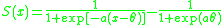Wilson-Cowan model
Encyclopedia
In computational neuroscience
, the Wilson-Cowan model describes the dynamics of interactions between populations of very simple excitatory and inhibitory model neurons. It was developed by Hugh R. Wilson
and Jack D. Cowan and extensions of the model have been widely used in modeling neuronal populations. The model is important historically because it uses phase plane methods and numerical solutions to describe the responses of neuronal populations to stimuli. Because the model neurons are simple, only elementary limit cycle behavior, i.e. neural oscillations
, and stimulus-dependent evoked responses are predicted. The key findings include the existence of multiple stable states, and hysteresis, in the population response.
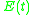 and
and 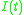 are respectively the proportions of excitatory and inhibitory cells firing at time t. They depend on the proportion of sensitive cells (that are not refractory) and on the proportion of these cells receiving at least threshold excitation.
are respectively the proportions of excitatory and inhibitory cells firing at time t. They depend on the proportion of sensitive cells (that are not refractory) and on the proportion of these cells receiving at least threshold excitation.
 )
)
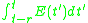
Proportion of sensitive cells (complement of refractory cells)
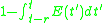
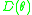 the distribution of neuronal thresholds
the distribution of neuronal thresholds
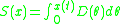
Subpopulation response function based on the distribution of afferent synapses per cell (all cells have the same threshold)
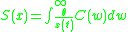
Average excitation level
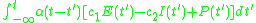
where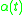 is the stimulus decay function,
is the stimulus decay function, 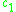 and
and 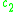 are respectively the connectivity coefficient giving the average number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses per cell, P(t) is the external input to the excitatory population.
are respectively the connectivity coefficient giving the average number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses per cell, P(t) is the external input to the excitatory population.
Excitatory subpopulation expression
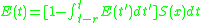
Complete Wilson-Cowan model
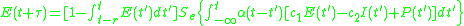
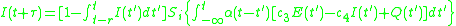
Time Coarse Graining
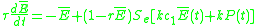
Isocline Equation
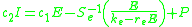
Sigmoid Function
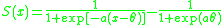
Computational neuroscience
Computational neuroscience is the study of brain function in terms of the information processing properties of the structures that make up the nervous system...
, the Wilson-Cowan model describes the dynamics of interactions between populations of very simple excitatory and inhibitory model neurons. It was developed by Hugh R. Wilson
Hugh R. Wilson
Hugh Robert Wilson was a member of the United States Foreign Service, who headed the U.S. mission to Switzerland for ten years beginning in 1927. He became Assistant Secretary of State in 1937 and served for several months in 1938 as U.S...
and Jack D. Cowan and extensions of the model have been widely used in modeling neuronal populations. The model is important historically because it uses phase plane methods and numerical solutions to describe the responses of neuronal populations to stimuli. Because the model neurons are simple, only elementary limit cycle behavior, i.e. neural oscillations
Neural oscillations
Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms localized within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons...
, and stimulus-dependent evoked responses are predicted. The key findings include the existence of multiple stable states, and hysteresis, in the population response.
Mathematical description
The Wilson-Cowan model considers a homogeneous population of interconnected neurons of excitatory and inhibitory subtypes. The fundamental quantity is the measure of the activity of an excitatory or inhibitory subtype within the population. More precisely,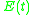 and
and 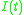 are respectively the proportions of excitatory and inhibitory cells firing at time t. They depend on the proportion of sensitive cells (that are not refractory) and on the proportion of these cells receiving at least threshold excitation.
are respectively the proportions of excitatory and inhibitory cells firing at time t. They depend on the proportion of sensitive cells (that are not refractory) and on the proportion of these cells receiving at least threshold excitation.Sensitive cells
Proportion of cells in refractory period (absolute refractory period )
)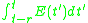
Proportion of sensitive cells (complement of refractory cells)
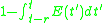
Excited cells
Subpopulation response function based on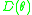 the distribution of neuronal thresholds
the distribution of neuronal thresholds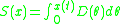
Subpopulation response function based on the distribution of afferent synapses per cell (all cells have the same threshold)
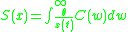
Average excitation level
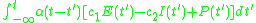
where
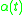 is the stimulus decay function,
is the stimulus decay function, 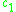 and
and 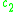 are respectively the connectivity coefficient giving the average number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses per cell, P(t) is the external input to the excitatory population.
are respectively the connectivity coefficient giving the average number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses per cell, P(t) is the external input to the excitatory population.Excitatory subpopulation expression
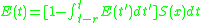
Complete Wilson-Cowan model
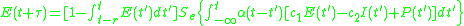
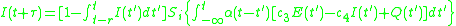
Time Coarse Graining
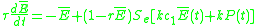
Isocline Equation
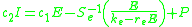
Sigmoid Function
Sigmoid function
Many natural processes, including those of complex system learning curves, exhibit a progression from small beginnings that accelerates and approaches a climax over time. When a detailed description is lacking, a sigmoid function is often used. A sigmoid curve is produced by a mathematical...