
Canton - Sam Shui Railway
Encyclopedia
The Canton – Sam Shui Railway is a railway line in Guangdong
, People's Republic of China
, opened in 1903 and 1904.
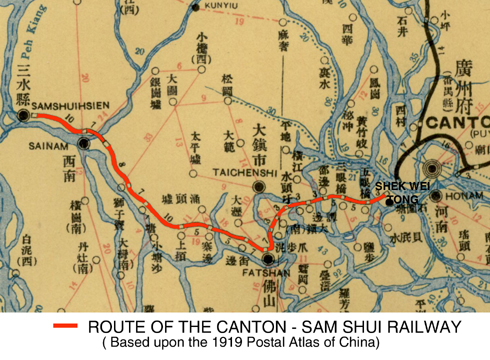
traditional Chinese:廣州, simplified Chinese:广州) to Sam Shui (pinyin: Sanshui
Chinese:三水 ) railway line was constructed between 1902 and 1904 by American engineers. Commencing from its Shek Wei Tong: (Shiweitang traditional Chinese 石圍塘, simplified Chinese 石围塘) terminus and depot in Canton this short line was built as a branch line of the Canton Hankow Railway and was the first portion of this southern trunk line to be constructed. The first 10 miles from Canton to Fatshan (pinyin:Foshan
Chinese:佛山) opened in late 1903 and the remainder to Sam Shui was completed and formally opened on 23 September 1904.
 The origins of this railway go back to the so called “Battle for Concessions” during 1898 when Western powers bickered among themselves over the extraction of railway concessions from the Qing Dynasty government, severely weakened by their loss of the war with Japan over Korea. Not wishing to be left out of the fray, a powerful American syndicate known as the American-China Development Company, formed under the auspices of financier Calvin Brice in April 1898, obtained a concession for the construction of the 750 mile-long Hankow –Canton (Wuhan-Guangzhou) Railway. In the autumn of 1898 a team of American engineers led by Chief Engineer William Barclay Parsons
The origins of this railway go back to the so called “Battle for Concessions” during 1898 when Western powers bickered among themselves over the extraction of railway concessions from the Qing Dynasty government, severely weakened by their loss of the war with Japan over Korea. Not wishing to be left out of the fray, a powerful American syndicate known as the American-China Development Company, formed under the auspices of financier Calvin Brice in April 1898, obtained a concession for the construction of the 750 mile-long Hankow –Canton (Wuhan-Guangzhou) Railway. In the autumn of 1898 a team of American engineers led by Chief Engineer William Barclay Parsons
was dispatched to China to conduct the survey. Barclay Parsons describes the difficulties endoured during this survey in his own account of this work “An American in China” published in 1900 after his return to USA.
 The American syndicate soon ran into all kinds of difficulties. The Spanish-American War had broken out causing a shortage of funds and a Belgian-French Syndicate, who were hoping to control all the planned trunk lines from Peking (Beijing 北京) to southern China, opposed the American syndicate and pressured the Chinese Government to rescind their agreement. On top of this, the leading driver of the scheme, Senator Brice, died leaving the syndicate without any enthusiastic and wealthy investors. Many of the Americans, who owned shares, became disillusioned and gradually sold out to French-Belgian interests, while the battle for control of the line continued. The next incident to delay the construction was the 1900 Boxer Uprising. However eventually in the autumn of 1902, with the American syndicate now under the presidency of Barclay Parsons, the short Canton-Sam Shui branch line was commenced. The American team of engineers sent to build the branch was headed by Chief Engineer C.W. Mead CE.
The American syndicate soon ran into all kinds of difficulties. The Spanish-American War had broken out causing a shortage of funds and a Belgian-French Syndicate, who were hoping to control all the planned trunk lines from Peking (Beijing 北京) to southern China, opposed the American syndicate and pressured the Chinese Government to rescind their agreement. On top of this, the leading driver of the scheme, Senator Brice, died leaving the syndicate without any enthusiastic and wealthy investors. Many of the Americans, who owned shares, became disillusioned and gradually sold out to French-Belgian interests, while the battle for control of the line continued. The next incident to delay the construction was the 1900 Boxer Uprising. However eventually in the autumn of 1902, with the American syndicate now under the presidency of Barclay Parsons, the short Canton-Sam Shui branch line was commenced. The American team of engineers sent to build the branch was headed by Chief Engineer C.W. Mead CE.
 The first section of about 10 miles from Canton to Fatshan was double-tracked standard gauge line using 75 lb steel rails. Because of the shortage of funds economies were made by purchasing used equipment from the United States and this included eight reconditioned ex-Manhattan Elevated Railway ‘Forney” type tank locomotives, which had been built in 1885-6 and were designed for running backwards (cab-first). Most of the stations along the route were initially small temporary mat-shed structures and the only permanent station erected in time for the opening of the railway was at Fatshan. This section was opened to traffic in late 1903.
The first section of about 10 miles from Canton to Fatshan was double-tracked standard gauge line using 75 lb steel rails. Because of the shortage of funds economies were made by purchasing used equipment from the United States and this included eight reconditioned ex-Manhattan Elevated Railway ‘Forney” type tank locomotives, which had been built in 1885-6 and were designed for running backwards (cab-first). Most of the stations along the route were initially small temporary mat-shed structures and the only permanent station erected in time for the opening of the railway was at Fatshan. This section was opened to traffic in late 1903.
of Pittsburgh in 1903. In later years it acquired similar locomotives from both the Baldwin
and Lima
locomotive companies

(Chinese: 茂名)http://www.hkrs.org.hk/members/rwong/sanmao98/index.htm
Guangdong
Guangdong is a province on the South China Sea coast of the People's Republic of China. The province was previously often written with the alternative English name Kwangtung Province...
, People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, opened in 1903 and 1904.

Introduction
The 32 mile-long Canton (GuangzhouGuangzhou
Guangzhou , known historically as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of the Guangdong province in the People's Republic of China. Located in southern China on the Pearl River, about north-northwest of Hong Kong, Guangzhou is a key national transportation hub and trading port...
traditional Chinese:廣州, simplified Chinese:广州) to Sam Shui (pinyin: Sanshui
Sanshui
For the style of Chinese painting, see Shan ShuiSanshui District , formerly Sanshui City, is a district with about 120,000 inhabitants in Guangdong province of the People's Republic of China...
Chinese:三水 ) railway line was constructed between 1902 and 1904 by American engineers. Commencing from its Shek Wei Tong: (Shiweitang traditional Chinese 石圍塘, simplified Chinese 石围塘) terminus and depot in Canton this short line was built as a branch line of the Canton Hankow Railway and was the first portion of this southern trunk line to be constructed. The first 10 miles from Canton to Fatshan (pinyin:Foshan
Foshan
Foshan is a city in central Guangdong province in southern China. The prefectural area under the city's jurisdiction over an area of about 3,840 km² and a population of 5.4 million of which 1.1 million reside in the city proper ....
Chinese:佛山) opened in late 1903 and the remainder to Sam Shui was completed and formally opened on 23 September 1904.
Financing and Survey

William Barclay Parsons
William Barclay Parsons was an American civil engineer. He founded the firm that became Parsons Brinckerhoff, one of the largest American civil engineering firms....
was dispatched to China to conduct the survey. Barclay Parsons describes the difficulties endoured during this survey in his own account of this work “An American in China” published in 1900 after his return to USA.
Construction delayed

Fatshan Section

Sam Shui Section
Construction of the next section from Fatshan to Sam Shui was then continued and a ceremony attended by the railway’s senior staff and a number of invited guests was held on 22 September 1904 to drive in the ‘last (silver) spike’, marking completion of the line. By this time the railway had received its first two passenger engines which were 4-4-0 tender locomotives built by the American Locomotive CompanyAmerican Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company, often shortened to ALCO or Alco , was a builder of railroad locomotives in the United States.-Early history:...
of Pittsburgh in 1903. In later years it acquired similar locomotives from both the Baldwin
Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works was an American builder of railroad locomotives. It was located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, originally, and later in nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania. Although the company was very successful as a producer of steam locomotives, its transition to the production of...
and Lima
Lima Locomotive Works
Lima Locomotive Works was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company took the most distinctive part of its name from its main shops location in Lima, Ohio. The shops were located between the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line...
locomotive companies

Shek Wei Tong depot and coach building shops
By 1909 the Shek Wei Tong maintenance depot in Canton had been enlarged and incorporated a machine shop and coach works capable of producing their own 60 feet (18.3 m) steel passenger coaches. The railway still exists and continues to be known as the Guang - San line as far as Sam Shui (Sanshui) from where the line now extends as part of a Provincially owned Sanmao Railway Company (traditional Chinese: 三茂線 simplified Chinese: 三茂线 ) line to MaomingMaoming
Maoming is located in southwestern Guangdong province, People's Republic of China. Facing the South China Sea to the city's south, Maoming city neighbors Zhanjiang in the west and is from Guangzhou and from Zhanjiang. The Maoming Port is a Grade I port that handled 16.8 million tons of cargo in...
(Chinese: 茂名)http://www.hkrs.org.hk/members/rwong/sanmao98/index.htm

