
Bid-ask matrix
Encyclopedia
The bid–ask matrix is a matrix
with elements corresponding with exchange rates between the assets. These rates are in physical units (e.g. number of stocks) and not with respect to any numeraire
. The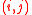 element of the matrix is the number of units of asset
element of the matrix is the number of units of asset 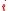 which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset
which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset 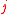 .
.
 matrix
matrix  is a bid-ask matrix, if
is a bid-ask matrix, if
 units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and
units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and 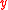 units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the bid–ask matrix
units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the bid–ask matrix  is:
is:
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
with elements corresponding with exchange rates between the assets. These rates are in physical units (e.g. number of stocks) and not with respect to any numeraire
Numéraire
Numéraire is a basic standard by which values are measured. Acting as the numéraire is one of the functions of money, to serve as a unit of account: to measure the worth of different goods and services relative to one another, i.e. in same units...
. The
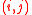 element of the matrix is the number of units of asset
element of the matrix is the number of units of asset  which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset
which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset 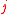 .
.Mathematical Definition
A matrix
matrix  is a bid-ask matrix, if
is a bid-ask matrix, if
-
 for
for 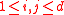 . Any trade has a positive exchange rate.
. Any trade has a positive exchange rate. -
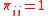 for
for 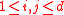 . Can always trade 1 unit with itself.
. Can always trade 1 unit with itself. -
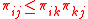 for
for 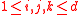 . A direct exchange is always at most as expensive as a chain of exchanges.
. A direct exchange is always at most as expensive as a chain of exchanges.
Example
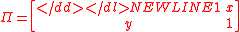
Assume a market with 2 assets (A and B), such that units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and
units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and 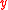 units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the bid–ask matrix
units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the bid–ask matrix  is:
is:-
Relation to solvency cone
If given a bid–ask matrix for
for 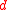 assets such that
assets such that  and
and 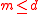 is the number of assets which with any non-negative quantity of them can be "discarded" (traditionally
is the number of assets which with any non-negative quantity of them can be "discarded" (traditionally  ). Then the solvency coneSolvency coneThe solvency cone is a concept used in financial mathematics which models the possible trades in the financial market. This is of particular interest to markets with transaction costs...
). Then the solvency coneSolvency coneThe solvency cone is a concept used in financial mathematics which models the possible trades in the financial market. This is of particular interest to markets with transaction costs...
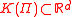 is the convex cone spanned by the unit vectors
is the convex cone spanned by the unit vectors 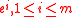 and the vectors
and the vectors 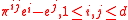 .
.
Similarly given a (constant) solvency cone it is possible to extract the bid–ask matrix from the bounding vectors.

