
Bayesian spam filtering
Encyclopedia
Bayesian spam filtering is a statistical
technique
of e-mail filtering
. It makes use of a naive Bayes classifier
to identify spam
e-mail.
Bayesian classifiers work by correlating the use of tokens (typically words, or sometimes other things), with spam and non spam e-mails and then using Bayesian inference
to calculate a probability that an email is or is not spam.
Bayesian spam filters are a very powerful technique for dealing with spam, that can tailor itself to the email needs of individual users, and gives low false positive spam detection rates that are generally acceptable to users.
to use a Bayes classifier was Jason Rennie's iFile program, released in 1996. The program was used to sort mail into folders
. The first scholarly publication on Bayesian spam filtering was by Sahami et al. in 1998. That work was soon thereafter deployed in commercial spam filters. However, in 2002 Paul Graham was able to greatly improve the false positive rate, so that it could be used on its own as a single spam filter.
Variants of the basic technique have been implemented in a number of research works and commercial software
products. Many modern mail clients
implement Bayesian spam filtering. Users can also install separate email filtering programs
. Server-side
email filters, such as DSPAM
, SpamAssassin
, SpamBayes
, Bogofilter
and ASSP
, make use of Bayesian spam filtering techniques, and the functionality is sometimes embedded within mail server software itself.
of occurring in spam email and in legitimate email. For instance, most email users will frequently encounter the word "Viagra" in spam email, but will seldom see it in other email. The filter doesn't know these probabilities in advance, and must first be trained so it can build them up. To train the filter, the user must manually indicate whether a new email is spam or not. For all words in each training email, the filter will adjust the probabilities that each word will appear in spam or legitimate email in its database. For instance, Bayesian spam filters will typically have learned a very high spam probability for the words "Viagra" and "refinance", but a very low spam probability for words seen only in legitimate email, such as the names of friends and family members.
After training, the word probabilities (also known as likelihood function
s) are used to compute the probability that an email with a particular set of words in it belongs to either category. Each word in the email contributes to the email's spam probability, or only the most interesting words. This contribution is called the posterior probability
and is computed using Bayes' theorem
. Then, the email's spam probability is computed over all words in the email, and if the total exceeds a certain threshold (say 95%), the filter will mark the email as a spam.
As in any other spam filtering technique, email marked as spam can then be automatically moved to a "Junk" email folder, or even deleted outright. Some software implement quarantine
mechanisms that define a time frame during which the user is allowed to review the software's decision.
The initial training can usually be refined when wrong judgements from the software are identified (false positives or false negatives). That allows the software to dynamically adapt to the ever evolving nature of spam.
Some spam filters combine the results of both Bayesian spam filtering and other heuristics
(pre-defined rules about the contents, looking at the message's envelope, etc.), resulting in even higher filtering accuracy, sometimes at the cost of adaptiveness.
. Bayes' theorem is used several times in the context of spam:
". Most people who are used to receiving e-mail know that this message is likely to be spam, more precisely a proposal to sell counterfeit copies of well-known brands of watches. The spam detection software, however, does not "know" such facts, all it can do is compute probabilities.
The formula used by the software to determine that is derived from Bayes' theorem
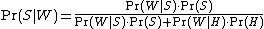
where:
(Demonstration : see Bayes' theorem#Alternative form)
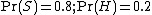
However, most bayesian spam detection software makes the assumption that there is no a priori reason for any incoming message to be spam rather than ham, and considers both cases to have equal probabilities of 50%:
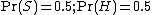
The filters that use this hypothesis are said to be "not biased", meaning that they have no prejudice regarding the incoming email. This assumption permits simplifying the general formula to:
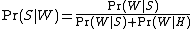
This quantity is called "spamicity" (or "spaminess") of the word "replica", and can be computed. The number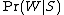 used in this formula is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as spam during the learning phase. Similarly,
used in this formula is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as spam during the learning phase. Similarly, 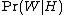 is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as ham during the learning phase. For these approximations to make sense, the set of learned messages needs to be big and representative enough. It is also advisable that the learned set of messages conforms to the 50% hypothesis about repartition between spam and ham, i.e. that the datasets of spam and ham are of same size.
is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as ham during the learning phase. For these approximations to make sense, the set of learned messages needs to be big and representative enough. It is also advisable that the learned set of messages conforms to the 50% hypothesis about repartition between spam and ham, i.e. that the datasets of spam and ham are of same size.
Of course, determining whether a message is spam or ham based only on the presence of the word "replica" is error-prone, which is why bayesian spam software tries to consider several words and combine their spamicities to determine a message's overall probability of being spam.
. That is wrong in natural languages like English, where the probability of finding an adjective, for example, is affected by the probability of having a noun. With that assumption, one can derive another formula from Bayes' theorem:
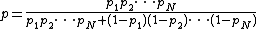
where:
(Demonstration:)
Such assumptions make the spam filtering software a naive Bayes classifier
.
The result p is usually compared to a given threshold to decide whether the message is spam or not. If p is lower than the threshold, the message is considered as likely ham, otherwise it is considered as likely spam.
. Instead, p can be computed in the log domain by rewriting the original equation as follows:
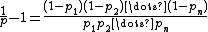
Taking logs on both sides:
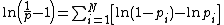
Let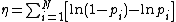 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
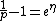
Hence the alternate formula for computing the combined probability:
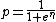
More generally, the words that were encountered only a few times during the learning phase cause a problem, because it would be an error to trust blindly the information they provide. A simple solution is to simply avoid taking such unreliable words into account as well.
Applying again Bayes' theorem, and assuming the classification between spam and ham of the emails containing a given word ("replica") is a random variable
with beta distribution, some other software decide to use a corrected probability:
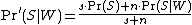
where:
(Demonstration:)
This corrected probability is used instead of the spamicity in the combining formula.
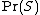 can again be taken equal to 0.5, to avoid being too suspicious about incoming email. 3 is a good value for s, meaning that the learned corpus must contain more than 3 messages with that word to put more confidence in the spamicity value than in the default value.
can again be taken equal to 0.5, to avoid being too suspicious about incoming email. 3 is a good value for s, meaning that the learned corpus must contain more than 3 messages with that word to put more confidence in the spamicity value than in the default value.
This formula can be extended to the case where n is equal to zero (and where the spamicity is not defined), and evaluates in this case to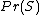 .
.
|0.5 − pI|.
Some software products take into account the fact that a given word appears several times in the examined message, others don't.
Some software products use patterns (sequences of words) instead of isolated natural languages words. For example, with a "context window" of four words, they compute the spamicity of "Viagra is good for", instead of computing the spamicities of "Viagra", "is", "good", and "for". This method gives more sensitivity to context and eliminates the Bayesian noise better, at the expense of a bigger database.
For example, assuming the individual probabilities follow a chi-squared distribution with 2N degrees of freedom, one could use the formula:
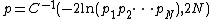
where C−1 is the inverse of the chi-squared function.
Individual probabilities can be combined with the techniques of the Markovian discrimination
too.
The spam that a user receives is often related to the online user's activities. For example, a user may have been subscribed to an online newsletter that the user considers to be spam. This online newsletter is likely to contain words that are common to all newsletters, such as the name of the newsletter and its originating email address. A Bayesian spam filter will eventually assign a higher probability based on the user's specific patterns.
The legitimate e-mails a user receives will tend to be different. For example, in a corporate environment, the company name and the names of clients or customers will be mentioned often. The filter will assign a lower spam probability to emails containing those names.
The word probabilities are unique to each user and can evolve over time with corrective training whenever the filter incorrectly classifies an email. As a result, Bayesian spam filtering accuracy after training is often superior to pre-defined rules.
It can perform particularly well in avoiding false positives, where legitimate email is incorrectly classified as spam. For example, if the email contains the word "Nigeria", which is frequently used in Advance fee fraud
spam, a pre-defined rules filter might reject it outright. A Bayesian filter would mark the word "Nigeria" as a probable spam word, but would take into account other important words that usually indicate legitimate e-mail. For example, the name of a spouse may strongly indicate the e-mail is not spam, which could overcome the use of the word "Nigeria."
, a technique used by spammers in an attempt to degrade the effectiveness of spam filters that rely on Bayesian filtering. A spammer practicing Bayesian poisoning will send out emails with large amounts of legitimate text (gathered from legitimate news or literary sources). Spammer
tactics include insertion of random innocuous words that are not normally associated with spam, thereby decreasing the email's spam score, making it more likely to slip past a Bayesian spam filter. However with (for example) Paul Graham's scheme only the most significant probabilities are used, so that padding the text out with non spam-related words does not affect the detection probability significantly.
Another technique used to try to defeat Bayesian spam filters is to replace text with pictures, either directly included or linked. The whole text of the message, or some part of it, is replaced with a picture where the same text is "drawn". The spam filter is usually unable to analyze this picture, which would contain the sensitive words like "Viagra". However, since many mail clients disable the display of linked pictures for security reasons, the spammer sending links to distant pictures might reach fewer targets. Also, a picture's size in bytes is bigger than the equivalent text's size, so the spammer needs more bandwidth to send messages directly including pictures. Finally, some filters are more inclined to decide that a message is spam if it has mostly graphical contents.
A probably more efficient solution has been proposed by Google and is used by its Gmail
email system, performing an OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
to every mid to large size image, analyzing the text inside.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
technique
Scientific technique
A scientific technique is any systematic way of obtaining information about a scientific nature or to obtain a desired material or product.Scientific techniques can be divided in many different groups, e.g.:# Preparative techniques...
of e-mail filtering
E-mail filtering
Email filtering is the processing of email to organize it according to specified criteria. Most often this refers to the automatic processing of incoming messages, but the term also applies to the intervention of human intelligence in addition to anti-spam techniques, and to outgoing emails as well...
. It makes use of a naive Bayes classifier
Naive Bayes classifier
A naive Bayes classifier is a simple probabilistic classifier based on applying Bayes' theorem with strong independence assumptions...
to identify spam
Spam (electronic)
Spam is the use of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk messages indiscriminately...
e-mail.
Bayesian classifiers work by correlating the use of tokens (typically words, or sometimes other things), with spam and non spam e-mails and then using Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
to calculate a probability that an email is or is not spam.
Bayesian spam filters are a very powerful technique for dealing with spam, that can tailor itself to the email needs of individual users, and gives low false positive spam detection rates that are generally acceptable to users.
History
The first known mail-filtering programComputer program
A computer program is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task with a computer. A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor. The program has an executable form that the computer can use directly to execute...
to use a Bayes classifier was Jason Rennie's iFile program, released in 1996. The program was used to sort mail into folders
Directory (file systems)
In computing, a folder, directory, catalog, or drawer, is a virtual container originally derived from an earlier Object-oriented programming concept by the same name within a digital file system, in which groups of computer files and other folders can be kept and organized.A typical file system may...
. The first scholarly publication on Bayesian spam filtering was by Sahami et al. in 1998. That work was soon thereafter deployed in commercial spam filters. However, in 2002 Paul Graham was able to greatly improve the false positive rate, so that it could be used on its own as a single spam filter.
Variants of the basic technique have been implemented in a number of research works and commercial software
Computer software
Computer software, or just software, is a collection of computer programs and related data that provide the instructions for telling a computer what to do and how to do it....
products. Many modern mail clients
Client (computing)
A client is an application or system that accesses a service made available by a server. The server is often on another computer system, in which case the client accesses the service by way of a network....
implement Bayesian spam filtering. Users can also install separate email filtering programs
E-mail filtering
Email filtering is the processing of email to organize it according to specified criteria. Most often this refers to the automatic processing of incoming messages, but the term also applies to the intervention of human intelligence in addition to anti-spam techniques, and to outgoing emails as well...
. Server-side
Server-side
Server-side refers to operations that are performed by the server in a client–server relationship in computer networking.Typically, a server is a software program, such as a web server, that runs on a remote server, reachable from a user's local computer or workstation...
email filters, such as DSPAM
DSPAM
DSPAM is a free software statistical spam filter written by Jonathan A. Zdziarski, author of the book Ending Spam and other books. It is intended to be a scalable, content-based spam filter for large multi-user systems...
, SpamAssassin
SpamAssassin
SpamAssassin is a computer program released under the Apache License 2.0 used for e-mail spam filtering based on content-matching rules. It is now part of the Apache Foundation....
, SpamBayes
SpamBayes
SpamBayes is a Bayesian spam filter written in Python which uses techniques laid out by Paul Graham in his essay "A Plan for Spam". It has subsequently been improved by Gary Robinson and Tim Peters, among others....
, Bogofilter
Bogofilter
Bogofilter is a mail filter that classifies e-mail as spam or ham by a statistical analysis of the message's header and content . The program is able to learn from the user's classifications and corrections. It was originally written by Eric S...
and ASSP
Anti-Spam SMTP Proxy
The Anti-Spam SMTP Proxy server project is an Open Source, Perl based, platform-independent transparent SMTP proxy server available at SourceForge.net that leverages numerous methodologies and technologies to both rigidly and adaptively identify e-mail spam...
, make use of Bayesian spam filtering techniques, and the functionality is sometimes embedded within mail server software itself.
Process
Particular words have particular probabilitiesProbability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
of occurring in spam email and in legitimate email. For instance, most email users will frequently encounter the word "Viagra" in spam email, but will seldom see it in other email. The filter doesn't know these probabilities in advance, and must first be trained so it can build them up. To train the filter, the user must manually indicate whether a new email is spam or not. For all words in each training email, the filter will adjust the probabilities that each word will appear in spam or legitimate email in its database. For instance, Bayesian spam filters will typically have learned a very high spam probability for the words "Viagra" and "refinance", but a very low spam probability for words seen only in legitimate email, such as the names of friends and family members.
After training, the word probabilities (also known as likelihood function
Likelihood function
In statistics, a likelihood function is a function of the parameters of a statistical model, defined as follows: the likelihood of a set of parameter values given some observed outcomes is equal to the probability of those observed outcomes given those parameter values...
s) are used to compute the probability that an email with a particular set of words in it belongs to either category. Each word in the email contributes to the email's spam probability, or only the most interesting words. This contribution is called the posterior probability
Posterior probability
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the conditional probability that is assigned after the relevant evidence is taken into account...
and is computed using Bayes' theorem
Bayes' theorem
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' theorem relates the conditional probabilities P and P. It is commonly used in science and engineering. The theorem is named for Thomas Bayes ....
. Then, the email's spam probability is computed over all words in the email, and if the total exceeds a certain threshold (say 95%), the filter will mark the email as a spam.
As in any other spam filtering technique, email marked as spam can then be automatically moved to a "Junk" email folder, or even deleted outright. Some software implement quarantine
Quarantine
Quarantine is compulsory isolation, typically to contain the spread of something considered dangerous, often but not always disease. The word comes from the Italian quarantena, meaning forty-day period....
mechanisms that define a time frame during which the user is allowed to review the software's decision.
The initial training can usually be refined when wrong judgements from the software are identified (false positives or false negatives). That allows the software to dynamically adapt to the ever evolving nature of spam.
Some spam filters combine the results of both Bayesian spam filtering and other heuristics
Metaheuristic
In computer science, metaheuristic designates a computational method that optimizes a problem by iteratively trying to improve a candidate solution with regard to a given measure of quality. Metaheuristics make few or no assumptions about the problem being optimized and can search very large spaces...
(pre-defined rules about the contents, looking at the message's envelope, etc.), resulting in even higher filtering accuracy, sometimes at the cost of adaptiveness.
Mathematical foundation
Bayesian email filters take advantage of Bayes' theoremBayes' theorem
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' theorem relates the conditional probabilities P and P. It is commonly used in science and engineering. The theorem is named for Thomas Bayes ....
. Bayes' theorem is used several times in the context of spam:
- a first time, to compute the probability that the message is spam, knowing that a given word appears in this message;
- a second time, to compute the probability that the message is spam, taking into consideration all of its words (or a relevant subset of them);
- sometimes a third time, to deal with rare words.
Computing the probability that a message containing a given word is spam
Let's suppose the suspected message contains the word "replicaReplica
A replica is a copy closely resembling the original concerning its shape and appearance. An inverted replica complements the original by filling its gaps. It can be a copy used for historical purposes, such as being placed in a museum. Sometimes the original never existed. For example, Difference...
". Most people who are used to receiving e-mail know that this message is likely to be spam, more precisely a proposal to sell counterfeit copies of well-known brands of watches. The spam detection software, however, does not "know" such facts, all it can do is compute probabilities.
The formula used by the software to determine that is derived from Bayes' theorem
Bayes' theorem
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' theorem relates the conditional probabilities P and P. It is commonly used in science and engineering. The theorem is named for Thomas Bayes ....
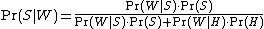
where:
-
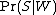 is the probability that a message is a spam, knowing that the word "replica" is in it;
is the probability that a message is a spam, knowing that the word "replica" is in it; -
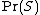 is the overall probability that any given message is spam;
is the overall probability that any given message is spam; -
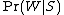 is the probability that the word "replica" appears in spam messages;
is the probability that the word "replica" appears in spam messages; -
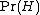 is the overall probability that any given message is not spam (is "ham");
is the overall probability that any given message is not spam (is "ham"); -
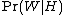 is the probability that the word "replica" appears in ham messages.
is the probability that the word "replica" appears in ham messages.
(Demonstration : see Bayes' theorem#Alternative form)
The spamicity of a word
Recent statistics show that the current probability of any message being spam is 80%, at the very least: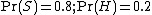
However, most bayesian spam detection software makes the assumption that there is no a priori reason for any incoming message to be spam rather than ham, and considers both cases to have equal probabilities of 50%:
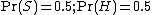
The filters that use this hypothesis are said to be "not biased", meaning that they have no prejudice regarding the incoming email. This assumption permits simplifying the general formula to:
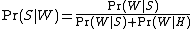
This quantity is called "spamicity" (or "spaminess") of the word "replica", and can be computed. The number
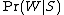 used in this formula is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as spam during the learning phase. Similarly,
used in this formula is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as spam during the learning phase. Similarly, 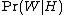 is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as ham during the learning phase. For these approximations to make sense, the set of learned messages needs to be big and representative enough. It is also advisable that the learned set of messages conforms to the 50% hypothesis about repartition between spam and ham, i.e. that the datasets of spam and ham are of same size.
is approximated to the frequency of messages containing "replica" in the messages identified as ham during the learning phase. For these approximations to make sense, the set of learned messages needs to be big and representative enough. It is also advisable that the learned set of messages conforms to the 50% hypothesis about repartition between spam and ham, i.e. that the datasets of spam and ham are of same size.Of course, determining whether a message is spam or ham based only on the presence of the word "replica" is error-prone, which is why bayesian spam software tries to consider several words and combine their spamicities to determine a message's overall probability of being spam.
Combining individual probabilities
The bayesian spam filtering software makes the "naïve" assumption that the words present in the message are independent eventsStatistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
. That is wrong in natural languages like English, where the probability of finding an adjective, for example, is affected by the probability of having a noun. With that assumption, one can derive another formula from Bayes' theorem:
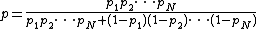
where:
-
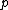 is the probability that the suspect message is spam;
is the probability that the suspect message is spam; -
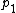 is the probability
is the probability 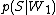 that it is a spam knowing it contains a first word (for example "replica");
that it is a spam knowing it contains a first word (for example "replica"); -
 is the probability
is the probability 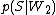 that it is a spam knowing it contains a second word (for example "watches");
that it is a spam knowing it contains a second word (for example "watches"); - etc...
-
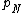 is the probability
is the probability 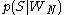 that it is a spam knowing it contains an Nth word (for example "home").
that it is a spam knowing it contains an Nth word (for example "home").
(Demonstration:)
Such assumptions make the spam filtering software a naive Bayes classifier
Naive Bayes classifier
A naive Bayes classifier is a simple probabilistic classifier based on applying Bayes' theorem with strong independence assumptions...
.
The result p is usually compared to a given threshold to decide whether the message is spam or not. If p is lower than the threshold, the message is considered as likely ham, otherwise it is considered as likely spam.
Other expression of the formula for combining individual probabilities
Usually p is not directly computed using the above formula due to floating-point underflowArithmetic underflow
The term arithmetic underflow is a condition in a computer program that can occur when the true result of afloating point operation is smaller in magnitude...
. Instead, p can be computed in the log domain by rewriting the original equation as follows:
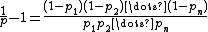
Taking logs on both sides:
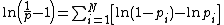
Let
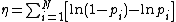 . Therefore,
. Therefore,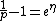
Hence the alternate formula for computing the combined probability:
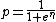
Dealing with rare words
In the case a word has never been met during the learning phase, both the numerator and the denominator are equal to zero, both in the general formula and in the spamicity formula. The software can decide to discard such words for which there is no information available.More generally, the words that were encountered only a few times during the learning phase cause a problem, because it would be an error to trust blindly the information they provide. A simple solution is to simply avoid taking such unreliable words into account as well.
Applying again Bayes' theorem, and assuming the classification between spam and ham of the emails containing a given word ("replica") is a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
with beta distribution, some other software decide to use a corrected probability:
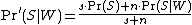
where:
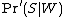 is the corrected probability for the message to be spam, knowing that it contains a given word ;
is the corrected probability for the message to be spam, knowing that it contains a given word ;-
 is the strength we give to background information about incoming spam ;
is the strength we give to background information about incoming spam ; -
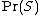 is the probability of any incoming message to be spam ;
is the probability of any incoming message to be spam ; -
 is the number of occurrences of this word during the learning phase ;
is the number of occurrences of this word during the learning phase ; -
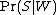 is the spamicity of this word.
is the spamicity of this word.
(Demonstration:)
This corrected probability is used instead of the spamicity in the combining formula.
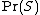 can again be taken equal to 0.5, to avoid being too suspicious about incoming email. 3 is a good value for s, meaning that the learned corpus must contain more than 3 messages with that word to put more confidence in the spamicity value than in the default value.
can again be taken equal to 0.5, to avoid being too suspicious about incoming email. 3 is a good value for s, meaning that the learned corpus must contain more than 3 messages with that word to put more confidence in the spamicity value than in the default value.This formula can be extended to the case where n is equal to zero (and where the spamicity is not defined), and evaluates in this case to
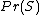 .
.Other heuristics
"Neutral" words like "the", "a", "some", or "is" (in English), or their equivalents in other languages, can be ignored. More generally, some bayesian filtering filters simply ignore all the words which have a spamicity next to 0.5, as they bring little to a good decision. The words taken into consideration are those whose spamicity is next to 0.0 (distinctive signs of legitimate messages), or next to 1.0 (distinctive signs of spam). A method can be for example to keep only those ten words, in the examined message, which have the greatest absolute valueAbsolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value |a| of a real number a is the numerical value of a without regard to its sign. So, for example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3...
|0.5 − pI|.
Some software products take into account the fact that a given word appears several times in the examined message, others don't.
Some software products use patterns (sequences of words) instead of isolated natural languages words. For example, with a "context window" of four words, they compute the spamicity of "Viagra is good for", instead of computing the spamicities of "Viagra", "is", "good", and "for". This method gives more sensitivity to context and eliminates the Bayesian noise better, at the expense of a bigger database.
Mixed methods
There are other ways of combining individual probabilities for different words than using the "naive" approach. These methods differ from it on the assumptions they make on the statistical properties of the input data. These different hypotheses result in radically different formulas for combining the individual probabilities.For example, assuming the individual probabilities follow a chi-squared distribution with 2N degrees of freedom, one could use the formula:
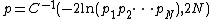
where C−1 is the inverse of the chi-squared function.
Individual probabilities can be combined with the techniques of the Markovian discrimination
Markovian discrimination
Markovian discrimination in spam filtering is a method used in CRM114 and other spam filters to model the statistical behaviors of spam and nonspam more accurately than in simple Bayesian methods. A simple Bayesian model of written text contains only the dictionary of legal words and their...
too.
Advantages
The advantage of Bayesian spam filtering is that it can be trained on a per-user basis.The spam that a user receives is often related to the online user's activities. For example, a user may have been subscribed to an online newsletter that the user considers to be spam. This online newsletter is likely to contain words that are common to all newsletters, such as the name of the newsletter and its originating email address. A Bayesian spam filter will eventually assign a higher probability based on the user's specific patterns.
The legitimate e-mails a user receives will tend to be different. For example, in a corporate environment, the company name and the names of clients or customers will be mentioned often. The filter will assign a lower spam probability to emails containing those names.
The word probabilities are unique to each user and can evolve over time with corrective training whenever the filter incorrectly classifies an email. As a result, Bayesian spam filtering accuracy after training is often superior to pre-defined rules.
It can perform particularly well in avoiding false positives, where legitimate email is incorrectly classified as spam. For example, if the email contains the word "Nigeria", which is frequently used in Advance fee fraud
Advance fee fraud
An advance-fee fraud is a confidence trick in which the target is persuaded to advance sums of money in the hope of realizing a significantly larger gain...
spam, a pre-defined rules filter might reject it outright. A Bayesian filter would mark the word "Nigeria" as a probable spam word, but would take into account other important words that usually indicate legitimate e-mail. For example, the name of a spouse may strongly indicate the e-mail is not spam, which could overcome the use of the word "Nigeria."
Disadvantages
Depending on the implementation, Bayesian spam filtering may be susceptible to Bayesian poisoningBayesian poisoning
Bayesian poisoning is a technique used by e-mail spammers to attempt to degrade the effectiveness of spam filters that rely on Bayesian spam filtering. Bayesian filtering relies on Bayesian probability to determine whether an incoming mail is spam or is not spam...
, a technique used by spammers in an attempt to degrade the effectiveness of spam filters that rely on Bayesian filtering. A spammer practicing Bayesian poisoning will send out emails with large amounts of legitimate text (gathered from legitimate news or literary sources). Spammer
E-mail spam
Email spam, also known as junk email or unsolicited bulk email , is a subset of spam that involves nearly identical messages sent to numerous recipients by email. Definitions of spam usually include the aspects that email is unsolicited and sent in bulk. One subset of UBE is UCE...
tactics include insertion of random innocuous words that are not normally associated with spam, thereby decreasing the email's spam score, making it more likely to slip past a Bayesian spam filter. However with (for example) Paul Graham's scheme only the most significant probabilities are used, so that padding the text out with non spam-related words does not affect the detection probability significantly.
Another technique used to try to defeat Bayesian spam filters is to replace text with pictures, either directly included or linked. The whole text of the message, or some part of it, is replaced with a picture where the same text is "drawn". The spam filter is usually unable to analyze this picture, which would contain the sensitive words like "Viagra". However, since many mail clients disable the display of linked pictures for security reasons, the spammer sending links to distant pictures might reach fewer targets. Also, a picture's size in bytes is bigger than the equivalent text's size, so the spammer needs more bandwidth to send messages directly including pictures. Finally, some filters are more inclined to decide that a message is spam if it has mostly graphical contents.
A probably more efficient solution has been proposed by Google and is used by its Gmail
Gmail
Gmail is a free, advertising-supported email service provided by Google. Users may access Gmail as secure webmail, as well via POP3 or IMAP protocols. Gmail was launched as an invitation-only beta release on April 1, 2004 and it became available to the general public on February 7, 2007, though...
email system, performing an OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
Optical character recognition
Optical character recognition, usually abbreviated to OCR, is the mechanical or electronic translation of scanned images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine-encoded text. It is widely used to convert books and documents into electronic files, to computerize a record-keeping...
to every mid to large size image, analyzing the text inside.
General applications of Bayesian filtering
While Bayesian filtering is used widely to identify spam email, the technique can classify (or "cluster") almost any sort of data. It has uses in science, medicine, and engineering. One example is a general purpose classification program called AutoClass which was originally used to classify stars according to spectral characteristics that were otherwise too subtle to notice. There is recent speculation that even the brain uses Bayesian methods to classify sensory stimuli and decide on behavioral responses.See also
- Bayesian poisoningBayesian poisoningBayesian poisoning is a technique used by e-mail spammers to attempt to degrade the effectiveness of spam filters that rely on Bayesian spam filtering. Bayesian filtering relies on Bayesian probability to determine whether an incoming mail is spam or is not spam...
- Bayesian inferenceBayesian inferenceIn statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
- Bayes's theorem
- Email filtering
- Markovian discriminationMarkovian discriminationMarkovian discrimination in spam filtering is a method used in CRM114 and other spam filters to model the statistical behaviors of spam and nonspam more accurately than in simple Bayesian methods. A simple Bayesian model of written text contains only the dictionary of legal words and their...
- Naive Bayes classifierNaive Bayes classifierA naive Bayes classifier is a simple probabilistic classifier based on applying Bayes' theorem with strong independence assumptions...
- Recursive Bayesian estimationRecursive Bayesian estimationRecursive Bayesian estimation, also known as a Bayes filter, is a general probabilistic approach for estimating an unknown probability density function recursively over time using incoming measurements and a mathematical process model.-In robotics:...
- Stopping e-mail abuseStopping e-mail abuseTo prevent e-mail spam , both end users and administrators of e-mail systems use various anti-spam techniques. Some of these techniques have been embedded in products, services and software to ease the burden on users and administrators...
External links
- Guide to Bayesian spam filters: part 1, part 2.
- Detailed explanation of Paul Graham's formulas by Tim Peters
- Gary Robinson's spam blog

