
(cytochrome c)-lysine N-methyltransferase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a [cytochrome c]-lysine N-methyltransferase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are S-adenosyl methionine
and cytochrome c
-L-lysine
, whereas its two products
are S-adenosylhomocysteine and cytochrome c
-N6-methyl-L-lysine.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
s, specifically those transferring one-carbon group methyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is S-adenosyl-L-methionine:[cytochrome c]-L-lysine N6-methyltransferase. Other names in common use include cytochrome c (lysine) methyltransferase, cytochrome c methyltransferase, cytochrome c-specific protein methylase III, cytochrome c-specific protein-lysine methyltransferase, S-adenosyl-L-methionine:[cytochrome c]-L-lysine, and 6-N-methyltransferase. This enzyme participates in lysine degradation.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine + [cytochrome c]-L-lysine
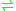 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + [cytochrome c]-N6-methyl-L-lysine
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + [cytochrome c]-N6-methyl-L-lysine
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are S-adenosyl methionine
S-Adenosyl methionine
S-Adenosyl methionine is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers. SAM was first discovered in Italy by G. L. Cantoni in 1952. It is made from adenosine triphosphate and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase . Transmethylation, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation are the...
and cytochrome c
Cytochrome c
The Cytochrome complex, or cyt c is a small heme protein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins. Cytochrome c is a highly soluble protein, unlike other cytochromes, with a solubility of about 100 g/L and is an...
-L-lysine
Lysine
Lysine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH4NH2. It is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body cannot synthesize it. Its codons are AAA and AAG....
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are S-adenosylhomocysteine and cytochrome c
Cytochrome c
The Cytochrome complex, or cyt c is a small heme protein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins. Cytochrome c is a highly soluble protein, unlike other cytochromes, with a solubility of about 100 g/L and is an...
-N6-methyl-L-lysine.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s, specifically those transferring one-carbon group methyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is S-adenosyl-L-methionine:[cytochrome c]-L-lysine N6-methyltransferase. Other names in common use include cytochrome c (lysine) methyltransferase, cytochrome c methyltransferase, cytochrome c-specific protein methylase III, cytochrome c-specific protein-lysine methyltransferase, S-adenosyl-L-methionine:[cytochrome c]-L-lysine, and 6-N-methyltransferase. This enzyme participates in lysine degradation.

