
Carson bandwidth rule
Encyclopedia
In telecommunication
, Carson's bandwidth rule defines the approximate bandwidth requirements of communications system
components for a carrier
signal that is frequency modulated by a continuous or broad spectrum of frequencies rather than a single frequency. Carson's rule does not apply well when the modulating signal contains discontinuities, such as a square wave. Carson's rule originates from John Renshaw Carson
's 1922 paper.
Carson's bandwidth rule is expressed by the relation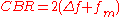 where CBR is the bandwidth requirement,
where CBR is the bandwidth requirement, 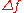 is the peak frequency deviation
is the peak frequency deviation
, and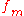 is the highest frequency in the modulating signal.
is the highest frequency in the modulating signal.
For example, an FM signal with 5 kHz peak deviation, and a maximum audio frequency of 3 kHz, would require an approximate bandwidth 2(5+3) = 16 kHz.
Carson's bandwidth rule is often applied to transmitter
s, antenna
s, optical sources, receiver
s, photodetector
s, and other communications system components.
Any modulated signal will have an infinite number of sidebands and hence an infinite bandwidth but in practice all significant sideband energy (98% or more) is concentrated within the bandwidth defined by Carson's rule. It is a useful approximation, but setting the arbitrary definition of occupied bandwidth at 98% of the power still means that the power outside the band is only about 17 dB less than the carrier inside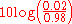 , therefore Carson's Rule is of little use in spectrum planning.
, therefore Carson's Rule is of little use in spectrum planning.
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, Carson's bandwidth rule defines the approximate bandwidth requirements of communications system
Communications system
In telecommunication, a communications system is a collection of individual communications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole...
components for a carrier
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
signal that is frequency modulated by a continuous or broad spectrum of frequencies rather than a single frequency. Carson's rule does not apply well when the modulating signal contains discontinuities, such as a square wave. Carson's rule originates from John Renshaw Carson
John Renshaw Carson
John Renshaw Carson , who published as J. R. Carson, was a noted transmission theorist for early communications systems...
's 1922 paper.
Carson's bandwidth rule is expressed by the relation
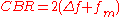 where CBR is the bandwidth requirement,
where CBR is the bandwidth requirement, 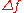 is the peak frequency deviation
is the peak frequency deviationFrequency deviation
Frequency deviation is used in FM radio to describe the maximum instantaneous difference between an FM modulated frequency and the nominal carrier frequency...
, and
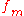 is the highest frequency in the modulating signal.
is the highest frequency in the modulating signal.For example, an FM signal with 5 kHz peak deviation, and a maximum audio frequency of 3 kHz, would require an approximate bandwidth 2(5+3) = 16 kHz.
Carson's bandwidth rule is often applied to transmitter
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications a transmitter or radio transmitter is an electronic device which, with the aid of an antenna, produces radio waves. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating...
s, antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
s, optical sources, receiver
Receiver (radio)
A radio receiver converts signals from a radio antenna to a usable form. It uses electronic filters to separate a wanted radio frequency signal from all other signals, the electronic amplifier increases the level suitable for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through...
s, photodetector
Photodetector
Photosensors or photodetectors are sensors of light or other electromagnetic energy. There are several varieties:*Active pixel sensors are image sensors consisting of an integrated circuit that contains an array of pixel sensors, each pixel containing a both a light sensor and an active amplifier...
s, and other communications system components.
Any modulated signal will have an infinite number of sidebands and hence an infinite bandwidth but in practice all significant sideband energy (98% or more) is concentrated within the bandwidth defined by Carson's rule. It is a useful approximation, but setting the arbitrary definition of occupied bandwidth at 98% of the power still means that the power outside the band is only about 17 dB less than the carrier inside
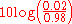 , therefore Carson's Rule is of little use in spectrum planning.
, therefore Carson's Rule is of little use in spectrum planning.

