies, including the US dollar and Euro, and is applied in ESCB
monetary policy operations. It is the convention used with Repurchase agreement
s. Each month is treated normally and the year is assumed to be 360 days. For example, in a period from February 1, 2005 to April 1, 2005, the Factor is 59 days divided by 360 days.
The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names:
Sources:
This convention requires a set of rules in order to determine the days in the year (DiY).

The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names:
Sources:
"Actual/Actual AFB/FBF Master Agreement" has the DiY equal to 365 (if the calculation period does not contain 29th February) or 366 (if 29 February falls within the Calculation Period or Compounding Period).
If the Calculation Period or Compounding Period is a term of more than one year, the basis shall be calculated as follows:
When counting backwards for this purpose, if the last day of the relevant period is 28th February, the full year should be counted back to the previous 28th February unless 29th February exists, in which case, 29th February should be used.

Sources:
The Actual/360 method calls for the borrower to pay interest for the actual number of days in a month. This effectively means that the borrower is paying interest for 5 or 6 additional days a year as compared to the 30/360 day count convention. Spreads and rates on Actual/360 transactions are typically lower, e.g., 9 basis points. Since monthly loan payments are the same for both methods and since the investor is being paid for an additional 5 or 6 days of interest with the Actual/360 year base, the loan’s principal is reduced at a slightly lower rate. This leaves the loan balance 1-2% higher than a 30/360 10-year loan with the same payment.
(business date) conventions are a common practice to adjust non-business days into business days.
Interest
Interest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
accrues over time for a variety of investment
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
s, including bonds
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a debt security, in which the authorized issuer owes the holders a debt and, depending on the terms of the bond, is obliged to pay interest to use and/or to repay the principal at a later date, termed maturity...
, notes, loan
Loan
A loan is a type of debt. Like all debt instruments, a loan entails the redistribution of financial assets over time, between the lender and the borrower....
s, mortgages
Mortgage loan
A mortgage loan is a loan secured by real property through the use of a mortgage note which evidences the existence of the loan and the encumbrance of that realty through the granting of a mortgage which secures the loan...
, medium-term notes, swaps, and forward rate agreements (FRAs)
Forward rate agreement
In finance, a forward rate agreement is a forward contract, an over-the-counter contract between parties that determines the rate of interest, or the currency exchange rate, to be paid or received on an obligation beginning at a future start date. The contract will determine the rates to be used...
. This determines the amount transferred on interest payment dates, and also the calculation of accrued interest
Accrued interest
In finance, accrued Interest is the interest that has accumulated since the principal investment, or since the previous interest payment if there has been one already. For a financial instrument such as a bond, interest is calculated and paid in set intervals...
for dates between payments. The day count is also used to quantify periods of time when discounting a cash-flow to its present value
Present value
Present value, also known as present discounted value, is the value on a given date of a future payment or series of future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money and other factors such as investment risk...
. When a security such as a bond is sold between interest payment dates, the seller is eligible to some fraction of the coupon amount.
The day count convention is used in many other formulae in financial mathematics as well.
Development
The need for day count conventions is a direct consequence of interest-earning investments. Different conventions were developed to address often conflicting requirements, including ease of calculation, constancy of time period (day, month, or year) and the needs of the Accounting department. This development occurred long before the advent of computers.There is no central authority defining day count conventions, so there is no standard terminology. Certain terms, such as "30/360", "Actual/Actual", and "money market basis" must be understood in the context of the particular market.
The conventions have evolved, and this is particularly true since the mid-1990s. Part of it has simply been providing for additional cases or clarification.
There has also been a move towards convergence in the marketplace, which has resulted in the number of conventions in use being reduced. Much of this has been driven by the introduction of the euro.
Definitions
Interest: Amount of interest accrued on an investment.CouponFactor: The Factor to be used when determining the amount of interest paid by the issuer on coupon payment dates. The periods may be regular or irregular.
CouponRate: The interest rate on the security or loan-type agreement, e.g., 5.25%. In the formulas this would be expressed as 0.0525.
Date1 (Y1.M1.D1): Starting date for the accrual. It is usually the coupon payment date preceding Date2.
Date2 (Y2.M2.D2): Date through which interest is being accrued. You could word this as the "to" date, with Date1 as the "from" date. For a bond trade, it is the settlement date of the trade.
Date3 (Y3.M3.D3): The coupon payment date following Date2.
Days(StartDate, EndDate): Function returning the number of days between StartDate and EndDate on a Julian basis (i.e., all days are counted). For instance, Days(15 October 2007, 15 November 2007) returns 31.
EOM: Indicates that the investment always pays interest on the last day of the month. If the investment is not EOM, it will always pay on the same day of the month (e.g., the 10th).
Factor: Figure representing the amount of the CouponRate to apply in calculating Interest. It is often expressed as "days in the accrual period / days in the year". If Date2 is a coupon payment date, Factor is zero.
Freq: The coupon payment frequency. 1 = annual, 2 = semi-annual, 4 = quarterly, 12 = monthly, etc.
Principal: Par value of the investment.
For all conventions, the Interest is calculated as:

30/360 methods
All conventions of this class calculate the Factor as: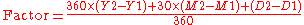
They calculate the CouponFactor as:
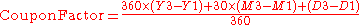
This is the same as the Factor calculation, with Date2 replaced by Date3. In the case that it is a regular coupon period, this is equivalent to:

The conventions are distinguished by the manner in which they adjust Date1 and/or Date2 for the end of the month. Each convention has a set of rules directing the adjustments.
Treating a month as 30 days and a year as 360 days was devised for its ease of calculation by hand compared with manually calculating the actual days between two dates. Also, because 360 is highly factorable, payment frequencies of semi-annual and quarterly and monthly will be 180, 90, and 30 days of a 360 day year, meaning the payment amount will not change between payment periods.
30/360 US
Date adjustment rules (more than one may take effect; apply them in order, and if a date is changed in one rule the changed value is used in the following rules):- If the investment is EOM and (Date1 is the last day of February) and (Date2 is the last day of February), then change D2 to 30.
- If the investment is EOM and (Date1 is the last day of February), then change D1 to 30.
- If D2 is 31 and D1 is 30 or 31, then change D2 to 30.
- If D1 is 31, then change D1 to 30.
This convention is used for US corporate bonds and many US agency issues. It is most commonly referred to as "30/360", but the term "30/360" may also refer to any of the other conventions of this class, depending on the context.
Other names:
- 30U/360
- Bond basis
- 360/360
Sources:
- ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(f), though the first two rules are not included
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
30E/360
Date adjustment rules:- If D1 is 31, then change D1 to 30.
- If D2 is 31, then change D2 to 30.
Other names:
- 30/360 ICMA
- 30S/360
- Eurobond basis (ISDA 2006)
- Special German
Sources:
- ICMAICMAThe International Capital Market Association is a unique organisation and an influential voice for the global capital market. It represents a broad range of capital market interests including global investment banks and smaller regional banks, as well as asset managers, exchanges, central banks,...
Rule 251.1(ii), 251.2 - ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(g)
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
30E/360 ISDA
Date adjustment rules:- If D1 is the last day of the month, then change D1 to 30.
- If D2 is the last day of the month (unless Date2 is the maturity date and D2 is February), then change D2 to 30.
Other names:
- 30E/360 ISDA
- Eurobond basis (ISDA 2000)
- German
Sources:
- ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(h)
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
30E+/360
Date adjustment rules:- If D1 is 31, then change D1 to 30.
- If D2 is 31, then increment M2 and change D2 to 1.
Sources:
- A normative source needs to be identified.
Actual methods
The conventions of this class calculate the number of days between two dates (e.g., between Date1 and Date2) as the Julian difference. This is the function Days(StartDate, EndDate).The conventions are distinguished primarily by the amount of the CouponRate they assign to each day of the accrual period.
Actual/Actual ICMA
Formulas: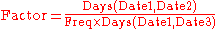
For regular coupon periods:

For irregular coupon periods, the period has to be divided into one or more quasi-coupon periods (also called notional periods) that match the normal frequency of payment dates. The interest in each such period (or partial period) is then computed, and then the amounts are summed over the number of quasi-coupon periods. For details, see or the SWX references (Accrued Interest Calculator and Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars).
This method ensures that all coupon payments are always for the same amount.
It also ensures that all days in a coupon period are valued equally. However, the coupon periods themselves may be of different lengths; in the case of semi-annual payment on a 365 day year, one period can be 182 days and the other 183 days. In that case, all the days in one period will be valued 1/182nd of the payment amount and all the days in the other period will be valued 1/183rd of the payment amount.
This is the convention used for US Treasury bonds and notes, among other securities.
Other names:
- Actual/Actual
- Act/Act ICMA
- ISMA-99
- Act/Act ISMA
Sources:
- ICMA Rule 251.1(iii)
- ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(c)
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
Actual/Actual ISDA
Formulas: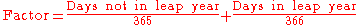
This convention accounts for days in the period based on the portion in a leap year and the portion in a non-leap year.
The days in the numerators are calculated on a Julian
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
day difference basis. In this convention the first day of the period is included and the last day is excluded.
The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names are:
- Actual/Actual
- Act/Act
- Actual/365
- Act/365
Sources:
- ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(b)
Actual/365 Fixed
Formulas:
Each month is treated normally and the year is assumed to be 365 days. For example, in a period from February 1, 2005 to April 1, 2005, the Factor is considered to be 59 days divided by 365.
The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names:
- Act/365 Fixed
- A/365 Fixed
- A/365F
- English
Sources:
- ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(d)
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
Actual/360
Formulas:
This convention is used in money market
Money market
The money market is a component of the financial markets for assets involved in short-term borrowing and lending with original maturities of one year or shorter time frames. Trading in the money markets involves Treasury bills, commercial paper, bankers' acceptances, certificates of deposit,...
s for short-term lending of currencies, including the US dollar and Euro, and is applied in ESCB
European System of Central Banks
The European System of Central Banks is composed of the European Central Bank and the national central banks of all 27 European Union Member States.-Functions:...
monetary policy operations. It is the convention used with Repurchase agreement
Repurchase agreement
A repurchase agreement, also known as a repo, RP, or sale and repurchase agreement, is the sale of securities together with an agreement for the seller to buy back the securities at a later date. The repurchase price should be greater than the original sale price, the difference effectively...
s. Each month is treated normally and the year is assumed to be 360 days. For example, in a period from February 1, 2005 to April 1, 2005, the Factor is 59 days divided by 360 days.
The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names:
- Act/360
- A/360
- French
Sources:
- ICMA Rule 251.1(i) (not sterling)
- ISDA 2006 Section 4.16(e)
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
Actual/365L
Formulas:This convention requires a set of rules in order to determine the days in the year (DiY).
- If Freq = 1 (annual coupons):
- If February 29 is in the range from Date1 (exclusive) to Date3 (inclusive), then DiY = 366, else DiY = 365.
- If Freq <> 1:
- If Date3 is in a leap year, then DiY = 366, else DiY = 365.

The CouponFactor uses the same formula, replacing Date2 by Date3. In general, coupon payments will vary from period to period, due to the differing number of days in the periods. The formula applies to both regular and irregular coupon periods.
Other names:
- ISMA-Year
Sources:
- ICMA Rule 251.1(i) (Euro-sterling)
- Accrued Interest & Yield Calculations and Determination of Holiday Calendars
Actual/Actual AFB
Formulas:"Actual/Actual AFB/FBF Master Agreement" has the DiY equal to 365 (if the calculation period does not contain 29th February) or 366 (if 29 February falls within the Calculation Period or Compounding Period).
If the Calculation Period or Compounding Period is a term of more than one year, the basis shall be calculated as follows:
- the number of complete years shall be counted back from the last day of the Calculation Period or Compounding Period; and
- this number shall be increased by the fraction for the relevant period calculated.
When counting backwards for this purpose, if the last day of the relevant period is 28th February, the full year should be counted back to the previous 28th February unless 29th February exists, in which case, 29th February should be used.

Sources:
- EMU and Market Conventions: Recent Developments
- Master Agreement for Financial Transactions / Supplement to the Derivatives Annex / INTEREST RATE TRANSACTIONS / Edition 2004
Comparison of 30/360 and Actual/360
The 30/360 methods assume every month has 30 days and each year has 360 days. The 30/360 calculation is listed on standard loan constant charts and is now typically used by a calculator or computer in determining mortgage payments. This method of treating a month as 30 days and a year as 360 days was originally devised for its ease of calculation by hand compared with the actual days between two dates. Because 360 is highly factorable, payment frequencies of semi-annual and quarterly and monthly will be 180, 90, and 30 days of a 360 day year, meaning the payment amount will not change between payment periods.The Actual/360 method calls for the borrower to pay interest for the actual number of days in a month. This effectively means that the borrower is paying interest for 5 or 6 additional days a year as compared to the 30/360 day count convention. Spreads and rates on Actual/360 transactions are typically lower, e.g., 9 basis points. Since monthly loan payments are the same for both methods and since the investor is being paid for an additional 5 or 6 days of interest with the Actual/360 year base, the loan’s principal is reduced at a slightly lower rate. This leaves the loan balance 1-2% higher than a 30/360 10-year loan with the same payment.
Business date convention
Date rollingDate rolling
In finance, date rolling occurs when a payment day or date used to calculate accrued interest falls on a holiday, according to a given business calendar. In this case the date is moved forward or backward in time such that it falls in a business day, according with the same business calendar.The...
(business date) conventions are a common practice to adjust non-business days into business days.
Further reading
- Financial Interest Calculator. Online calculation of interest with different day count conventions, created by eTradeTech.com.
- Accrued Interest Calculator. MS Excel spreadsheet implementation of some conventions, created by SIX Swiss Exchange.
- Pricing of Game Options (in a market with stochastic interest rates) - Section Chapter II: A Little Bit of Finance, Section 1: Brief introduction to Financial Securities, from pages 26 to 33, formally mention day count conventions.
- Practical Issues Arising from the Introduction of the Euro - Issue 7 (March 1998) - Chapter 4: Financial Markets and Exchanges: discusses European nations' day-count conventions and changes required to unify the day-count conventions for the EU member states.
- jFin pure Java open source implementation of financial date arithmetic.
- comparison of financial day count convention used in Excel and OOXML

