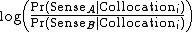Yarowsky algorithm
Encyclopedia
In computational linguistics
the Yarowsky algorithm is an unsupervised learning
algorithm
for word sense disambiguation
that uses the "one sense per collocation
" and the "one sense per discourse" properties of human languages
for word sense disambiguation. From observation, words tend to exhibit only one sense in most given discourse and in a given collocation.
, in which it identifies examples of the given polysemous
word, and stores all the relevant sentence
s as lines. For instance, Yarowsky uses the word "plant" in his 1995 paper to demonstrate the algorithm. If it is assumed that there are two possible senses of the word, the next step is to identify a small number of seed collocations representative of each sense, give each sense a label (i.e. sense A and B), then assign the appropriate label to all training examples containing the seed collocations. In this case, the words "life" and "manufacturing" are chosen as initial seed collocations for senses A and B respectively. The residual examples (85%–98% according to Yarowsky) remain untagged.
The algorithm should initially choose seed collocations representative that will distinguish sense A and B accurately and productively. This can be done by selecting seed words from a dictionary
’s entry for that sense. The collocations tend to have stronger effect if they are adjacent to the target word, the effect weakens with distance. According to the criteria given in Yarowsky (1993), seed words that appear in the most reliable collocational relationships with the target word will be selected. The effect is much stronger for words in a predicate-argument relationship than for arbitrary associations at the same distance to the target word, and is much stronger for collocations with content words than with function words. Having said this, a collocation word can have several collocational relationships with the target word throughout the corpus. This could give the word different rankings or even different classifications. Alternatively, it can be done by identifying a single defining collocate for each class, and using for seeds only those contexts containing one of these defining words. A publicly available database WordNet
can be used as an automatic source for such defining terms. In addition, words that occur near the target word in great frequency can be selected as seed collocations representative. This approach is not fully automatic, a human judge must decide which word will be selected for each target word’s sense, the outputs will be reliable indicators of the senses.
A decision list algorithm is then used to identify other reliable collocations. This training algorithm calculates the probability Pr(Sense | Collocation), and the decision list is ranked by the log-likelihood ratio:
A smoothing
algorithm will then be used to avoid 0 values. The decision-list algorithm resolves many problems in a large set of non-independent evidence source by using only the most reliable piece of evidence rather than the whole matching collocation set.
The new resulting classifier will then be applied to the whole sample set. Add those examples in the residual
that are tagged as A or B with probability above a reasonable threshold to the seed sets. The decision-list algorithm and the above adding step are applied iteratively
. As more newly-learned collocations are added to the seed sets, the sense A or sense B set will grow, and the original residual will shrink. However, these collocations stay in the seed sets only if their probability of classification remains above the threshold, otherwise they are returned to the residual for later classification. At the end of each iteration, the "one sense per discourse" property can be used to help preventing initially mistagged collocates and hence improving the purity of the seed sets.
In order to avoid strong collocates becoming indicators for the wrong class, the class-inclusion threshold needs to be randomly altered. For the same purpose, after intermediate convergence the algorithm will also need to increase the width of the context window.
The algorithm will continue to iterate until no more reliable collocations are found. The ‘One sense per discourse’ property can be used here for error correction. For a target word that has a binary sense partition, if the occurrences of the majority sense A exceed that of the minor sense B by a certain threshold, the minority ones will be relabeled as A. According to Yarowsky, for any sense to be clearly dominant, the occurrences of the target word should not be less than 4.
When the algorithm converges on a stable residual set, a final decision list of the target word is obtained. The most reliable collocations are at the top of the new list instead of the original seed words. The original untagged corpus is then tagged with sense labels and probabilities. The final decision list may now be applied to new data, the collocation with the highest rank in the list is used to classify the new data. For example, if the highest ranking collocation of the target word in the new data set is of sense A, then the target word is classified as sense A.
Computational linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective....
the Yarowsky algorithm is an unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning
In machine learning, unsupervised learning refers to the problem of trying to find hidden structure in unlabeled data. Since the examples given to the learner are unlabeled, there is no error or reward signal to evaluate a potential solution...
algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
for word sense disambiguation
Word sense disambiguation
In computational linguistics, word-sense disambiguation is an open problem of natural language processing, which governs the process of identifying which sense of a word is used in a sentence, when the word has multiple meanings...
that uses the "one sense per collocation
Collocation
In corpus linguistics, collocation defines a sequence of words or terms that co-occur more often than would be expected by chance. In phraseology, collocation is a sub-type of phraseme. An example of a phraseological collocation is the expression strong tea...
" and the "one sense per discourse" properties of human languages
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
for word sense disambiguation. From observation, words tend to exhibit only one sense in most given discourse and in a given collocation.
Application
The algorithm starts with a large, untagged corpusText corpus
In linguistics, a corpus or text corpus is a large and structured set of texts...
, in which it identifies examples of the given polysemous
Polysemy
Polysemy is the capacity for a sign or signs to have multiple meanings , i.e., a large semantic field.Charles Fillmore and Beryl Atkins’ definition stipulates three elements: the various senses of a polysemous word have a central origin, the links between these senses form a network, and ...
word, and stores all the relevant sentence
Sentence (linguistics)
In the field of linguistics, a sentence is an expression in natural language, and often defined to indicate a grammatical unit consisting of one or more words that generally bear minimal syntactic relation to the words that precede or follow it...
s as lines. For instance, Yarowsky uses the word "plant" in his 1995 paper to demonstrate the algorithm. If it is assumed that there are two possible senses of the word, the next step is to identify a small number of seed collocations representative of each sense, give each sense a label (i.e. sense A and B), then assign the appropriate label to all training examples containing the seed collocations. In this case, the words "life" and "manufacturing" are chosen as initial seed collocations for senses A and B respectively. The residual examples (85%–98% according to Yarowsky) remain untagged.
The algorithm should initially choose seed collocations representative that will distinguish sense A and B accurately and productively. This can be done by selecting seed words from a dictionary
Dictionary
A dictionary is a collection of words in one or more specific languages, often listed alphabetically, with usage information, definitions, etymologies, phonetics, pronunciations, and other information; or a book of words in one language with their equivalents in another, also known as a lexicon...
’s entry for that sense. The collocations tend to have stronger effect if they are adjacent to the target word, the effect weakens with distance. According to the criteria given in Yarowsky (1993), seed words that appear in the most reliable collocational relationships with the target word will be selected. The effect is much stronger for words in a predicate-argument relationship than for arbitrary associations at the same distance to the target word, and is much stronger for collocations with content words than with function words. Having said this, a collocation word can have several collocational relationships with the target word throughout the corpus. This could give the word different rankings or even different classifications. Alternatively, it can be done by identifying a single defining collocate for each class, and using for seeds only those contexts containing one of these defining words. A publicly available database WordNet
WordNet
WordNet is a lexical database for the English language. It groups English words into sets of synonyms called synsets, provides short, general definitions, and records the various semantic relations between these synonym sets...
can be used as an automatic source for such defining terms. In addition, words that occur near the target word in great frequency can be selected as seed collocations representative. This approach is not fully automatic, a human judge must decide which word will be selected for each target word’s sense, the outputs will be reliable indicators of the senses.
A decision list algorithm is then used to identify other reliable collocations. This training algorithm calculates the probability Pr(Sense | Collocation), and the decision list is ranked by the log-likelihood ratio:
A smoothing
Smoothing
In statistics and image processing, to smooth a data set is to create an approximating function that attempts to capture important patterns in the data, while leaving out noise or other fine-scale structures/rapid phenomena. Many different algorithms are used in smoothing...
algorithm will then be used to avoid 0 values. The decision-list algorithm resolves many problems in a large set of non-independent evidence source by using only the most reliable piece of evidence rather than the whole matching collocation set.
The new resulting classifier will then be applied to the whole sample set. Add those examples in the residual
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
that are tagged as A or B with probability above a reasonable threshold to the seed sets. The decision-list algorithm and the above adding step are applied iteratively
Iteration
Iteration means the act of repeating a process usually with the aim of approaching a desired goal or target or result. Each repetition of the process is also called an "iteration," and the results of one iteration are used as the starting point for the next iteration.-Mathematics:Iteration in...
. As more newly-learned collocations are added to the seed sets, the sense A or sense B set will grow, and the original residual will shrink. However, these collocations stay in the seed sets only if their probability of classification remains above the threshold, otherwise they are returned to the residual for later classification. At the end of each iteration, the "one sense per discourse" property can be used to help preventing initially mistagged collocates and hence improving the purity of the seed sets.
In order to avoid strong collocates becoming indicators for the wrong class, the class-inclusion threshold needs to be randomly altered. For the same purpose, after intermediate convergence the algorithm will also need to increase the width of the context window.
The algorithm will continue to iterate until no more reliable collocations are found. The ‘One sense per discourse’ property can be used here for error correction. For a target word that has a binary sense partition, if the occurrences of the majority sense A exceed that of the minor sense B by a certain threshold, the minority ones will be relabeled as A. According to Yarowsky, for any sense to be clearly dominant, the occurrences of the target word should not be less than 4.
When the algorithm converges on a stable residual set, a final decision list of the target word is obtained. The most reliable collocations are at the top of the new list instead of the original seed words. The original untagged corpus is then tagged with sense labels and probabilities. The final decision list may now be applied to new data, the collocation with the highest rank in the list is used to classify the new data. For example, if the highest ranking collocation of the target word in the new data set is of sense A, then the target word is classified as sense A.