
C-mole
Encyclopedia
A C-mole of an organic
or generalised compound
is the number of carbon
atoms expressed as multiple of the number of Avogadro. So 1 mole
of glucose
equals 6 C-moles of glucose. The concept is of importance to keep track of mass balance
s in work with organisms, where the frequency of other chemical elements is expressed relative to that of carbon.So the chemical formula for glucose then simplifies to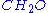 .
.
The concept becomes useful for the more complex situation of generalized compounds, where the exact chemical composition is not known.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
or generalised compound
Generalised compound
A generalized compound is a mixture of chemical compounds of constant composition, despite possible changes in the total amount. The concept is used in the Dynamic Energy Budget theory, where biomass is partitioned into a limited set of generalised compounds, which contain a high percentage of...
is the number of carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atoms expressed as multiple of the number of Avogadro. So 1 mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
of glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
equals 6 C-moles of glucose. The concept is of importance to keep track of mass balance
Mass balance
A mass balance is an application of conservation of mass to the analysis of physical systems. By accounting for material entering and leaving a system, mass flows can be identified which might have been unknown, or difficult to measure without this technique...
s in work with organisms, where the frequency of other chemical elements is expressed relative to that of carbon.So the chemical formula for glucose then simplifies to
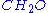 .
.The concept becomes useful for the more complex situation of generalized compounds, where the exact chemical composition is not known.

