
Wiedemann effect
Encyclopedia
The twisting of a ferromagnetic rod through which an electric current is flowing when the rod is placed in a longitudinal magnetic field. It was discovered by the German physicist Gustav Wiedemann
in 1858
. The Wiedemann effect is one of the manifestations of magnetostriction
in a field formed by the combination of a longitudinal magnetic field and a circular magnetic field that is created by an electric current. If the electric current (or the magnetic field) is alternating, the rod will begin torsional oscillation.
In linear approach angle of rod torsion α does not depend on its cross-section form and is defined only by current density and magnetoelastic properties of the rod :
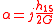 ,
,
where
Gustav Heinrich Wiedemann
Gustav Heinrich Wiedemann was a German physicist known mostly for his literary work.-Education:Wiedemann was born at Berlin. After attending the Cologne gymnasium, he entered the university of Berlin in 1844, and took his doctor's degree there three years later...
in 1858
. The Wiedemann effect is one of the manifestations of magnetostriction
Magnetostriction
Magnetostriction is a property of ferromagnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of material's magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ...
in a field formed by the combination of a longitudinal magnetic field and a circular magnetic field that is created by an electric current. If the electric current (or the magnetic field) is alternating, the rod will begin torsional oscillation.
In linear approach angle of rod torsion α does not depend on its cross-section form and is defined only by current density and magnetoelastic properties of the rod :
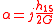 ,
,where
-
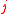 is current densityCurrent densityCurrent density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
is current densityCurrent densityCurrent density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
; -
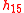 is magnetoelastic parameter, proportional to longitudinal magnetic field value;
is magnetoelastic parameter, proportional to longitudinal magnetic field value; -
 is the shear modulus.
is the shear modulus.

