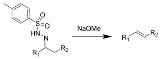
Bamford-Stevens reaction
Overview
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
whereby treatment of tosylhydrazone
Tosylhydrazone
A tosylhydrazone in organic chemistry is a functional group with the general structure RR'C=NH-Ts where Ts is a tosyl group. Organic compounds having this functional group can be accessed by reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with tosylhydrazine.-Synthesis:...
s with strong base gives alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
s. It is named for the British chemist William Randall Bamford and the Scottish chemist Thomas Stevens Stevens (1900–2000). The usage of aprotic solvents gives predominantly Z-alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
s, while protic solvent
Protic solvent
In chemistry a protic solvent is a solvent that has a hydrogen atom bound to an oxygen or a nitrogen . In general terms, any molecular solvent that contains dissociable H+ is called a protic solvent. The molecules of such solvents can donate an H+...
gives a mixture of E- and Z-alkenes.

