
Xenotosaurus
Encyclopedia
Xenotosuchus is an extinct genus
of mastodonsauroid
temnospondyl within the family
Mastodonsauridae
. The genus is based on a skull originally described as Parotosuchu, an animal which it resembled in general build and habit.
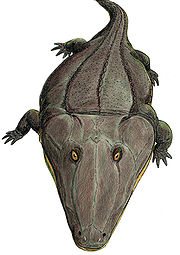 Like many mastodontosaurids, it was a large animal with a large head. It's amphibian
Like many mastodontosaurids, it was a large animal with a large head. It's amphibian
life history meant that the distinct shape of the skull roof
would change from a general tadpole
-like skull type through to the distinct adult shape. The head bones are covered in large pits and grooves, indicating extensive dermal armour on the head. Both the upper and lower jaw had tusk
s, those of the upper jaw being situated on a 2nd row of teeth on the vomer
and palatine bone
. Contrary to related forms like Mastodonsaurus
, the tusks of the lower jaw were of moderate size and did not penetrate the premaxilla
.
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of mastodonsauroid
Mastodonsauroidea
The Mastodonsauroidea are an extinct superfamily of temnospondyl amphibians known from the Triassic and Jurassic. Fossils belonging to this superfamily have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia...
temnospondyl within the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Mastodonsauridae
Mastodonsauridae
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The family Capitosauridae is synonymous with...
. The genus is based on a skull originally described as Parotosuchu, an animal which it resembled in general build and habit.
Xenotosuchus in life

Amphibian
Amphibians , are a class of vertebrate animals including animals such as toads, frogs, caecilians, and salamanders. They are characterized as non-amniote ectothermic tetrapods...
life history meant that the distinct shape of the skull roof
Skull roof
The skull roof , or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone, hence the alternative name dermatocranium...
would change from a general tadpole
Tadpole
A tadpole or polliwog is the wholly aquatic larval stage in the life cycle of an amphibian, particularly that of a frog or toad.- Appellation :...
-like skull type through to the distinct adult shape. The head bones are covered in large pits and grooves, indicating extensive dermal armour on the head. Both the upper and lower jaw had tusk
Tusk
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth, usually but not always in pairs, that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canines, as with warthogs, wild boar, and walruses, or, in the case of elephants and narwhals, elongated incisors...
s, those of the upper jaw being situated on a 2nd row of teeth on the vomer
Vomer
The vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones.-Biology:...
and palatine bone
Palatine bone
The palatine bone is a bone in many species of the animal kingdom, commonly termed the palatum .-Human anatomy:...
. Contrary to related forms like Mastodonsaurus
Mastodonsaurus
Mastodonsaurus was a large-headed temnospondyl that belonged to a group of advanced, mostly Triassic amphibians called capitosaurids. It was a giant among the stegocephalians and the largest animal of its time...
, the tusks of the lower jaw were of moderate size and did not penetrate the premaxilla
Premaxilla
The incisive bone is the portion of the maxilla adjacent to the incisors. It is a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the jaws of many animals, usually bearing teeth, but not always. They are connected to the maxilla and the nasals....
.
See also
- Prehistoric amphibian
- List of prehistoric amphibians

