
COSMO Solvation Model
Encyclopedia
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
with a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
.
In COSMO the solvent is treated as a continuum with a permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
ε, and therefore belongs to the "continuum solvation" group of models. As in all these models COSMO approximates the solvent by a dielectric continuum, surrounding the solute molecules outside of a molecular cavity. The details of the cavity construction differ in different COSMO implementations. In most cases it is constructed as an assembly of atom centered spheres with radii approximately 20% larger than the Van der Waals radius
Van der Waals radius
The van der Waals radius, r, of an atom is the radius of an imaginary hard sphere which can be used to model the atom for many purposes. It is named after Johannes Diderik van der Waals, winner of the 1910 Nobel Prize in Physics, as he was the first to recognise that atoms had a finite size and to...
. For the actual calculation the cavity surface is approximated by segments, e.g., hexagons, pentagons, or triangles.
In difference to other continuum solvation models, COSMO derives the polarization charges of the continuum, caused by the polarity of the solute, from a scaled-conductor approximation. If the solvent were an ideal conductor the electric potential
Electric potential
In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there...
on the cavity surface must disappear. If the distribution of the electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
in the molecule is known, e.g. from quantum chemistry, then it is possible to calculate the charge q* on the surface segments. For solvents with finite dielectric constant this charge q is lower by approximately a factor ƒ(ε):
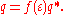
The factor ƒ(ε) is approximately
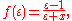
where the value of x is set to 0.5 based on theoretical arguments. Some re-implementations of COSMO use x = 0.
From the thus determined solvent charges q and the known charge distribution of the molecule, the energy of the interaction between the solvent and the solute molecule can be calculated.
The COSMO method can be used for all methods in theoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry seeks to provide theories that explain chemical observations. Often, it uses mathematical and computational methods that, at times, require advanced knowledge. Quantum chemistry, the application of quantum mechanics to the understanding of valency, is a major component of...
where the charge distribution of a molecule can be determined, for example semiempirical calculations, Hartree–Fock-method calculations or density functional theory
Density functional theory
Density functional theory is a quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. With this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by...
(quantum physics) calculations.
Comparison with other methods
While models based on the multipole expansionMultipole expansion
A multipole expansion is a mathematical series representing a function that depends on angles — usually the two angles on a sphere. These series are useful because they can often be truncated, meaning that only the first few terms need to be retained for a good approximation to the original...
of the charge distribution of a molecule are limited to small, quasi-spherical or ellipsoidal molecules, the COSMO method has the advantage that it can be applied to large and irregularly formed molecular structures.
The COSMO method is more accurate for solvents with a higher permittivity because a solvent with infinite permittivity behaves like an ideal conductor. With water (ε ≈ 80) a very good accuracy is achieved. Nevertheless, with the choice of x = 0.5 even at low permittivities it is almost as accurate as a complete solution of the electrostatic equations, though at much lower numerical costs. Apart from the numerical effciciency, another big advantage of COSMO compared to other dielectric continuum methods is its huge reduction of the artifacts caused by the small part of the electron density reaching outside of the cavity, the so-called outlying charge errors.
In contrast to molecular dynamic
Discrete element method
A discrete element method , also called a distinct element method is any of family of numerical methods for computing the motion of a large number of particles of micrometre-scale size and above...
calculations in which the motion of the molecules is calculated and the position and density averaged over time, the COSMO model, as is the case with all continuum models, has the advantage of a substantial lower computational effort.

