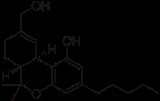
11-Hydroxy-THC
Encyclopedia
11-Hydroxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, abbreviated as 11-OH-THC, is the main active metabolite
of THC
which is formed in the body after cannabis
consumption. 11-Hydroxy-THC has been shown to be active in its own right, but the effects produced are not necessarily identical to those of THC. This might partially explain the biphasic effects of cannabis, whereby some effects such as increased appetite tend to be delayed rather than occurring immediately when the drug is consumed.
11-Hydroxy-THC is subsequently metabolised further to 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC
, which is not psychoactive but might still play a role in the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of cannabis.
Metabolite
Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial...
of THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol , also known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol , Δ1-THC , or dronabinol, is the main chemical psychoactive substance found in the cannabis plant. It was first isolated in 1964. In pure form, it is a glassy solid when cold, and becomes viscous and sticky if warmed...
which is formed in the body after cannabis
Cannabis
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants that includes three putative species, Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis. These three taxa are indigenous to Central Asia, and South Asia. Cannabis has long been used for fibre , for seed and seed oils, for medicinal purposes, and as a...
consumption. 11-Hydroxy-THC has been shown to be active in its own right, but the effects produced are not necessarily identical to those of THC. This might partially explain the biphasic effects of cannabis, whereby some effects such as increased appetite tend to be delayed rather than occurring immediately when the drug is consumed.
11-Hydroxy-THC is subsequently metabolised further to 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC
11-nor-9-Carboxy-THC
11-nor-9-Carboxy-THC, also known as 11-nor-9-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, 11-COOH-THC, THC-COOH, and THC-11-oic acid, is the main secondary metabolite of THC which is formed in the body after Cannabis is consumed....
, which is not psychoactive but might still play a role in the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of cannabis.

